Historical linguistics
Historical linguistics, also termed diachronic linguistics, is the scientific study of language change over time.[1] Principal concerns of historical linguistics include:[2]
- to describe and account for observed changes in particular languages
- to reconstruct the pre-history of languages and to determine their relatedness, grouping them into language families (comparative linguistics)
- to develop general theories about how and why language changes
- to describe the history of speech communities
- to study the history of words, i.e. etymology
| Part of a series on |
| Linguistics |
|---|
|
|
|
| Part of a series on |
| Anthropology |
|---|
 |
|
Historical linguistics is founded on the Uniformitarian Principle, which is defined by linguist Donald Ringe as:[3]
Unless we can demonstrate significant changes in the conditions of language acquisition and use between some time in the unobservable past and the present, we must assume that the same types and distributions of structures, variation, changes, etc. existed at that time in the past as in the present.
History and development
Western modern historical linguistics dates from the late-18th century. It grew out of the earlier discipline of philology,[4] the study of ancient texts and documents dating back to antiquity.
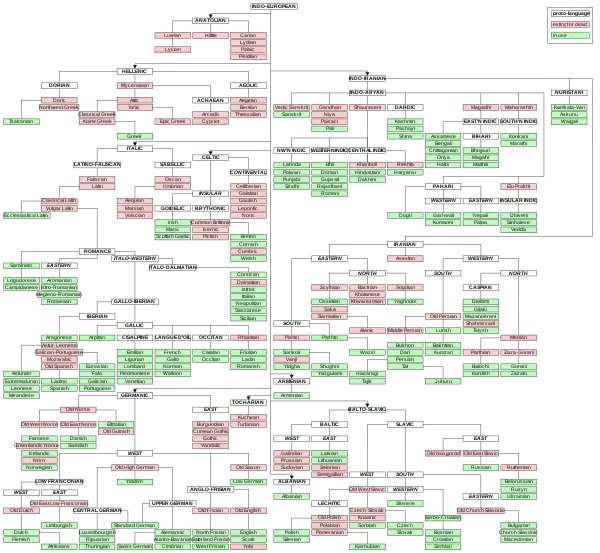
At first, historical linguistics served as the cornerstone of comparative linguistics, primarily as a tool for linguistic reconstruction.[5] Scholars were concerned chiefly with establishing language families and reconstructing unrecorded proto-languages, using the comparative method and internal reconstruction.[5] The focus was initially on the well-known Indo-European languages, many of which had long written histories; scholars also studied the Uralic languages, another Eurasian language-family for which less early written material exists. Since then, there has been significant comparative linguistic work expanding outside of European languages as well, such as on the Austronesian languages and on various families of Native American languages, among many others. Comparative linguistics became only a part of a more broadly-conceived discipline of historical linguistics. For the Indo-European languages, comparative study is now a highly specialized field.
Some scholars have undertaken studies attempting to establish super-families, linking, for example, Indo-European, Uralic, and other families into Nostratic. These attempts have not met with wide acceptance. The information necessary to establish relatedness becomes less available as the time increases. The time-depth of linguistic methods is limited due to chance word resemblances and variations between language groups, but a limit of around 10,000 years is often assumed.[6] The dating of the various proto-languages is also difficult; several methods are available for dating, but only approximate results can be obtained.
Diachronic and synchronic analysis
In linguistics, a synchronic analysis is one that views linguistic phenomena only at a given time, usually the present, but a synchronic analysis of a historical language form is also possible. It may be distinguished from diachronic, which regards a phenomenon in terms of developments through time. Diachronic analysis is the main concern of historical linguistics. However, most other branches of linguistics are concerned with some form of synchronic analysis. The study of language change offers a valuable insight into the state of linguistic representation, and because all synchronic forms are the result of historically-evolving diachronic changes, the ability to explain linguistic constructions necessitates a focus on diachronic processes.[7]
Initially, all of modern linguistics was historical in orientation. Even the study of modern dialects involved looking at their origins. Ferdinand de Saussure's distinction between synchronic and diachronic linguistics is fundamental to the present day organization of the discipline. Primacy is accorded to synchronic linguistics, and diachronic linguistics is defined as the study of successive synchronic stages. Saussure's clear demarcation, however, has had both defenders and critics.
In practice, a purely-synchronic linguistics is not possible for any period before the invention of the gramophone, as written records always lag behind speech in reflecting linguistic developments. Written records are difficult to date accurately before the development of the modern title page. Often, dating must rely on contextual historical evidence such as inscriptions, or modern technology, such as carbon dating, can be used to ascertain dates of varying accuracy. Also, the work of sociolinguists on linguistic variation has shown synchronic states are not uniform: the speech habits of older and younger speakers differ in ways that point to language change. Synchronic variation is linguistic change in progress.
Synchronic and diachronic approaches can reach quite different conclusions. For example, a Germanic strong verb like English sing – sang – sung is irregular when it is viewed synchronically: the native speaker's brain processes them as learned forms, but the derived forms of regular verbs are processed quite differently, by the application of productive rules (for example, adding -ed to the basic form of a verb as in walk – walked). That is an insight of psycholinguistics, which is relevant also for language didactics, both of which are synchronic disciplines. However, a diachronic analysis shows that the strong verb is the remnant of a fully regular system of internal vowel changes, in this case the Indo-European ablaut; historical linguistics seldom uses the category "irregular verb".
The principal tools of research in diachronic linguistics are the comparative method and the method of internal reconstruction. Less-standard techniques, such as mass lexical comparison, are used by some linguists to overcome the limitations of the comparative method, but most linguists regard them as unreliable.
The findings of historical linguistics are often used as a basis for hypotheses about the groupings and movements of peoples, particularly in the prehistoric period. In practice, however, it is often unclear how to integrate the linguistic evidence with the archaeological or genetic evidence. For example, there are numerous theories concerning the homeland and early movements of the Proto-Indo-Europeans, each with its own interpretation of the archaeological record.
Sub-fields of study
Comparative linguistics
Comparative linguistics (originally comparative philology) is a branch of historical linguistics that is concerned with comparing languages in order to establish their historical relatedness. Languages may be related by convergence through borrowing or by genetic descent, thus languages can change and are also able to cross-relate.
Genetic relatedness implies a common origin or proto-language. Comparative linguistics has the goal of constructing language families, reconstructing proto-languages, and specifying the changes that have resulted in the documented languages. To maintain a clear distinction between attested language and reconstructed forms, comparative linguists will prefix an asterisk to any form that is not found in surviving texts.
Etymology
Etymology is the study of the history of words: when they entered a language, from what source, and how their form and meaning have changed over time. A word may enter a language as a loanword (as a word from one language adopted by speakers of another language), through derivational morphology by combining pre-existing elements in the language, by a hybrid of these two processes called phono-semantic matching, or in several other minor ways.
In languages with a long and detailed history, etymology makes use of philology, the study of how words change from culture to culture over time. Etymologists also apply the methods of comparative linguistics to reconstruct information about languages that are too old for any direct information (such as writing) to be known. By analyzing related languages with a technique known as the comparative method, linguists can make inferences about their shared parent language and its vocabulary. In that way, word roots that can be traced all the way back to the origin of, for instance, the Indo-European language family have been found. Although originating in the philological tradition, much current etymological research is done in language families for which little or no early documentation is available, such as Uralic and Austronesian.
Dialectology
Dialectology is the scientific study of linguistic dialect, the varieties of a language that are characteristic of particular groups, based primarily on geographic distribution and their associated features. This is in contrast to variations based on social factors, which are studied in sociolinguistics, or variations based on time, which are studied in historical linguistics. Dialectology treats such topics as divergence of two local dialects from a common ancestor and synchronic variation.
Dialectologists are concerned with grammatical features that correspond to regional areas. Thus, they are usually dealing with populations living in specific locales for generations without moving, but also with immigrant groups bringing their languages to new settlements.
Phonology
Phonology is a sub-field of linguistics which studies the sound system of a specific language or set of languages. Whereas phonetics is about the physical production and perception of the sounds of speech, phonology describes the way sounds function within a given language or across languages.
An important part of phonology is studying which sounds are distinctive units within a language. For example, the "p" in "pin" is aspirated, but the "p" in "spin" is not. In English these two sounds are used in complementary distribution and are not used to differentiate words so they are considered allophones of the same phoneme. In some other languages like Thai and Quechua, the same difference of aspiration or non-aspiration differentiates words and so the two sounds (or phones) are therefore considered two distinct phonemes.
In addition to the minimal meaningful sounds (the phonemes), phonology studies how sounds alternate, such as the /p/ in English, and topics such as syllable structure, stress, accent, and intonation.
The principles of phonological theory have also been applied to the analysis of sign languages, but the phonological units do not consist of sounds. The principles of phonological analysis can be applied independently of modality because they are designed to serve as general analytical tools, not language-specific ones.
Morphology
Morphology is the study of the formal means of expression in a language; in the context of historical linguistics, how the formal means of expression change over time; for instance, languages with complex inflectional systems tend to be subject to a simplification process. This field studies the internal structure of words as a formal means of expression.[8]
Words as units in the lexicon are the subject matter of lexicology. While words are generally accepted as being (with clitics) the smallest units of syntax, it is clear that, in most (if not all) languages, words can be related to other words by rules. The rules understood by the speaker reflect specific patterns (or regularities) in the way words are formed from smaller units and how those smaller units interact in speech. In this way, morphology is the branch of linguistics that studies patterns of word-formation within and across languages, and attempts to formulate rules that model the knowledge of the speakers of those languages, in the context of historical linguistics, how the means of expression change over time. See grammaticalisation.
Syntax
Syntax is the study of the principles and rules for constructing sentences in natural languages. The term syntax is used to refer directly to the rules and principles that govern the sentence structure of any individual language, as in "the syntax of Modern Irish". Modern researchers in syntax attempt to describe languages in terms of such rules. Many professionals in this discipline attempt to find general rules that apply to all natural languages in the context of historical linguistics, how characteristics of sentence structure in related languages changed over time. See grammaticalisation.
Rates of change and varieties of adaptation
Studies in historical linguistics often use the terms "conservative" or "innovative" to characterize the extent of change occurring in a particular language or dialect as compared with related varieties. In particular, a conservative variety changes relatively less than an innovative variety. The variations in plasticity are often related to the socio-economic situation of the language speakers. An example of an innovative dialect would be American English because of the vast number of speakers and the open interaction its speakers have with other language groups; the changes can be seen in the terms developed for business and marketing, among other fields such as technology.
The converse of an innovative language is a conservative language, which is generally defined by its static nature and imperviousness to outside influences. Most but not all conservative languages are spoken in secluded areas that lack any other primary language speaking population.
Neither descriptive terms carries any value judgment in linguistic studies or determines any form of worthiness a language has, compared to any other language.
A particularly-conservative variety that preserves features that have long since vanished elsewhere is sometimes said to be "archaic". There are few examples of archaic language in modern society, but some have survived in set phrases or in nursery rhymes.
Evolutionary context
In terms of evolutionary theory, historical linguistics (as opposed to research into the origin of language) studies Lamarckian acquired characteristics of languages.[9]
See also
- Comparative method
- Etymological dictionary
- Genetic linguistics
- Glottochronology
- Grammaticalization
- Historical dictionary
- Language families
- Lexicostatistics
- List of languages by first written accounts
- Mass lexical comparison
- Paleolinguistics
- Proto-language
- Real-time sociolinguistics
- Wave model
Citations
- Bynon 1977, p. 1.
- Radford 1999, pp. 17–18
- Ringe, Donald (2009). "The Linguistic Diversity of Aboriginal Europe". Language Log. Retrieved 2020-03-22.
- Campbell, Lyle (1998). Historical Linguistics: An Introduction. Edinburgh: Edinburgh University Press. p. 391. ISBN 978-0-7486-4601-2.
- "Editors' Introduction: Foundations of the new historical linguistics." In: The Routledge Handbook of Historical Linguistics. Routledge, 2015, p. 25.
- Baldi, Philip (2012). "Historical Linguistics and Cognitive Science" (PDF). Rheis, International Journal of Linguistics, Philology and Literature. 3 (1): 5–27. p. 11.
- Bybee, Joan L. "Diachronic Linguistics." The Oxford Handbook of Cognitive Linguistics, June 2010.
- A formal language is a set of words, i.e. finite strings of letters or symbols. The inventory from which these letters are taken is the alphabet through which the language is defined. A formal language is often defined by means of a formal grammar, but it does not describe their semantics (i.e., what they mean).
-
Studdert-Kennedy, Michael (1991). "1: Language Development from an Evolutionary Perspective". In Krasnegor, Norman A.; Rumbaugh, Duane M.; Schiefelbusch, Richard L.; Studdert-Kennedy, Michael; Thelen, Esther (eds.). Biological and Behavioral Determinants of Language Development. New York: Psychology Press (published 2014). p. 6. ISBN 9781317783893. Retrieved 2016-12-27.
[...] biological evolution does not proceed by the transmission of acquired characters across generations, and this is precisely what an evolutionary model of language change requires. We therefore must distinguish the cultural, or Lamarckian, evolution of language, a concern of historical linguistics, from its biological, or neo-Darwinian, evolution, a concern of developmental biology.
General and cited sources
- Bynon, Theodora (1977). Historical Linguistics. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. p. 1. ISBN 9780521215824.
Historical linguistics.
- Kortmann, Bernd: English Linguistics: Essentials, Anglistik-Amerikanistik, Cornlesen, pp. 37–49
- Radford, Andrew (1999). Linguistics: An Introduction. With co-authors Martin Atkinson, David Britain, Harald Clahsen, Andrew Spencer. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press.
Further reading
- Raimo Anttila, Historical and Comparative Linguistics (2nd ed.) (John Benjamins, 1989) ISBN 90-272-3557-0
- Karl Brugmann, Berthold Delbrück, Grundriß der vergleichenden Grammatik der indogermanischen Sprachen (1886–1916).
- Theodora Bynon, Historical Linguistics (Cambridge University Press, 1977) ISBN 0-521-29188-7
- Henry M. Hoenigswald, Language change and linguistic reconstruction (Chicago: Univ. of Chicago Press 1960).
- Richard D. Janda and Brian D. Joseph (Eds), The Handbook of Historical Linguistics (Blackwell, 2004) ISBN 1-4051-2747-3
- Roger Lass, Historical linguistics and language change. (Cambridge University Press, 1997) ISBN 0-521-45924-9
- Winfred P. Lehmann, Historical Linguistics: An Introduction (Second Edition) (Holt, 1973) ISBN 0-03-078370-4
- April McMahon, Understanding Language Change (Cambridge University Press, 1994) ISBN 0-521-44665-1
- James Milroy, Linguistic Variation and Change (Blackwell, 1992) ISBN 0-631-14367-X
- A. C. Partridge, Tudor to Augustan English: a Study in Syntax and Style, from Caxton to Johnson, in series, The Language Library, London: A. Deutsch, 1969; 242 p. SBN 233-96092-9
- M.L. Samuels, Linguistic Evolution (Cambridge University Press, 1972) ISBN 0-521-29188-7
- R. L. Trask (ed.), Dictionary of Historical and Comparative Linguistics (Fitzroy Dearborn, 2001) ISBN 1-57958-218-4
- August Schleicher: Compendium der vergleichenden Grammatik der indogermanischen Sprachen. (Kurzer Abriss der indogermanischen Ursprache, des Altindischen, Altiranischen, Altgriechischen, Altitalischen, Altkeltischen, Altslawischen, Litauischen und Altdeutschen.) (2 vols.) Weimar, H. Boehlau (1861/62); reprinted by Minerva GmbH, Wissenschaftlicher Verlag, ISBN 3-8102-1071-4
- Zuckermann, Ghil'ad (2003). Language Contact and Lexical Enrichment in Israeli Hebrew. Palgrave Macmillan. ISBN 1-4039-1723-X.
External links
 The dictionary definition of Swadesh list of languages at Wiktionary
The dictionary definition of Swadesh list of languages at Wiktionary