Sherbrooke
Sherbrooke (/ˈʃɜːrbrʊk/ SHUR-bruuk; Quebec French pronunciation [ʃɛʁbʁʊk]) is a city in southern Quebec, Canada. It is at the confluence of the Saint-François and Magog rivers in the heart of the Estrie administrative region. Sherbrooke is also the name of a territory equivalent to a regional county municipality (TE) and census division (CD) of Quebec, coextensive with the city of Sherbrooke. With 172,950 residents at the Canada 2021 Census,[3] It is the sixth largest city in the province and the 30th largest in Canada. The Sherbrooke Census Metropolitan Area had 227,398 inhabitants, making it the fourth largest metropolitan area in Quebec and 19th in Canada.
Sherbrooke | |
|---|---|
City | |
| Ville de Sherbrooke | |
 From top, left to right: Downtown Sherbrooke, Wellington Street, Sherbrooke City Hall, Plymouth-Trinity United Church, clocktower at the Sherbrooke History Museum | |
 Flag .svg.png.webp) Coat of arms Logo | |
| Nickname: Queen of the Eastern Townships | |
| Motto: Ne quid nimis | |
 Sherbrooke Location of Sherbrooke in Quebec  Sherbrooke Sherbrooke (Quebec)  Sherbrooke Sherbrooke (Canada) | |
| Coordinates: 45°24′N 71°54′W[1] | |
| Country | |
| Province | |
| Region | Estrie |
| RCM | None |
| Settled | 1793 |
| Constituted | 1 January 2002 |
| Boroughs | List
|
| Government | |
| • Type | Sherbrooke City Council |
| • Mayor | Évelyne Beaudin |
| • Federal riding | Compton—Stanstead / Sherbrooke |
| • Prov. riding | Richmond / Saint-François / Sherbrooke |
| Area | |
| • City | 367.10 km2 (141.74 sq mi) |
| • Land | 353.40 km2 (136.45 sq mi) |
| • Urban | 102.61 km2 (39.62 sq mi) |
| • Metro | 1,458.10 km2 (562.98 sq mi) |
| Highest elevation | 378 m (1,240 ft) |
| Lowest elevation | 128 m (420 ft) |
| Population (2021) | |
| • City | 172,950 |
| • Density | 489.4/km2 (1,268/sq mi) |
| • Urban | 151,157 |
| • Urban density | 1,473.1/km2 (3,815/sq mi) |
| • Metro | 227,398(19th) |
| • Metro density | 156/km2 (400/sq mi) |
| • Pop 2016–2021 | |
| • Dwellings | 86,019 |
| Time zone | UTC−5 (EST) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−4 (EDT) |
| Postal code(s) | J1C to J1R |
| Area code | 819 |
| Highways | |
| Telephone Exchanges | -212 239 340 345-9 432 434 437 446 542 560 -6 569 570 - 4 575 577 |
| NTS Map | 21E5 Sherbrooke |
| GNBC Code | EIDHN[5] |
| GDP (Sherbrooke CMA) | CA$8.0 billion (2016)[6] |
| GDP per capita (Sherbrooke CMA) | CA$37,797 (2016) |
| Website | www |
Sherbrooke is the primary economic, political, cultural and institutional centre of Estrie, and was known as the Queen of the Eastern Townships at the beginning of the 20th century.
There are eight institutions educating 40,000 students and employing 11,000 people, 3,700 of whom are professors, teachers and researchers. The direct economic impact of these institutions exceeds 1 billion dollars. The proportion of university students is 10.32 students per 100 inhabitants, giving Sherbrooke the largest concentration of students in Quebec.[7]
Sherbrooke rose as a manufacturing centre in the 1800s, and today the service sector is prominent.
The Sherbrooke region is surrounded by mountains, rivers and lakes. There are several ski hills nearby and various tourist attractions in regional flavour. Mont-Bellevue Park, a large park in the city, is used for downhill skiing.
Toponymy
The city was named in 1818 for John Coape Sherbrooke, a former Governor General of Canada.[8]
History

First Nations settled the region 8,000-3,000 years ago.[9] The Abenaki called it Ktinékétolékouac (The Large Forks),[10] or Shacewanteku (where one smokes).[1]
The first settler was the farmer Jean-Baptiste Nolain, in 1779.[1] The area was first surveyed in 1792.[11] Americans from Vermont built mills in the area in 1802. Gilbert Hyatt led a group of loyalists, who settled around 1803. He dammed the Magog River and a gristmill and a sawmill were soon built nearby. The settlement was then known as Hyatt's Mills.[12] The first immigrants from England arrived in 1815.[13]

The British American Land Company was formed in 1832[14] to acquire and develop almost 1,100,000 acres (1,719 sq mi; 4,452 km2) of Crown land and other lands in the area. It prioritized speculation over immigration.[15]
In 1852 a railway linked Montreal and Portland, Maine via Sherbrooke. By the 1890s there were rail connections to Boston, Halifax, and New York City.
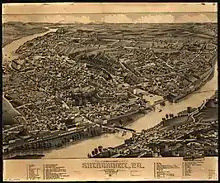
Immigration from the rest of Quebec began in 1850, and by 1871 francophones were in the majority.[13]
By the turn of the 20th century, Sherbrooke was a thriving industrial city, with manufacturing benefiting from locally-produced hydroelectricity. From the 1950s, some the steel and textile industries declined, giving way to government services and education.

As part of the 2000–2006 municipal reorganization in Quebec, the city grew considerably on 1 January 2002, with the amalgamation of Sherbrooke, Ascot, Bromptonville, Deauville, Fleurimont, Lennoxville, Rock Forest, and Saint-Élie-d'Orford. Part of Stoke was also annexed to the newly expanded Sherbrooke.
In 2012, a local Vitamin production factory suffered an explosion, which killed 2, and injured 19, some severely. A large toxic cloud enveloped part of the city, raising health concerns.[16][17]
Geography
Located at the confluence of the Saint-François (St. Francis) and Magog rivers in the heart of the Eastern Townships and the Estrie administrative region. Sherbrooke is also the name of a territory equivalent to a regional county municipality (TE) and census division (CD) of Quebec, coextensive with the city of Sherbrooke. Its geographical code is 43.
Climate
Sherbrooke has a humid continental climate (Köppen Dfb), with long, cold, and snowy winters, warm summers, and short but crisp springs and autumns. Highs range from −5.8 °C (21.6 °F) in January to 24.6 °C (76.3 °F) in July. In an average year, there are 34 nights at or colder than −20 °C (−4 °F), and 6.5 nights at or colder than −30 °C (−22 °F); 4.1 days will see highs reaching 30 °C (86 °F).[18] Annual snowfall is large, averaging at 287 centimetres (113 in), sometimes falling in May and October. Precipitation is not sparse any time of the year, but is the greatest in summer and fall and at its least from January to April, totalling 1,100 millimetres (43.3 in) annually.
The highest temperature ever recorded in Sherbrooke was 36.7 °C (98 °F) on 1 & 2 July 1931.[19] The coldest temperature ever recorded was −41.2 °C (−42.2 °F) on 15 January 2004.[20]
| Climate data for Sherbrooke Airport, 1981−2010 normals, extremes 1900−present | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high humidex | 17.4 | 17.1 | 27.0 | 31.5 | 38.3 | 43.9 | 46.5 | 43.4 | 38.7 | 31.8 | 26.3 | 19.0 | 46.5 |
| Record high °C (°F) | 15.0 (59.0) |
17.1 (62.8) |
25.3 (77.5) |
30.0 (86.0) |
33.5 (92.3) |
35.0 (95.0) |
36.7 (98.1) |
36.1 (97.0) |
34.0 (93.2) |
28.3 (82.9) |
23.9 (75.0) |
17.8 (64.0) |
36.7 (98.1) |
| Average high °C (°F) | −5.8 (21.6) |
−2.8 (27.0) |
2.3 (36.1) |
10.4 (50.7) |
18.3 (64.9) |
22.2 (72.0) |
24.6 (76.3) |
23.7 (74.7) |
19.2 (66.6) |
12.2 (54.0) |
5.1 (41.2) |
−2.1 (28.2) |
10.6 (51.1) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −11.9 (10.6) |
−9.4 (15.1) |
−3.7 (25.3) |
4.5 (40.1) |
11.4 (52.5) |
15.5 (59.9) |
18.2 (64.8) |
17.3 (63.1) |
12.3 (54.1) |
6.3 (43.3) |
0.6 (33.1) |
−7.3 (18.9) |
4.5 (40.1) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −17.9 (−0.2) |
−15.9 (3.4) |
−9.7 (14.5) |
−1.4 (29.5) |
4.3 (39.7) |
8.8 (47.8) |
11.7 (53.1) |
10.8 (51.4) |
6.3 (43.3) |
0.5 (32.9) |
−4 (25) |
−12.4 (9.7) |
−1.6 (29.1) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −41.2 (−42.2) |
−40 (−40) |
−35 (−31) |
−21.1 (−6.0) |
−6.7 (19.9) |
−2.2 (28.0) |
0.5 (32.9) |
−1.7 (28.9) |
−7.4 (18.7) |
−15 (5) |
−25.5 (−13.9) |
−39.4 (−38.9) |
−41.2 (−42.2) |
| Record low wind chill | −47.2 | −48 | −42.4 | −29.7 | −12.8 | −5.4 | 0.0 | −4.7 | −8.6 | −16.7 | −27.9 | −48.3 | −48.3 |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 74.3 (2.93) |
61.7 (2.43) |
71.3 (2.81) |
84.0 (3.31) |
94.3 (3.71) |
108.4 (4.27) |
109.5 (4.31) |
126.1 (4.96) |
94.8 (3.73) |
90.4 (3.56) |
99.1 (3.90) |
86.5 (3.41) |
1,100.4 (43.32) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 17.3 (0.68) |
16.6 (0.65) |
27.6 (1.09) |
63.3 (2.49) |
94.0 (3.70) |
108.4 (4.27) |
109.5 (4.31) |
126.1 (4.96) |
94.7 (3.73) |
87.5 (3.44) |
70.8 (2.79) |
32.0 (1.26) |
847.9 (33.38) |
| Average snowfall cm (inches) | 68.2 (26.9) |
54.2 (21.3) |
48.2 (19.0) |
21.2 (8.3) |
0.37 (0.15) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.03 (0.01) |
3.2 (1.3) |
29.1 (11.5) |
62.1 (24.4) |
286.5 (112.8) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.2 mm) | 19.7 | 15.5 | 16.0 | 14.9 | 15.7 | 15.2 | 14.0 | 13.3 | 12.6 | 14.0 | 17.2 | 19.1 | 187.1 |
| Average rainy days (≥ 0.2 mm) | 3.5 | 3.3 | 6.4 | 12.2 | 15.1 | 15.1 | 13.8 | 14.5 | 13.0 | 13.7 | 11.5 | 5.4 | 127.5 |
| Average snowy days (≥ 0.2 cm) | 18.9 | 14.3 | 10.9 | 5.6 | 0.21 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.07 | 1.5 | 8.6 | 16.2 | 76.3 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 84.5 | 107.8 | 137.7 | 159.8 | 212.3 | 234.6 | 257.0 | 231.3 | 165.6 | 118.9 | 67.9 | 67.6 | 1,844.9 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 29.8 | 36.9 | 37.4 | 39.5 | 46.1 | 50.1 | 54.2 | 52.9 | 43.9 | 34.9 | 23.7 | 24.8 | 39.5 |
| Source: Environment Canada[18][21][22][23][24] | |||||||||||||
Cityscape

Neighbourhoods
The city includes several neighbourhoods:
- Le quartier universitaire
- Le Vieux-Nord
- Collinsville
- Secteur Galvin
- L'Est
- Ascot
- Mi-Vallon
- du Pin-Solitaire
- Le Petit Canada
Demographics
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1871 | 4,432 | — |
| 1881 | 7,227 | +63.1% |
| 1891 | 10,097 | +39.7% |
| 1901 | 11,765 | +16.5% |
| 1911 | 16,405 | +39.4% |
| 1921 | 23,515 | +43.3% |
| 1931 | 28,933 | +23.0% |
| 1941 | 35,965 | +24.3% |
| 1951 | 50,543 | +40.5% |
| 1956 | 58,668 | +16.1% |
| 1961 | 66,554 | +13.4% |
| 1966 | 75,690 | +13.7% |
| 1971 | 80,711 | +6.6% |
| 1976 | 76,804 | −4.8% |
| 1981 | 74,075 | −3.6% |
| 1986 | 74,478 | +0.5% |
| 1991 | 76,429 | +2.6% |
| 1996 | 76,786 | +0.5% |
| 2001 | 75,916 | −1.1% |
| 2006* | 147,427 | +94.2% |
| 2011 | 154,601 | +4.9% |
| 2016 | 161,323 | +4.3% |
| 2021 | 172,950 | +7.2% |
(*) Sherbrooke annexed the City of Bromptonville, the City of Fleurimont, the City of Lennoxville, the City of Rock-Forest, the Municipality of Ascot and the Municipality of Deauville. | ||
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1871 | 8,532 | — |
| 1881 | 12,410 | +45.5% |
| 1891 | 15,930 | +28.4% |
| 1901 | 18,724 | +17.5% |
| 1911 | 23,865 | +27.5% |
| 1921 | 33,624 | +40.9% |
| 1931 | 39,323 | +16.9% |
| 1941 | 47,614 | +21.1% |
| 1951 | 63,608 | +33.6% |
| 1956 | 72,789 | +14.4% |
| 1961 | 82,939 | +13.9% |
| 1966 | 94,988 | +14.5% |
| 1971 | 103,083 | +8.5% |
| 1976 | 111,137 | +7.8% |
| 1981 | 117,848 | +6.0% |
| 1986 | 122,282 | +3.8% |
| 1991 | 131,123 | +7.2% |
| 1996 | 136,681 | +4.2% |
| 2001 | 139,388 | +2.0% |
| 2006 | 147,427 | +5.8% |
| 2011 | 154,601 | +4.9% |
| 2016 | 161,323 | +4.3% |
| 2021 | 172,950 | +7.2% |
In the 2021 Census of Population conducted by Statistics Canada, Sherbrooke had a population of 172,950 living in 80,476 of its 86,019 total private dwellings, a change of 7.2% from its 2016 population of 161,323. With a land area of 353.4 km2 (136.4 sq mi), it had a population density of 489.4/km2 (1,267.5/sq mi) in 2021.[27]
| 2021 | 2016 | 2011 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Population | 172,950 (+7.2% from 2016) | 161,323 (+4.3% from 2011) | 154,601 (+4.9% from 2006) |
| Land area | 353.40 km2 (136.45 sq mi) | 353.76 km2 (136.59 sq mi) | 353.49 km2 (136.48 sq mi) |
| Population density | 489.4/km2 (1,268/sq mi) | 456.0/km2 (1,181/sq mi) | 437.4/km2 (1,133/sq mi) |
| Median age | 41.2 (M: 39.2, F: 42.8) | 40.5 (M: 38.5, F: 42.5) | 40.2 (M: 38.0, F: 42.3) |
| Total private dwellings | 86,019 | 80,341 | 75,880 |
| Median household income | $62,400 | $51,706 | $46,468 |
| Ethnic origin | Population | Percent |
|---|---|---|
| Canadian | 106,695 | 68.3 |
| French | 42,315 | 27.1 |
| Irish | 8,855 | 5.7 |
| North American Aboriginal | 6,100 | 3.9 |
| English | 4,570 | 2.9 |
| Québécois | 3,750 | 2.4 |
| Scottish | 3,445 | 2.2 |
| Italian | 2,550 | 1.6 |
| German | 2,390 | 1.5 |
86.4% of Sherbrooke residents spoke French as a first language in 2021, while those whose mother tongue was English accounted for 3.9%. The next most common first languages were Spanish (2%), Arabic (1.3%) and Dari (0.7%)
As of 2016, approximately 88.8% of Sherbrooke residents were white, while 7.3% were visible minorities and 3.9% were aboriginal. The largest visible minority groups in Sherbrooke were Black (2.2%), Latin American (1.7%), Arab (1.2%), and West Asian (0.8%).
Census metropolitan area
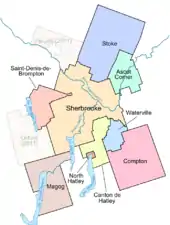
The Census Metropolitan Area (CMA) comprises the cities of Sherbrooke, Magog and Waterville, the municipalities of Ascot Corner, Compton, Saint-Denis-de-Brompton, Stoke and Val-Joli; the township municipalities of Hatley and Orford; and the village municipality of North Hatley. The population in 2021 was 227,398. The median age was 43.
Approximately 90.3% of the greater Sherbrooke area residents were white, while 5.8% were visible minorities and 3.9% were Aboriginal.[32]
French was mother tongue to 87.3% of residents. The next most common mother tongues were English (4.5%), Spanish (1.6%), Arabic (1.0%) Dari (0.5%), Mandarin (0.2%), Portugese (0.2%) and Serbian (0.2%).[3]
About 78.4% of the population identified as Catholic in 2011 while 13.8% said they had no religious affiliation, 1.7% were Muslim 0.6% Anglican, 0.6% Baptists, 0.6% Eastern Orthodox and 0.5% United Church. Pentecostals, Hindus and Buddhists made up 0.2% of the population each.
Economy

Sherbrooke, which is the economic centre of Estrie, is a significant cultural, industrial, and academic hub in the province. The city is directly served by two railways: the St. Lawrence and Atlantic Railroad and the Canadian Pacific Railway. Sherbrooke is also served by four highways as well as the regional airport named Sherbrooke Airport but located in the nearby city of Cookshire-Eaton. Sherbrooke Airport no longer offers scheduled passenger services as of March 2010.
According to data from the Institut de la statistique du Québec, average personal income per capita in the Census Metropolitan Area (CMA) of Sherbrooke amounted to Can$30,976 in 2010.[33] Estrie's GDP for the same year was $9.59 billion.[34]
- Largest employers
As of 2010, the largest employers in Sherbrooke are Université de Sherbrooke (6,000 employees), Centre hospitalier universitaire de Sherbrooke (5,511), Commission scolaire de la Région-de-Sherbrooke (3,050), Centre de santé et de services sociaux – Institut universitaire de gériatrie de Sherbrooke (2,650), City of Sherbrooke (1,913), Desjardins Group (1,713), Cégep de Sherbrooke (800), Centre Jeunesse de l'Estrie (527), Nordia Inc. (500), Canada Post (497), Kruger Inc. - Publication papers business unit (455), Bishop's University (450) and McDonald's (400).[35] These include enterprises operating in Sherbrooke only and having 400 or more employees.
Culture

In the summer season, several festivals, concerts, and events are held in the city, such as the Fête du Lac des Nations, Sherblues & Folk, and the Festival des traditions du monde. Come winter, the city hosts the Carnaval de Sherbrooke.
The city has British architectural heritage, as seen in the buildings in Vieux-Nord.
Sherbrooke has the fourth largest theatre in Quebec, the Maurice O'Bready University Cultural Centre of Sherbrooke (Salle Maurice-O’bready du centre culturel de l’Université de Sherbrooke). Music, theatre, and dance shows are staged there. The Centennial Theatre of Bishop's University also hosts music and dance concerts from around the world. The Vieux Clocher, owned by the Université de Sherbrooke, has two stages, the primary being used by various music groups and comedians from around the province. The Théâtre Granada, designated as a historical site by the Canadian government, holds music concerts. It has retained its original architecture since its opening. The Petit Théâtre de Sherbrooke, located downtown, presents musicals and plays for children.[37]
Since 2007, the Centre des arts de la scène Jean-Besré (CASJB), built by the city with the support of the Ministry of Culture and Communications, has assisted in the creation and production of material for the region's artistic community.[38] It serves as the location for training theatre, music, and dance professionals. It contains three rehearsal studios, a production room, a decoration workshop, and a costume workshop, as well as administrative offices for each of its resident companies.

Auditoriums
- Salle Maurice-O'Bready
- Granada Theatre
- Centennial Theatre
- Vieux Clocher
- Le Petit Théâtre de Sherbrooke
- Théâtre Léonard Saint-Laurent
- Salle Alfred-Des Rochers
Libraries
- La bibliothèque municipale Éva-Senécal, the main city library (opened 22 December 1990), is named for Éva Senécal (1905-1988), poet, novelist and journalist.
- La bibliothèque du secteur de Rock Forest
- La bibliothèque du secteur de Saint-Élie
- La bibliothèque Gisèle-Bergeron
- La bibliothèque de Lennoxville, at the intersection of rue Queen and rue College, near Bishop's University, offers a book lending service in French and English.
Attractions

Museums and visitors' centres
- Sherbrooke Nature and Science Museum
- Centre d'interprétation de l'histoire de Sherbrooke
- Sherbrooke Museum of Fine Arts
- Centre culturel et du patrimoine Uplands
- Art gallery at the Centre Culturel of Sherbrooke University
- Centre d'art actuel Sporobole
- Prison Winter
Parks
- Johnville Bog & Forest Park
- Forêt jardinée de l'aéroport de Sherbrooke Sherbrooke has parks and greenspaces that encompass a variety of recreational activities. In total, there are 108 in the municipality.[39] Parks Jacques-Cartier, Mont Bellevue, Bois Beckett, Lucien-Blanchard, Central, Quintal, Victoria, and Marais Réal-D.-Carbonneau are among the most popular destinations.
- Jacques-Cartier Park
 Jacques-Cartier Park
Jacques-Cartier Park
- Situated along lac des Nations, this park is about 1 kilometre (0.62 mi) away from the downtown area and is connected to the lac des Nations promenade. It contains several sports facilities including soccer fields and tennis courts. Several festivals are held here including the Fête du Lac des Nations, the Carnaval de Sherbooke, the festivities for the Fête Nationale and Canada Day.
- Mont Bellevue Park
 Mounts Bellevue (left) and John-S.-Bourque (right), as seen across the Magog River
Mounts Bellevue (left) and John-S.-Bourque (right), as seen across the Magog River
- This park is the largest in Sherbrooke, with an area of 200 hectares (490 acres). Situated partially on the campus of the Université de Sherbrooke, it is managed by the city and developed by volunteer organization Regroupement du Mont-Bellevue. Within the park are mounts Bellevue and John-S.-Bourque, the former of which has a small ski station. The park is also used for cross-country skiing, snowshoeing, walking, and tubing in winter; as well as hiking, mountain biking, archery, tennis, and jogging in summer. The park contains a total of 30 kilometres (19 mi) of trails and several different types of ecosystems.[40]
- Bois Beckett Park
- This park was established on an old maple grove that belonged to Major Henry Beckett between 1834 and 1870. The property remained in his family until it was acquired by the city in 1963.[41] In 2000, the Ministère de Ressources naturelles et de la Faune recognized the property as an old-growth forest.[42] The oldest tree is said to be 270 years old.[43] The park is maintained, protected and promoted by a volunteer group. Several trails have been built by the city which are open year-round. Within the park, there are several artifacts left behind by Beckett, such as foundations, wells, and farm equipment.
- Lucien-Blanchard Park
 Armand-Nadeau Pavilion in Jacques-Cartier Park
Armand-Nadeau Pavilion in Jacques-Cartier Park
- Situated 3 kilometres (1.9 mi) west of downtown on the bank of the Magog River, this park is open to several outdoor activities such as swimming and beach volleyball. Bicycles, canoes, kayaks, paddle boats, and dragon boats are available for rent. There is an interpretation centre with an emphasis on the reptiles and amphibians of the region as well as a boutique.
- Central Park
- At the heart of the Rock Forest–Saint-Élie–Deauville borough, this park is equipped for soccer, tennis, baseball, beach volleyball, and has a playground and an outdoor pool.
- Quintal Park
- Formerly called Parc Central de Fleurimont, this park is situated in the borough of Fleurimont, and mirrors Central Park of Rock Forest-Saint-Élie-Deauville. In early July, the Pif Classic baseball tournament is held in the park, and in August, it hosts the Festival des Traditions du Monde.
- Victoria and Sylvie-Daigle Parks
- Across Terrill Street from one another, these parks are situated just east of downtown. Inside these parks lie pedestrian trails, Olympic-size soccer fields, a handicap accessible outdoor pool, and a sports complex.[44] This multifunctional facility, called the Centre MultiSport Roland-Dussault, has an artificial turf allowing local teams the opportunity to practise indoor soccer, baseball, football, rugby, and so on. There is a hockey arena.
- Marais Réal-D.-Carbonneau
 Le Marais Réal-D.-Carbonneau
Le Marais Réal-D.-Carbonneau
- Located near the Saint-François River, this marsh was developed by CHARMES, a non-profit management corporation that seeks to promote ecotourism in and around Sherbrooke.[45] The park is located on 40 hectares (99 acres) of land and allows visitors access to wooden piers and observation towers, where there are over 50 tree and shrub species and birds.[46]
Sports
Baseball
The Sherbrooke Expos of the Ligue de Baseball Majeur du Québec, an amateur baseball league, play their home games at Amedée Roy Stadium.
The city also hosted some games of the 2002 World Junior Baseball Championship,[47] and the 2013 Canada Games.[48]
Historically, several professional teams based in Sherbrooke competed in Minor League Baseball or in independent baseball leagues:[49]
| Season(s) | Team | League | Classification |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1940 | Sherbrooke Braves | Quebec Provincial League | Class B |
| 1946 | Sherbrooke Canadians | Border League | Class C |
| 1947 | Sherbrooke Black Sox | Quebec Provincial League | Independent |
| 1948–1949 | Sherbrooke Athletics | Provincial League | |
| 1950–1951 | Class C | ||
| 1953–1955 | Sherbrooke Indians | ||
| 1972–1973 | Sherbrooke Pirates | Eastern League | Double-A |
Ice hockey
The Sherbrooke Phoenix is a junior hockey team playing in the Quebec Major Junior Hockey League.
The Sherbrooke Canadiens competed in the American Hockey League from 1984 to 1990.
Government
Sherbrooke is the seat of the judicial district of Saint-François.[50]
Municipal
Local governance is provided by the Sherbrooke City Council. The mayor is Évelyne Beaudin.[51]
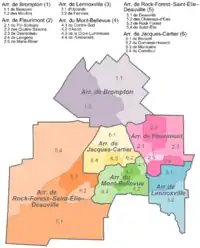
Under the 2000–2006 municipal reorganization in Quebec, Sherbrooke merged with most of the suburban municipalities in the surrounding area: Rock Forest, Saint-Élie-d'Orford, Deauville, Fleurimont, Bromptonville, Ascot, and Lennoxville. This resulted in the creation of six Boroughs of Sherbrooke: Brompton, Fleurimont, Lennoxville, Mont-Bellevue, Rock Forest–Saint-Élie–Deauville, and Jacques-Cartier. Each of the boroughs is subdivided into electoral districts, with the number varying based on population. For example, there are only two districts in Brompton, which only has 6,314 inhabitants, whereas Fleurimont (pop. 40,824) has five. Sherbrooke has 21 districts total, for which the average population is 7,200 inhabitants.
| Borough | Population | City Councillors |
|---|---|---|
| Brompton | 5,956 | 3 |
| Fleurimont | 41,276 | 5 |
| Jacques-Cartier | 30,229 | 4 |
| Lennoxville | 5,195 | 3 |
| Mont-Bellevue | 33,377 | 4 |
| Rock Forest–Saint-Élie–Deauville | 29,191 | 4 |
Federal and provincial
Sherbrooke is split into the federal electoral districts of Sherbrooke, represented by Élisabeth Brière of the Liberal party of Canada and Compton—Stanstead, represented by Marie-Claude Bibeau of the Liberals.
Provincially, Sherbrooke is divided into three electoral districts. Sherbrooke is represented by Christine Labrie of the Québec solidaire (QS), Saint-François is represented by Guy Hardy of the PLQ and Richmond is represented by Karine Vallières of the PLQ.
Public safety
In 2007, the crime rate was 5,491 per 100,000.[52]
Military

Sherbrooke does not host any units from the Regular Force with the exception of a recruiting centre, but four Primary Reserve units are stationed in the city:
- 52nd Field Ambulance, formerly known as 8th Medical Company.
- 714th Communication Squadron
- Les Fusiliers de Sherbrooke
- The Sherbrooke Hussars, formed from the amalgamation of The Sherbrooke Regiment and the 7th/11th Hussars in 1965.
A Canadian military artifact is preserved at the William Street Armoury, the Sherman tank "Bomb" which helped liberate Europe fighting with the Sherbrooke Fusilier Regiment and is the only Canadian tank to have landed on the Normandy beach on D-Day and fought through to VE Day without being knocked out.
Infrastructure
Transportation
Transdev Limocar provides bus service to Montreal via Granby and Magog. Formerly, Autobus Jordez linked Sherbrooke to Drummondville and Trois-Rivières, and also to Victoriaville and Quebec City, but since the company lost their licence to operate heavy vehicles,[53] they have sold their licence to Autobus La Québécoise, who now provide the service.
Société de transport de Sherbrooke (STS) provides bus service within the city. It operates 17 bus routes, 11 minibus routes, and 5 taxibus routes.
The city is located at the eastern terminus of A-10, and directly on the Autoroute Trans-Québécoise (A-55). A-10 provides a direct freeway connection to Montreal and points west, while A-55 connects directly to Trois-Rivières, Shawinigan, and points north, as well as to Interstate 91 to the south (Vermont). A-410 and A-610 are the southern and northern bypass roads, respectively.
The last passenger train for the city was VIA Rail's Montreal – Saint John, New Brunswick Atlantic, which ended service in 1994. There have been recent proposals to provide rail service from Montreal to Boston with a stop in Sherbrooke.[54]
Sherbrooke Airport, in Cookshire-Eaton is just east of the city. There are currently no scheduled flights operating out of the airport.
Public health
The suburban Sherbrooke University Hospital ("CHUS"[55] or "Centre Hospitalier Universitaire de Sherbooke) has over 5,200 employees, including 550 doctors. It includes a clinical research facility, the Étienne-Lebel Research Centre.
Education
Sherbrooke has eight institutions that make up the Sherbrooke University Pole, which educates some 40,000 students and employs about 11,000 persons.[56] University students comprise 10.32% of the population, the highest concentration in Quebec.[57]
The city is the location of one French-language university, the Université de Sherbrooke, and an English-language university, Bishop's University. Université de Sherbrooke is a comprehensive university with schools of medicine and law and extensive graduate programs. Bishop's University is smaller and predominantly undergraduate. There are three CEGEPs in Sherbrooke, two of them French-language, the Cégep de Sherbrooke and the Séminaire de Sherbrooke, and one English-language, Champlain College Lennoxville. CCSQ and CDE College which currently enrols International Students. In the past over 100 International students have graduated and landed jobs in Sherbrooke City itself, making it an attraction to the Indian student division. There currently over 100 South Asians residing in the City of Sherbrooke which consists of Hindu, Punjabi and Gujrati ethnic background.
There are also public high school boards such as the English Eastern Townships School Board, French Commission scolaire de la Région-de-Sherbrooke and private high schools such as Séminaire de Sherbrooke founded in 1875, Bishop's College School founded in 1836, etc.
See also
- List of mayors of Sherbrooke
- List of people from Sherbrooke
- List of regional county municipalities and equivalent territories in Quebec
References
- "Sherbrooke". Commission de toponymie. Retrieved 29 December 2021.
- "Répertoire des municipalités: Sherbrooke". Ministère des Affaires municipales et de l'Habitation (in French). Government of Quebec. Retrieved 29 December 2021.
- "Census Profile – Sherbrooke, Ville". Canada 2021 Census. Statistics Canada. 17 August 2022. Retrieved 19 September 2022.
- "Census Profile – Sherbrooke (Population centre)". Canada 2011 Census. Statistics Canada. 6 June 2012. Retrieved 29 July 2012.
- "Sherbrooke". Geographical Names Data Base. Natural Resources Canada.
- "Table 36-10-0468-01 Gross domestic product (GDP) at basic prices, by census metropolitan area (CMA) (x 1,000,000)". Statistics Canada. 27 January 2017. Archived from the original on 22 January 2021. Retrieved 27 April 2021.
- "Sherbrooke Population 2021". World Population Review. Retrieved 31 December 2021.
- "Sherbrooke". l'Encyclopédie Canadienne. Retrieved 29 December 2021.
- Kesteman, Jean-Pierre, Histoire de Sherbrooke Take I: l'âge de l'eau à l'ère of vapeur (1802-1866), ed. GGC, 2000, p.14 353.
- "Sherbrooke | The Canadian Encyclopedia". www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca. Retrieved 31 December 2021.
- "Hyatt, Gilbert". Dictionary of Canadian Biography. Retrieved 31 December 2021.
- "Sherbrooke". Canadian Travel Guide. Retrieved 29 December 2021.
- Sherbrooke, Destination. "A brief history of Sherbrooke". Destination Sherbrooke. Retrieved 31 December 2021.
- Baskerville, Peter A. (6 February 2006). "British American Land Company". thecanadianencyclopedia.ca. Canadian Encyclopedia.
- Browde, Anatole (2002). "Settling the Canadian Colonies: A Comparison of Two Nineteenth-Century Land Companies". Business History Review. 76 (2): 299–335. doi:10.2307/4127841. ISSN 0007-6805. JSTOR 4127841. Retrieved 31 December 2021.
- Macdonald, Roy (8 November 2012). "2 killed, 19 injured in Sherbrooke Factory explosion". CBC News. Retrieved 17 November 2020.
- "Pharmaceutical plant explosion injures 17, leaves cloud of toxic smoke looming over Sherbrooke". National Post. 8 November 2012. Retrieved 18 November 2020.
- "Sherbrooke A, Quebec". Canadian Climate Normals 1981–2010. Environment Canada. Archived from the original on 17 July 2020. Retrieved 12 October 2013.
- "July 1931". Canadian Climate Data. Environment Canada. 31 October 2011. Retrieved 27 March 2016.
- "January 2004". Canadian Climate Data. Environment Canada. 31 October 2011. Retrieved 27 March 2016.
- "Sherbrooke (1900-1972)". Canadian Climate Data. Environment Canada. 31 October 2011. Retrieved 27 March 2016.
- "Sherbrooke (Universite)". Canadian Climate Data. Environment Canada. 31 October 2011. Retrieved 27 March 2016.
- "Sherbrooke Quebec". Canadian Climate Data. Environment Canada. 31 October 2011. Retrieved 13 May 2022.
- "Sherbrooke". Canadian Climate Data. Environment Canada. 31 October 2011. Retrieved 27 March 2016.
- Statistics Canada: 1871, 1881, 1891, 1901, 1911, 1921, 1931, 1941, 1951, 1956, 1961, 1966, 1971, 1976, 1981, 1986, 1991, 1996, 2001, 2006, 2011, 2016, 2021 census
- "Évolution démographique des 10 principales villes du Québec (Sur la base de 2006) selon leur limites territoriales actuelles1, Recensements du Canada de 1871 à 2006". www.stat.gouv.qc.ca. Archived from the original on 6 October 2013. Retrieved 19 October 2022.
- "Population and dwelling counts: Canada, provinces and territories, and census subdivisions (municipalities), Quebec". Statistics Canada. 9 February 2022. Retrieved 29 August 2022.
- "2016 Community Profiles". 2016 Canadian Census. Statistics Canada. 12 August 2021. Retrieved 14 September 2022.
- "2011 Community Profiles". 2011 Canadian Census. Statistics Canada. 21 March 2019. Retrieved 14 September 2022.
- "2006 Community Profiles". 2006 Canadian Census. Statistics Canada. 20 August 2019.
- "2001 Community Profiles". 2001 Canadian Census. Statistics Canada. 18 July 2021.
- Government of Canada, Statistics Canada (8 February 2017). "Census Profile, 2016 Census - Sherbrooke [Census metropolitan area], Quebec and Sherbrooke, Territoire équivalent [Census division], Quebec". www12.statcan.gc.ca. Retrieved 16 July 2019.
- "Per capita personal income and its components, RCMs and equivalent territory of the Estrie region, 2006-2010". Institut de la statistique du Québec. 14 December 2011. Retrieved 24 July 2012.
- "Gross domestic product (GDP) at basic prices, Estrie and all of Québec, 2006-2010". Institut de la statistique du Québec. 18 August 2011. Retrieved 24 July 2012.
- "Les 500 plus grands employeurs de l'Estrie" (PDF). La Tribune. 18 March 2010. Retrieved 24 July 2012.
- Bombardier, David (16 September 2008). "Le cénotaphe sera restauré" (in French). La Tribune. Retrieved 12 August 2014.
- "Mission" (in French). Retrieved 13 August 2014.
- "Accueil". CASJB. Retrieved 29 December 2021.
- "Sports, recreation, and outdoor activities". Sherbrooke Innopole. Retrieved 6 July 2012.
- City of Sherbrooke (24 March 2010). "Un peu d'histoire" (in French). Archived from the original on 16 December 2012. Retrieved 1 June 2011.
- "Histoire du parc du Bois-Beckett" (in French). Le Regroupement du Bois Beckett. Retrieved 26 August 2010.
- "Parc du Bois-Beckett" (in French). City of Sherbrooke. 20 March 2008. Retrieved 6 July 2012.
- "Bois-Beckett Park". Destination Sherbrooke. Retrieved 6 July 2012.
- "Parcs et équipements" (in French). City of Sherbrooke. Retrieved 6 July 2012.
- "Historique du Marais" (in French). Official site of Marais Réal-D.-Carbonneau. Retrieved 6 July 2012.
- "Marais Réal-D.-Carbonneau". Destination Sherbrooke. Retrieved 6 July 2012.
- Richard, Jean-Paul (31 July 2002). "Between specialists, one understands..." La Tribune. Sherbrooke. Retrieved 31 December 2011.
- "Amédée-Roy Stadium". Sport venue. 2013 Canada Games. 2011. Archived from the original on 17 January 2012. Retrieved 31 December 2011.
- "Sherbrooke, Quebec, Canada Encyclopedia". Baseball-Reference.com. Retrieved 20 December 2021.
- Territorial Division Act. Revised Statutes of Quebec D-11.
- "Mayor of Sherbrooke". Ville de Sherbrooke. Retrieved 1 December 2021.
- "Best places to do business in Canada". Canadian Business. 10 September 2007. Retrieved 13 February 2008.
- "Autocars Jordez a mis ses passagers en danger - ICI.Radio-Canada.ca". Radio-Canada.ca. Retrieved 26 April 2015.
- Muther, Christopher (1 September 2022). "Plan to launch Montreal-to-Boston train service gains steam". The Boston Globe. Retrieved 2 September 2022.
- pronounced "Shoe"
- "Home: Pôle universitaire de Sherbrooke - Université de Sherbrooke: Pôle universitaire de Sherbrooke - Université de Sherbrooke". Retrieved 26 April 2015.
- Ville de Sherbrooke: "Proportion d'étudiants à Sherbrooke"(in French)