Rhesus macaque
The rhesus macaque (Macaca mulatta), colloquially rhesus monkey, is a species of Old World monkey. There are between six and nine recognised subspecies that are split between two groups, the Chinese-derived and the Indian-derived. Generally brown or grey in colour, it is 47–53 cm (19–21 in) in length with a 20.7–22.9 cm (8.1–9.0 in) tail and weighs 5.3–7.7 kg (12–17 lb). It is native to South, Central, and Southeast Asia and has the widest geographic range of all non-human primates, occupying a great diversity of altitudes and a great variety of habitats, from grasslands to arid and forested areas, but also close to human settlements. Feral colonies are found in the United States, thought to be either released by humans or escapees after hurricanes destroyed zoo and wildlife park facilities.
| Rhesus macaque | |
|---|---|
%252C_male%252C_Gokarna.jpg.webp) | |
| Male, Gokarna Forest, Nepal | |
 | |
| Female with infant in Galtaji, Jaipur | |
Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Primates |
| Suborder: | Haplorhini |
| Infraorder: | Simiiformes |
| Family: | Cercopithecidae |
| Genus: | Macaca |
| Species: | M. mulatta |
| Binomial name | |
| Macaca mulatta (Zimmermann, 1780)[2] | |
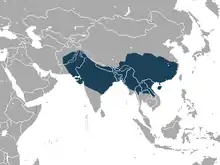 | |
| Rhesus macaque native range | |
| Synonyms[3] | |
|
Species synonymy
| |
The rhesus macaque is diurnal, arboreal, and terrestrial. It is mostly herbivorous, mainly eating fruit, but will also consume seeds, roots, buds, bark, and cereals. Studies show almost 100 different plant species in its diet. It will also eat invertebrates, drink water from streams and rivers, and has specialised cheek pouches where it can temporarily store food.
Like other macaques, the rhesus macaque is gregarious, with troops comprising 20-200 individuals. The social groups are matrilineal, whereby a female's rank is decided by the rank of her mother. There has been extensive research into female philopatry, common in social animals, as females tend not to leave the social group. The rhesus macaque communicates with a variety of facial expressions, vocalisations, body postures, and gestures. Facial expressions are used to appease or redirect aggression, assert dominance, and threaten other individuals, and vocalisations may be made to elicit grooming, while moving, or in threatening situations. It spends most of its day feeding and resting; the rest is occupied with traveling, grooming, and playing.
Due to its relatively easy upkeep, wide availability, and closeness to humans anatomically and physiologically, it has been used extensively in medical and biological research on human and animal health-related topics. It has facilitated many scientific breakthroughs including vaccines for rabies, smallpox, and polio and antiretroviral medication to treat HIV/AIDS. A rhesus macaque became the first primate astronaut in 1948, but died during the flight, followed on 14 June 1949 by Albert II, who became the first primate and first mammal in space. It is listed as Least Concern in the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species in view of its wide distribution, presumed large population, and its tolerance of a broad range of habitats.
Etymology
The name "rhesus" is reminiscent of the mythological king Rhesus of Thrace, a minor character in the Iliad. However, the French naturalist Jean-Baptiste Audebert, who applied the name to the species, stated: "it has no meaning".[4] The rhesus macaque is also known colloquially as the "rhesus monkey".[5][6]
Taxonomy


According to Zimmermann's first description of 1780, the rhesus macaque is distributed in eastern Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, as far east as the Brahmaputra Valley, Barak valley and in peninsular India, Nepal, and northern Pakistan. Today, this is known as the Indian rhesus macaque M. m. mulatta, which includes the morphologically similar M. rhesus villosus, described by True in 1894, from Kashmir, and M. m. mcmahoni, described by Pocock in 1932 from Kootai, Pakistan. Several Chinese subspecies of rhesus macaques were described between 1867 and 1917. The molecular differences identified among populations, however, are alone not consistent enough to conclusively define any subspecies.[7]
The Chinese subspecies can be divided as follows:
- M. m. mulatta is found in western and central China, in the south of Yunnan, and southwest of Guangxi;[8]
- M. m. lasiota (Gray, 1868), the west Chinese rhesus macaque, is distributed in the west of Sichuan, northwest of Yunnan, and southeast of Qinghai;[8] it is possibly synonymous with M. m. sanctijohannis (R. Swinhoe, 1867), if not with M. m. mulatta.[7]
- M. m. tcheliensis (Milne-Edwards, 1870), the north Chinese rhesus macaque, lives in the north of Henan, south of Shanxi, and near Beijing. Some consider it as the most endangered subspecies.[9] Others consider it possibly synonymous with M. m. sanctijohannis, if not with M. m. mulatta.[7]
- M. m. vestita (Milne-Edwards, 1892), the Tibetan rhesus macaque, lives in the southeast of Tibet, northwest of Yunnan (Deqing), and perhaps including Yushu;[8] it is possibly synonymous with M. m. sanctijohannis, if not with M. m. mulatta.[7]
- M. m. littoralis (Elliot, 1909), the south Chinese rhesus macaque, lives in Fujian, Zhejiang, Anhui, Jiangxi, Hunan, Hubei, Guizhou, northwest of Guangdong, north of Guangxi, northeast of Yunnan, east of Sichuan, and south of Shaanxi;[8] it is possibly synonymous with M. m. sanctijohannis, if not with M. m. mulatta.[7]
- M. m. brevicaudus, also referred to as Pithecus brevicaudus (Elliot, 1913), lives on the Hainan Island and Wanshan Islands in Guangdong, and the islands near Hong Kong;[8] it may be synonymous with M. m. mulatta.[7]
- M. m. siamica (Kloss, 1917), the Indochinese rhesus macaque, is distributed in Myanmar, in the north of Thailand and Vietnam, in Laos, and in the Chinese provinces of Anhui, northwest Guangxi, Guizhou, Hubei, Hunan, central and eastern Sichuan, and western and south-central Yunnan; possibly synonymous with M. m. sanctijohannis, if not with M. m. mulatta.[7]
Description

The rhesus macaque is brown or grey in color and has a pink face, which is bereft of fur. It has, on average, 50 vertebrae and a wide rib cage. Its tail averages between 20.7 and 22.9 cm (8.1 and 9.0 in).[10] Adult males measure about 53 cm (21 in) on average and weigh about 7.7 kg (17 lb). Females are smaller, averaging 47 cm (19 in) in length and 5.3 kg (12 lb) in weight.[10][11] The ratio of arm length to leg length is 89.6–94.3%.[12]
The rhesus macaque has a dental formula of 2.1.2.32.1.2.3 × 2 = 32 and bilophodont molar teeth.[13]
Distribution and habitat
Rhesus macaques are native to India, Bangladesh, Pakistan, Nepal, Myanmar, Thailand, Afghanistan, Vietnam, southern China, and some neighboring areas. They have the widest geographic ranges of any non-human primate, occupying a great diversity of altitudes throughout Central, South, and Southeast Asia. Inhabiting arid, open areas, rhesus macaques may be found in grasslands, woodlands, and in mountainous regions up to 2,500 m (8,200 ft) in elevation. They are strong swimmers,[14] and can swim across rivers.[15] Rhesus macaques are noted for their tendency to move from rural to urban areas, coming to rely on handouts or refuse from humans.[16] They adapt well to human presence, and form larger troops in human-dominated landscapes than in forests.[17]
The southern and the northern distributional limits for rhesus and bonnet macaques, respectively, currently run parallel to each other in the western part of India, are separated by a large gap in the center, and converge on the eastern coast of the peninsula to form a distribution overlap zone. This overlap region is characterized by the presence of mixed-species troops, with pure troops of both species sometimes occurring even in close proximity to one another. The range extension of rhesus macaque – a natural process in some areas, and a direct consequence of introduction by humans in other regions – poses grave implications for the endemic and declining populations of bonnet macaques in southern India.[18]
Fossil record
Fossilized isolated teeth and mandible fragments from Tianyuan Cave and a juvenile maxilla from Wanglaopu Cave near Zhoukoudian represent the first recognized occurrence of rhesus macaque fossils in the far north of China, and thus the population of rhesus macaques which lived around Beijing decades ago is believed to have originated from Pleistocene ancestors rather than being human-introduced.[19] Fossil mandible fragments from the Taedong River Basin around Pyongyang, North Korea, have also been assigned to this species.[20]
Feral colonies
Rhesus macaques have also been introduced to other areas, such as the United States, and become feral.
Around the spring of 1938, a colony of rhesus macaques was released in and around Silver Springs in Florida by a tour boat operator known locally as "Colonel Tooey" to enhance his "Jungle Cruise". A traditional story that the monkeys were released for scenery enhancement in the Tarzan movies that were filmed at that location is false, as the only Tarzan movie filmed in the area, 1939's Tarzan Finds a Son!, does not contain rhesus macaques.[21]
Various colonies of rhesus macaque are speculated to be the result of zoos and wildlife parks destroyed in hurricanes, most notably Hurricane Andrew.[22] A 2020 estimate put the number at 550–600 rhesus macaques living in the state;[23] officials have caught more than 1000 of the monkeys in the past decade. Most of the captured monkeys tested positive for herpes B virus, which leads wildlife officials to consider the animals a public health hazard.[24]
Feral colonies have also resulted from research activities. There is a colony of rhesus macaques on Morgan Island, one of the Sea Islands in the South Carolina Lowcountry. They were imported in the 1970s for use in the local labs.[25][26] Another research colony was established by the Caribbean Primate Research Center of the University of Puerto Rico on the island of Cayo Santiago,[27] off of Puerto Rico. There are no predators on the island, and humans are not permitted to land, except as part of the research program. Another Puerto Rico research colony was released into the Desecheo National Wildlife Refuge in 1966. As of 2022 they are continuing to do ecological harm, damage crops amounting to $300,000/year and cost $1,000,000/year to manage.[28]
Ecology and behavior

Rhesus macaques are diurnal animals, and both arboreal and terrestrial. They are quadrupedal and, when on the ground, they walk digitigrade and plantigrade. They are mostly herbivorous, feeding mainly on fruit, but also eating seeds, roots, buds, bark, and cereals. They are estimated to consume around 99 different plant species in 46 families. During the monsoon season, they get much of their water from ripe and succulent fruit. Macaques living far from water sources lick dewdrops from leaves and drink rainwater accumulated in tree hollows.[29] They have also been observed eating termites, grasshoppers, ants, and beetles.[30] When food is abundant, they are distributed in patches, and forage throughout the day in their home ranges. They drink water when foraging, and gather around streams and rivers.[31] Rhesus macaques have specialized pouch-like cheeks, allowing them to temporarily hoard their food.[32]
In psychological research, rhesus macaques have demonstrated a variety of complex cognitive abilities, including the ability to make same-different judgments, understand simple rules, and monitor their own mental states.[33][34] They have even been shown to demonstrate self-agency,[35] an important type of self-awareness. In 2014, onlookers at a train station in Kanpur, India, documented a rhesus monkey, knocked unconscious by overhead power lines, that was revived by another rhesus that systematically administered a series of resuscitative actions.[36]
Group structure

Like other macaques, rhesus troops comprise a mixture of 20–200 males and females.[37] Females may outnumber the males by a ratio of 4:1. Males and females both have separate hierarchies. Female philopatry, common among social mammals, has been extensively studied in rhesus macaques. Females tend not to leave the social group, and have highly stable matrilineal hierarchies in which a female's rank is dependent on the rank of her mother. In addition, a single group may have multiple matrilineal lines existing in a hierarchy, and a female outranks any unrelated females that rank lower than her mother.[38] Rhesus macaques are unusual in that the youngest females tend to outrank their older sisters.[39] This is likely because young females are more fit and fertile. Mothers seem to prevent the older daughters from forming coalitions against her. The youngest daughter is the most dependent on the mother, and would have nothing to gain from helping her siblings in overthrowing their mother. Since each daughter had a high rank in her early years, rebelling against her mother is discouraged.[40] Juvenile male macaques also exist in matrilineal lines, but once they reach four to five years of age, they are driven out of their natal groups by the dominant male. Thus, adult males gain dominance by age and experience.[31]
In the group, macaques position themselves based on rank. The "central male subgroup" contains the two or three oldest and most dominant males which are codominant, along with females, their infants, and juveniles. This subgroup occupies the center of the group and determines the movements, foraging, and other routines.[31] The females of this subgroup are also the most dominant of the entire group. The farther to the periphery a subgroup is, the less dominant it is. Subgroups on the periphery of the central group are run by one dominant male, of a rank lower than the central males, and he maintains order in the group, and communicates messages between the central and peripheral males. A subgroup of subordinate, often subadult, males occupy the very edge of the groups, and have the responsibility of communicating with other macaque groups and making alarm calls.[41] Rhesus social behaviour has been described as despotic, in that high-ranking individuals often show little tolerance, and frequently become aggressive towards non-kin.[42] Top-ranking female rhesus monkeys are known to sexually coerce unreceptive males and also physically injure them, biting off digits and damaging their genitals.[43]
Rhesus macaques have been observed engaging in interspecies grooming with Hanuman langurs and with Sambar deer.[44]
Communication
Rhesus macaques interact using a variety of facial expressions, vocalizations, body postures, and gestures. Perhaps the most common facial expression the macaque makes is the "silent bared teeth" face.[45] This is made between individuals of different social ranks, with the lower-ranking one giving the expression to its superior. A less-dominant individual also makes a "fear grimace", accompanied by a scream, to appease or redirect aggression.[46] Another submissive behavior is the "present rump", where an individual raises its tail and exposes its genitals to the dominant one.[45] A dominant individual threatens another individual by standing quadrupedally and making a silent "open mouth stare" accompanied by the tail sticking straight.[47] During movements, macaques make coos and grunts. These are also made during affiliative interactions, and approaches before grooming.[48] When they find rare food of high quality, macaques emit warbles, harmonic arches, or chirps. When in threatening situations, macaques emit a single loud, high-pitched sound called a shrill bark.[49] Screeches, screams, squeaks, pant-threats, growls, and barks are used during aggressive interactions.[49] Infants "gecker" to attract their mother's attention.[50]
Reproduction
_Rhesus_macaque.jpg.webp)
Adult male macaques try to maximize their reproductive success by entering into sex with females both in and outside the breeding period. Females prefer to mate with males that are not familiar to them. Outsider males who are not members of the female's own troop are preferred over higher-ranking males. Outside of the consortship period, males and females return the prior behavior of not exhibiting preferential treatment or any special relationship. The breeding period can last up to eleven days, and a female usually mates with numerous males during that time. Male rhesus macaques have been observed to fight for access to sexually receptive females and they suffer more wounds during the mating season.[51] Female macaques first breed when they are four years old and reach menopause at around twenty-five years of age.[52] Male macaques generally play no role in raising the young but do have peaceful relationships with the offspring of their consort pairs.[31]
Manson and Parry[53] found that free-ranging rhesus macaques avoid inbreeding. Adult females were never observed to copulate with males of their own matrilineage during their fertile periods.
Mothers with one or more immature daughters in addition to their infants are in contact with their infants less than those with no older immature daughters, because the mothers may pass the parenting responsibilities to their daughters. High-ranking mothers with older immature daughters also reject their infants significantly more than those without older daughters and tend to begin mating earlier in the mating season than expected based on their dates of parturition the preceding birth season.[54] Infants farther from the center of the groups are more vulnerable to infanticide from outside groups.[31] Some mothers abuse their infants, which is believed to be the result of controlling parenting styles.[55]
Self-awareness
In several experiments giving mirrors to rhesus monkeys, they looked into the mirrors and groomed themselves, as well as flexed various muscle groups. This behaviour indicates that they recognised and were aware of themselves.[56]
Conflict with humans
Towards the end of March 2018, it was reported that a monkey had entered a house in the village of Talabasta, Indian state of Odisha, and kidnapped a baby. The baby was later found dead in a well. Though monkeys are known to attack people, enter homes, and damage property, this reported behaviour was unusual.[57][58]
In science

The rhesus macaque is well known to science. Due to its relatively easy upkeep in captivity, wide availability, and closeness to humans anatomically and physiologically, it has been used extensively in medical and biological research on human and animal health-related topics. It has given its name to the Rh factor, one of the elements of a person's blood group, by the discoverers of the factor, Karl Landsteiner and Alexander Wiener. The rhesus macaque was also used in the well-known experiments on maternal deprivation carried out in the 1950s by controversial comparative psychologist Harry Harlow. Other medical breakthroughs facilitated by the use of the rhesus macaque include:[59]
- development of the rabies, smallpox, and polio vaccines
- creation of drugs to manage HIV/AIDS
- understanding of the female reproductive cycle and development of the embryo and the propagation of embryonic stem cells.
The U.S. Army, the U.S. Air Force, and NASA launched rhesus macaques into outer space during the 1950s and 1960s, and the Soviet/Russian space program launched them into space as recently as 1997 on the Bion missions. Albert II became the first primate and first mammal in space during a U.S. V-2 rocket suborbital flight on 14 June 1949, and died on impact when a parachute failed.
Another rhesus monkey, Able, was launched on a suborbital spaceflight in 1959, and was among the first living beings (along with Miss Baker, a squirrel monkey on the same mission) to travel in space and return alive.[60]
On 25 October 1999, the rhesus macaque became the first cloned primate with the birth of Tetra. January 2001 had the birth of ANDi, the first transgenic primate; ANDi carries foreign genes originally from a jellyfish.[61]
Though most studies of the rhesus macaque are from various locations in northern India, some knowledge of the natural behavior of the species comes from studies carried out on a colony established by the Caribbean Primate Research Center of the University of Puerto Rico on the island of Cayo Santiago, off Puerto Rico. No predators are on the island, and humans are not permitted to land except as part of the research programmes. The colony is provisioned to some extent, but about half of its food comes from natural foraging.
Rhesus macaques, like many macaques, carry the herpes B virus. This virus does not typically harm the monkey, but is very dangerous to humans in the rare event that it jumps species, for example in the 1997 death of Yerkes National Primate Research Center researcher Elizabeth Griffin.[62][63][64]
Genome sequencing
| NCBI genome ID | 215 |
|---|---|
| Ploidy | diploid |
| Genome size | 3,097.37 Mb |
| Number of chromosomes | 21 pairs |
| Year of completion | 2007 |
Work on the genome of the rhesus macaque was completed in 2007, making the species the second nonhuman primate whose genome was sequenced.[65] Humans and macaques apparently share about 93% of their DNA sequence and shared a common ancestor roughly 25 million years ago.[66] The rhesus macaque has 21 pairs of chromosomes.[67]
Comparison of rhesus macaques, chimpanzees, and humans revealed the structure of ancestral primate genomes, positive selection pressure and lineage-specific expansions, and contractions of gene families. "The goal is to reconstruct the history of every gene in the human genome," said Evan Eichler, University of Washington, Seattle. DNA from different branches of the primate tree will allow us "to trace back the evolutionary changes that occurred at various time points, leading from the common ancestors of the primate clade to Homo sapiens," said Bruce Lahn, University of Chicago.[68]
After the human and chimpanzee genomes were sequenced and compared, it was usually impossible to tell whether differences were the result of the human or chimpanzee gene changing from the common ancestor. After the rhesus macaque genome was sequenced, three genes could be compared. If two genes were the same, they were presumed to be the original gene.[69]
The chimpanzee and human genome diverged 6 million years ago. They have 98% identity and many conserved regulatory regions. Comparing the macaque and human genomes, which diverged 25 million years ago and had 93% identity, further identified evolutionary pressure and gene function. Like the chimpanzee, changes were on the level of gene rearrangements rather than single mutations. Frequent insertions, deletions, changes in the order and number of genes, and segmental duplications near gaps, centromeres and telomeres occurred. So, macaque, chimpanzee, and human chromosomes are mosaics of each other.
Some normal gene sequences in healthy macaques and chimpanzees cause profound disease in humans. For example, the normal sequence of phenylalanine hydroxylase in macaques and chimpanzees is the mutated sequence responsible for phenylketonuria in humans. So, humans must have been under evolutionary pressure to adopt a different mechanism. Some gene families are conserved or under evolutionary pressure and expansion in all three primate species, while some are under expansion uniquely in human, chimpanzee, or macaque. For example, cholesterol pathways are conserved in all three species (and other primate species). In all three species, immune response genes are under positive selection, and genes of T cell-mediated immunity, signal transduction, cell adhesion, and membrane proteins generally. Genes for keratin, which produce hair shafts, were rapidly evolving in all three species, possibly because of climate change or mate selection. The X chromosome has three times more rearrangements than other chromosomes. The macaque gained 1,358 genes by duplication. Triangulation of human, chimpanzee, and macaque sequences showed expansion of gene families in each species.
The PKFP gene, important in sugar (fructose) metabolism, is expanded in macaques, possibly because of their high-fruit diet. So are genes for the olfactory receptor, cytochrome P450 (which degrades toxins), and CCL3L1-CCL4 (associated in humans with HIV susceptibility). Immune genes are expanded in macaques, relative to all four great ape species. The macaque genome has 33 major histocompatibility genes, three times those of human. This has clinical significance because the macaque is used as an experimental model of the human immune system.
In humans, the preferentially expressed antigen of melanoma (PRAME) gene family is expanded. It is actively expressed in cancers, but normally is testis-specific, possibly involved in spermatogenesis. The PRAME family has 26 members on human chromosome 1. In the macaque, it has eight, and has been very simple and stable for millions of years. The PRAME family arose in translocations in the common mouse-primate ancestor 85 million years ago, and is expanded on mouse chromosome 4.
DNA microarrays are used in macaque research. For example, Michael Katze of University of Washington, Seattle, infected macaques with 1918 and modern influenzas. The DNA microarray showed the macaque genomic response to human influenza on a cellular level in each tissue. Both viruses stimulated innate immune system inflammation, but the 1918 flu stimulated stronger and more persistent inflammation, causing extensive tissue damage, and it did not stimulate the interferon-1 pathway. The DNA response showed a transition from innate to adaptive immune response over seven days.[70][71]
The full sequence and annotation of the macaque genome is available on the Ensembl genome browser.[72]
Conservation status
The rhesus macaque is listed as Least Concern on the IUCN Red List and estimated to exist in large numbers; it is tolerant of a broad range of habitats, including urban environments.[1]
The Thai population is locally threatened. In addition to habitat destruction and agricultural encroachment, pet releases of the different species into existing troops are diluting the gene pool and putting its genetic integrity at risk.[73][74]
Trivia
An archaic name for the rhesus macaque is bruh. This, however, is not a common name in contemporary times.[75]
See also
- Girneys
References
- Singh, M.; Kumar, A.; Kumara, H.N. (2020). "Macaca mulatta". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2020: e.T12554A17950825. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-2.RLTS.T12554A17950825.en. Retrieved 10 January 2022.
- Groves, C. P. (2005). "Species Macaca mulatta". In Wilson, D. E.; Reeder, D. M. (eds.). Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference (3rd ed.). Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press. p. 163. ISBN 0-801-88221-4. OCLC 62265494.
- "Macaca mulatta". Integrated Taxonomic Information System.
- Jaeger, E. (1972). A source-book of biological names and terms. Springfield, Illinois: Charles C. Thomas.
- "Rhesus macaque monkey (1932)". British Society for Immunology. Archived from the original on 2020-11-08.
- "Frequently asked questions about nonhuman primates in research". National Primate Research Centers. Archived from the original on 2015-11-23.
- Brandon-Jones, D.; Eudey, A. A.; Geissmann, T.; Groves, C. P.; Melnick, D. J.; Morales, J. C.; Shekelle, M.; Stewart, C.-B. (2004). Asian primate classification (PDF). Vol. 25. International Journal of Primatology. pp. 97–164. Retrieved 5 January 2016.
- Jiang, X.; Wang, Y.; Ma, S. (1991). "Taxonomic revision and distribution of subspecies of rhesus monkey (Macaca mulatta) in China". Zoological Research. 12.
- Zhang, Y.; Shi, L. (1993). "Phylogeny of rheusus monkeys (Macaca mulatta) as revealed by mitochondrial DNA restriction enzyme analysis". International Journal of Primatology. 14 (4): 587. doi:10.1007/BF02215449. S2CID 21883524.
- Fooden, J. (2000). "Systematic review of the rhesus macaque, Macaca mulatta (Zimmermann, 1780)". Fieldiana. 96: 1–180. doi:10.5962/bhl.title.7192.
- Singh, M.; Sinha, A. (2004). "Life history traits: ecological adaptations or phylogenetic relics?". In Thierry, B.; Singh, M.; Kaumanns, W. (eds.). Macaque societies: a model for the study of social organization. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press. pp. 80–83. ISBN 9780521521680.
- Hamada, Y.; Watanabe, T.; Chatani, K.; Hayakawa, S.; Iwamoto, M. (2005). "Morphometrical comparison between Indian- and Chinese-derived rhesus macaques (Macaca mulatta)". Anthropological Science. 113 (2): 183–188. doi:10.1537/ase.03104.
- Pocock, R. I. (1939). "Catarhini". The fauna of British India, including Ceylon and Burma: Mammalia volume I. London: Taylor and Francis. pp. 15–185.
- Lewis, A. D.; Prongay, K. (2015). "Basic physiology of Macaca mulatta". The nonhuman primate in nonclinical drug development and safety assessment. pp. 87–113. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-417144-2.00006-8. ISBN 9780124171442.
- Anderson, C. J.; Johnson, S. A.; Hostetler, M. E.; Summers, M. G. (2016). History and status of introduced rhesus macaques (Macaca mulatta) in Silver Springs State Park, Florida (Report). Department of Wildlife Ecology and Conservation, UF/IFAS Extension.
- Ciani, A. C. (1986). "Intertroop agonistic behavior of a feral rhesus macaque troop in ranging in town and forest areas in India" (PDF). Aggressive Behavior. 12 (6): 433–439. doi:10.1002/1098-2337(1986)12:6<433::AID-AB2480120606>3.0.CO;2-C. Retrieved 5 January 2016.
- Rishi, K.; Anindya, S.; Sindhu, R. (2013). "Comparative demography of two commensal macaques in India: implications for population status and conservation". Folia Primatologica. 84 (6): 384–393. doi:10.1159/000351935. PMID 24022675. S2CID 45152033.
- Kumar, R. R.; Sinha, A. (2011). "Of least concern? Range extension by rhesus macaques (Macaca mulatta) threatens long-term survival of bonnet macaques (M. radiata) in Peninsular India". International Journal of Primatology. 32 (4): 945–959. doi:10.1007/s10764-011-9514-y. S2CID 35227050. Retrieved 5 January 2016.
- Tong, Haowen (October 2014). "Fossils of Macaca mulatta from Tianyuan Cave, with Notes on Some Previously Unpublished Specimens of Macaca from Zhoukoudian Area". Acta Geologica Sinica - English Edition. 88 (5): 1397–1408. doi:10.1111/1755-6724.12307.
- Han, Kum Sik; So, Kwang Sik; Choe, Rye Sun; Kang, Jun Chol; Kang, Il; Ri, Chol Ung (2022-10-08). "First record of Macaca mulatta (Cercopithecidae: Papionini) from the Taedong River Basin, the Democratic People's Republic of Korea". Palaeoworld. doi:10.1016/j.palwor.2022.09.008. ISSN 1871-174X.
- Wolfe, L. (2002). Primates face to face. Cambridge University Press. p. 320. ISBN 0-521-79109-X.
- Bilger, B. (20 April 2009). "The natural world, swamp things". The New Yorker. p. 80. Retrieved 5 January 2016.
- Knowles, Hannah (25 February 2020). "People can't agree on what to do about Florida's herpes-infected monkeys". The Washington Post. Retrieved 5 September 2021.
- O'Neill, Natalie (12 September 2013). "Herpes-infected monkeys terrorize Florida". New York Post.
- The State | Homepage Archived 2004-08-26 at the Wayback Machine
- Taub DM, Mehlman PT (April 1989). "Development of the Morgan Island rhesus monkey colony". P R Health Sci J. 8 (1): 159–69. PMID 2780958.
- Rawlins, Richard G.; Kessler, Matt J. (1986). The Cayo Santiago Macaques: History, Behavior, and Biology. SUNY series in primatology. Albany: State University of New York Press. p. 306. ISBN 978-0-88706-135-6. OCLC 42855829.
- "WEC367/UW412: History and Status of Introduced Rhesus Macaques (Macaca mulatta) in Silver Springs State Park, Florida". Ask IFAS, Electronic Data Information Source (EDIS). Institute of Food and Agricultural Sciences (IFAS), UF. 2022-01-21. Retrieved 2022-02-09.
- Makwana, S. (1979). "Field ecology and behavior of the rhesus macaque. Food, feeding and drinking in Dehra Dun forests". Indian Journal of Forestry. 2 (3): 242–253.
- Lindburg, D. G. (1971). "The rhesus monkeys in north India: an ecological and behavioural study". In Rosenblum, L. A. (ed.). Primate behaviour: developments in the field and laboratory research. Vol. 1. New York: Academic Press. pp. 83–104. ISBN 012534001X.
- Southwick, C.; Beg, M.; Siddiqi, R. (1965). "Rhesus monkeys in North India". In DeVore, I. (ed.). Primate behavior: field studies of monkeys and apes. San Francisco, USA: Holt, Rinehart and Winston. ISBN 978-0-03-050340-5.
- Burrows, A. M.; Waller, B. M.; Parr, L. A. (2009). "Facial musculature in the rhesus macaque (Macaca mulatta): evolutionary and functional contexts with comparisons to chimpanzees and humans". Journal of Anatomy. 215 (3): 320–334. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7580.2009.01113.x. ISSN 0021-8782. PMC 2750044. PMID 19563473.
- Couchman, J. J.; et al. (2010). "Beyond stimulus cues and reinforcement signals: a new approach to animal metacognition". Journal of Comparative Psychology. 124 (4): 356–368. doi:10.1037/a0020129. PMC 2991470. PMID 20836592.
- Blanchard, T. C.; Wolfe, L. S.; Vlaev, I.; Winston, J. S.; Hayden, B. Y. (2014). "Biases in preferences for sequences of outcomes in monkeys". Cognition. 130 (3): 289–299. doi:10.1016/j.cognition.2013.11.012. PMC 3969290. PMID 24374208.
- Couchman, J. J. (2011). "Self-agency in rhesus monkeys". Biology Letters. 8 (1): 39–41. doi:10.1098/rsbl.2011.0536. PMC 3259954. PMID 21733868.
- Waxman, O. B. (2014-12-22). "Hero monkey revives simian pal electrocuted in India". Time.
- Teas, J.; Richie, T.; Taylor, H.; Southwick, C. (1980). "Population patterns and behavioral ecology of rhesus monkeys (Macaca mulatta) in Nepal". In Lindenburg, D. (ed.). The macaques: studies in ecology, behavior, and evolution. San Francisco: Van Nostrand Reinhold Company. ISBN 0442248172.
- Judge, P. & Waal, F. (1997). "Rhesus monkey behaviour under diverse population densities: coping with long-term crowding". Animal Behaviour. 54 (3): 643–662. doi:10.1006/anbe.1997.0469. PMID 9299049. S2CID 22512222.
- Waal, F. (1993). "Codevelopment of dominance relations and affiliative bonds in rhesus monkeys". In Pereira, M.; Fairbanks, L. (eds.). Juvenile primates: life history, development, and behavior. Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0226656225.
- Hill, D.; Okayasu, N. (1996). "Determinants of dominance among female macaques: nepotism, demography and danger". In Fa, J.; Lindburg, D. (eds.). Evolution and ecology of macaque societies. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0521416809.
- Gouzoules, H.; Gouzoules, S.; Tomaszycki, M. (1998). "Agonistic screams and the classification of dominance relationships: are rhesus monkeys fuzzy logicians?". Animal Behaviour. 55 (1): 51–60. doi:10.1006/anbe.1997.0583. PMID 9480671. S2CID 25747013.
- Thierry, B. (1985). "Social development in three species of macaque (Macaca mulatta, M. fasicularis, M. tonkeana): A preliminary report on the first ten weeks of life". Behavioural Processes. 11 (1): 89–95. doi:10.1016/0376-6357(85)90105-6. PMID 24924364. S2CID 140208622.
- "Queen Kong? In rhesus realm, females rule". chicagotribune.com. Retrieved 2021-02-12.
- Lee, Z.H.; Ang, A.; Ruppert, N. (26 August 2021). "First record of interspecies grooming between Raffles' banded langur and long-tailed macaque". Journal of Threatened Taxa. 13 (9): 19246–19253. doi:10.11609/jott.7510.13.9.19246-19253. Retrieved 2021-09-05.
- Maestripieri, D. (1999). "Primate social organization, gestural repertoire size, and communication dynamics: a comparative study of macaques". In King, B. J. (ed.). The origins of language: what nonhuman primates can tell us. Santa Fe, NM, USA: School American Research Press. pp. 55–77. ISBN 0852559046.
- Rowe, N. (1996). The pictorial guide to the living primates. East Hampton, NY, USA: Pogonias Press.
- Partan, S. R. (2002). "Single and multichannel signal composition: facial expressions and vocalizations of rhesus macaques (Macaca mulatta)". Behaviour. 139 (2–3): 993–1027. doi:10.1163/15685390260337877.
- Hauser, M. D. (1998). "Functional referents and acoustic similarity field playback experiments with rhesus monkeys". Animal Behaviour. 55 (6): 1647–58. doi:10.1006/anbe.1997.0712. PMID 9642008. S2CID 8253916.
- Lindburg, D. G. (1971). "The rhesus monkey in north India: an ecological and behavioral study". In Rosenblum, L. A. (ed.). Primate behavior: developments in field and laboratory research. Vol. 2. New York: Academic Press. pp. 1–106. ISBN 1483244407.
- Patel, E. R.; Owren, M. J. (2004). "Acoustic and behavioral analyses of 'gecker' distress vocalizations in young rhesus macaques (Macaca mulata)". American Journal of Primatology. 62 (5): 48. Bibcode:2004ASAJ..115.2485P. doi:10.1002/ajp.20027.
- Bercovitch, F. (1997). "Reproductive strategies of rhesus macaques". Primates. 38 (3): 247–263. doi:10.1007/BF02381613. S2CID 8372920.
- Walker, M. L.; Herndon, J. G. (2008). "Menopause in nonhuman primates?". Biology of Reproduction. 79 (3): 398–406. doi:10.1095/biolreprod.108.068536. PMC 2553520. PMID 18495681.
- Manson, J. H.; Perry, S. E. (1993). "Inbreeding avoidance in rhesus macaques: whose choice?" (PDF). American Journal of Physical Anthropology. 90 (3): 335–44. doi:10.1002/ajpa.1330900307. hdl:2027.42/37662. PMID 8460656.
- Berman, C. (1992). "Immature siblings and mother-infant relationships among free-ranging rhesus monkeys on Cayo Santiago". Animal Behaviour. 44: 247–258. doi:10.1016/0003-3472(92)90031-4. S2CID 53171870.
- Maestripieri, D. (1998). "Parenting styles of abusive mothers in group-living rhesus macaques". Animal Behaviour. 55 (1): 1–11. doi:10.1006/anbe.1997.0578. PMID 9480666. S2CID 8348608.
- Rajala, A. Z.; Reininger, K. R.; Lancaster, K. M. & Populin, L. C. (2010). "Rhesus monkeys (Macaca mulatta) do recognize themselves in the mirror: implications for the evolution of self-recognition". PLOS ONE. 5 (9): e12865. Bibcode:2010PLoSO...512865R. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0012865. PMC 2947497. PMID 20927365.
- "Indian police search for monkey that snatched baby". BBC. 2018-04-02. Retrieved 2018-04-03.
- "Baby stolen by monkey in India found dead". 9news.com.au. 2018-04-03. Retrieved 2018-04-03.
- Mitruka, B. M. (1976). "Introduction". In Mitruka, B. M.; Rawnsley, H. M.; Vadehra, D. V. (eds.). Animals for medical research: models for the study of human disease. New York: Wiley & Sons. pp. 1–21. ISBN 0898741564.
- "Kansan among first to go to space". Wichita Eagle and Kansas.com. 22 March 2010.
- "GM monkey first". BBC News. BBC. 11 January 2001. Retrieved 13 February 2015.
- "About Elizabeth (Beth) R. Griffin (1975–1997)". Elizabeth R. Griffin Research Foundation. Archived from the original on 1 November 2012.
- Bragg, R. (1997-12-14). "A drop of virus from a monkey kills a researcher in 6 weeks". New York Times.
- "Yerkes 'family' pulled together after death of young researcher from rare Herpes B infection". Emory.edu. 1998-01-12. Retrieved 2015-03-09.
- Zahn, L. M.; Jasny, B. R.; Culotta, E. & Pennisi, E. (2007). "A barrel of monkey genes". Science. 316 (5822): 215. doi:10.1126/science.316.5822.215.
- "DNA sequence of rhesus macaque has evolutionary, medical implications" (Press release). Human Genome Sequencing Center. 13 April 2007. Retrieved 15 April 2007.
- Perticone, P.; Rizzoni, M.; Palitti, F.; Di Chiara, P. (1974). "Banding patterns of the chromosomes of the rhesus monkey (Macaca mulatta)". Journal of Human Evolution. 3 (4): 291–295. doi:10.1016/0047-2484(74)90023-2.
- Harris, R. A.; Rogers, J.; Milosavljevic, A. (2007). "Human-specific changes of genome structure detected by genomic triangulation". Science. 316 (5822): 235–7. Bibcode:2007Sci...316..235H. doi:10.1126/science.1139477. PMID 17431168.
- Rhesus macaque genome sequencing analysis consortium; Gibbs, R. A.; Rogers, J.; et al. (2007). "Evolutionary and biomedical insights from the rhesus macaque genome". Science. 316 (5822): 222–234. Bibcode:2007Sci...316..222.. doi:10.1126/science.1139247. PMID 17431167.
- Cilloniz, C.; Shinya, K. P.; Korth, X.; Proll, M. J.; Aicher, S. C.; Carter, L. D.; Chang, V. S.; Kobasa, J. H.; Feldmann, D.; Strong, F.; Feldmann, J. E.; Kawaoka, H.; Katze, Y.; Michael, G. (2009). "Lethal influenza virus infection in macaques is associated with early dysregulation of inflammatory related genes". PLOS Pathogens. 5 (10): e1000604. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1000604. PMC 2745659. PMID 19798428.
- Brown, J. N.; Palermo, R. E. B.; Gritsenko, C. R.; Sabourin, M.; Long, P. J.; Sabourin, J. P.; Bielefeldt-Ohmann, C. L.; García-Sastre, H.; Albrecht, A.; Tumpey, R.; Jacobs, T. M.; Smith, J. M.; Katze, R. D.; Michael, G. (2010). "Macaque proteome response to highly pathogenic avian influenza and 1918 reassortant influenza virus infections". Journal of Virology. 84 (22): 12058–12068. doi:10.1128/jvi.01129-10. PMC 2977874. PMID 20844032.
- "Macaca mulatta - Ensembl genome browser 96".
- Malaivijitnond, S.; Takenaka, O.; Kawamoto, Y.; Urasopon, N.; Hadi, I.; Hamada, Y. (2007). "Anthropogenic macaque hybridization and genetic pollution of a threatened population". 7 (1). Tropical Natural History: 11–23.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - Kyes, P.; Thamsenanupap, P.; Tanee, T.; Intralawan, A.; Kyes, R. C. (2018). "Previously unreported population of rhesus macaques Macaca mulatta in Chang Rai province, Thailand: preliminary observations". Asian Primates Journal. 7 (1): 6–13. PMC 6914309. PMID 31844847.
- Rennie, James (1838). The Menageries: The Natural History of Monkeys, Opossums, and Lemurs, Volume 1. Charles Knight and Company. p. 377.
External links
- ARKive: images and movies of the rhesus macaque Macaca mulatta
- Brain maps and brain atlases of rhesus macaque
- Primate Info Net: Macaca mulatta Factsheet
- University of Michigan Museum of Zoology's Animal Diversity Web: Macaca mulatta
- Macaca mulatta Genome
- Rhesus Play Film analysis of agonistic play by Donald Symons (UCSB) on DVD
- View the Macaque genome in Ensembl.
- View the rheMac8 genome assembly in the UCSC Genome Browser.
