Washington–Baltimore combined statistical area
The Washington–Baltimore combined statistical area is a statistical area consisting of the two overlapping labor-market metropolitan areas of Washington, D.C. and Baltimore, Maryland. The region includes Central Maryland, Northern Virginia, three counties in the Eastern Panhandle of West Virginia, and one county in South Central Pennsylvania. It is the most educated, highest-income, and third-largest combined statistical area in the United States, behind only New York–Newark and Los Angeles–Long Beach.[1][2]
Washington–Baltimore combined statistical area | |
|---|---|
CSA | |
   The National Mall in Washington, D.C., Baltimore's Inner Harbor, and Rosslyn in Arlington | |
| Coordinates: 38.97°N 77.32°W | |
| Country | United States |
| State or area | |
| Constituent Metropolitan & Micropolitan Areas | Core areas:
Outlying areas:
|
| Principal cities |
|
| Population (2020) | |
| • CSA | 9,973,383 (4th) |
| Time zone | UTC-5 (EST) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC-4 (EDT) |
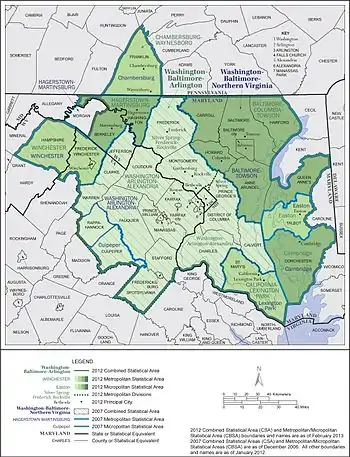
Officially, the area is designated by the Office of Management and Budget (OMB) as the Washington–Baltimore–Arlington, DC–MD–VA–WV–PA Combined Statistical Area. It is composed primarily of two major Metropolitan Statistical Areas (MSAs): the Washington–Arlington–Alexandria, DC–VA–MD–WV MSA and the Baltimore–Columbia–Towson, MD Metropolitan Statistical Area. In addition, five other smaller urban areas not contiguous to the main urban area but having strong commuting ties with the main area are included in the metropolitan area.[3] These are: the Hagerstown–Martinsburg, MD–WV MSA, the Chambersburg–Waynesboro, PA MSA, the Winchester, VA–WV MSA, the California–Lexington Park, MD MSA, and the Easton, MD micropolitan statistical area (µSA).
Some counties, such as Caroline and King George County, Virginia, are not officially designated by the OMB as members of this metropolitan area, but still consider themselves members anyway.[4][5][6][7][8] This is mostly due to their proximity to the area, the size of their commuter population, and by the influence of local broadcasting stations. The population of the entire Washington–Baltimore Combined Statistical Area as of the Census Bureau's 2020 data is 9,973,383. The most populous city is Washington, D.C., with a population of 689,545. The most populous county is Fairfax County, Virginia, with a population of 1,150,309.[9]
Components of the combined statistical area
The counties and independent cities and their groupings that comprise the area are listed below with their 2012 population estimates. Central counties/cities (designated as such by OMB) for each MSA are shown in italics.
- Washington–Arlington–Alexandria, DC–VA–MD–WV Metropolitan Area (5,860,342)
- Silver Spring–Frederick–Rockville, MD Metropolitan Division (1,244,291)
- Washington–Arlington–Alexandria, DC–VA–MD–WV Metropolitan Division (4,616,051)
- Washington, District of Columbia
- Calvert County, Maryland
- Charles County, Maryland
- Prince George's County, Maryland
- Arlington County, Virginia
- Clarke County, Virginia
- Culpeper County, Virginia
- Fairfax County, Virginia
- Fauquier County, Virginia
- Loudoun County, Virginia
- Prince William County, Virginia
- Woodbridge, Virginia
- Rappahannock County, Virginia
- Spotsylvania County, Virginia
- Stafford County, Virginia
- Warren County, Virginia
- Alexandria, Virginia
- Fairfax, Virginia
- Falls Church, Virginia
- Fredericksburg, Virginia
- Manassas, Virginia
- Manassas Park, Virginia
- Jefferson County, West Virginia
- Baltimore–Columbia–Towson, MD Metropolitan Area (2,753,149)
- Baltimore City
- Anne Arundel County
- Baltimore County
- Carroll County
- Harford County
- Howard County
- Queen Anne's County
- Hagerstown–Martinsburg, MD–WV Metropolitan Area (256,278)
- Washington County, Maryland
- Berkeley County, West Virginia
- Chambersburg–Waynesboro, PA Metropolitan Area (151,275)
- Franklin County, Pennsylvania
- Winchester, VA–WV Metropolitan Area (130,907)
- Frederick County, Virginia
- Winchester city, Virginia
- Hampshire County, West Virginia
- California–Lexington Park, MD Metropolitan Area (108,987)
- Easton, MD Micropolitan Area (38,098)
- Talbot County, Maryland
Regional organizations
Metropolitan Washington Council of Governments
Founded in 1957, the Metropolitan Washington Council of Governments (MWCOG) is a regional organization of 23 Washington-area local governments, as well as area members of the Maryland and Virginia state legislatures, the U.S. Senate, and the U.S. House of Representatives. MWCOG provides a forum for discussion and the development of regional responses to issues regarding the environment, transportation, public safety, homeland security, affordable housing, community planning, and economic development.[10]
The National Capital Region Transportation Planning Board, a component of MWCOG, is the federally designated Metropolitan Planning Organization for the metropolitan Washington area.[11]
Baltimore Metropolitan Council
The Baltimore Metropolitan Council is the equivalent organization for the Baltimore portion of the combined Baltimore–Washington metropolitan area.[12] The BMC, which was created in 1992 as the successor to the Regional Planning Council and Baltimore Regional Council of Governments, consists of the Baltimore region's elected executives, representing Baltimore City and Anne Arundel, Baltimore, Carroll, Harford and Howard counties.[13]
The Baltimore Regional Transportation Board is the federally recognized Metropolitan Planning Organization for transportation planning in the Baltimore region.[13]
List of principal cities
See List of cities in the Baltimore–Washington metropolitan area for a full list.[14]
Baltimore area
- Baltimore, Maryland
- Aberdeen, Maryland
- Annapolis, Maryland
- Arbutus, Maryland
- Bel Air, Maryland
- Brooklyn, Maryland
- Brooklyn Park, Maryland
- Catonsville, Maryland
- Cockeysville, Maryland
- Columbia, Maryland
- Curtis Bay, Maryland
- Dundalk, Maryland
- Eldersburg, Maryland
- Elkridge, Maryland
- Ellicott City, Maryland
- Essex, Maryland
- Fullerton, Maryland
- Glen Burnie, Maryland
- Halethorpe, Maryland
- Linthicum, Maryland
- Lutherville-Timonium, Maryland
- Middle River, Maryland
- North Laurel, Maryland
- Owings Mills, Maryland
- Overlea, Maryland
- Parkville, Maryland
- Pasadena, Maryland
- Perry Hall, Maryland
- Pikesville, Maryland
- Randallstown, Maryland
- Reisterstown, Maryland
- Savage, Maryland
- Severna Park, Maryland
- Towson, Maryland
- Westminster, Maryland
- Woodlawn, Maryland
Washington area
- Washington, District of Columbia
- Bethesda, Maryland
- Bowie, Maryland
- Chevy Chase, Maryland
- College Park, Maryland
- Frederick, Maryland
- Gaithersburg, Maryland
- Germantown, Maryland
- Laurel, Maryland
- Potomac, Maryland
- Rockville, Maryland
- Silver Spring, Maryland
- Upper Marlboro, Maryland
- Alexandria, Virginia
- Annandale, Virginia
- Arlington, Virginia
- Ashburn, Virginia
- Chantilly, Virginia
- Fairfax, Virginia
- Falls Church, Virginia
- Fredericksburg, Virginia
- Great Falls, Virginia
- Herndon, Virginia
- Langley, Virginia
- Leesburg, Virginia
- Manassas, Virginia
- Manassas Park, Virginia
- Massaponax, Virginia
- McLean, Virginia
- Mt. Vernon, Virginia
- Reston, Virginia
- Springfield, Virginia
- Tysons, Virginia
- Vienna, Virginia
- Charles Town, West Virginia
- Martinsburg, West Virginia
Economy
Biotechnology
Not limited to its proximity to the National Institutes of Health in Bethesda, Maryland's Washington suburbs are a major center for biotechnology. Prominent local biotechnology companies include MedImmune, United Therapeutics, The Institute for Genomic Research, Human Genome Sciences and the Howard Hughes Medical Institute.
Defense contracting
Many defense contractors are based in Northern Virginia and Montgomery County, Maryland to be close to the Pentagon in Arlington. Local defense contractors include Lockheed Martin, the largest, as well as Northrop Grumman, General Dynamics, BAE Systems Inc., Computer Sciences Corporation (CSC), Booz Allen Hamilton, Leidos, Science Applications International Corporation (SAIC), and Orbital Sciences Corporation.
Notable company headquarters in the region
Numbers denote Fortune 500 ranking.
Maryland
Baltimore area:
- Advertising.com (Baltimore)
- Allegis Group (Hanover)
- Black & Decker (Towson)
- Ciena Corporation (Hanover)
- Colfax Corporation (Annapolis Junction)
- Constellation Energy (Baltimore)
- Corporate Office Properties Trust (Columbia)
- The Cordish Companies (Baltimore)
- CoverGirl (Hunt Valley)
- Fila USA (Sparks)
- Firaxis Games (Sparks)
- Legg Mason (Baltimore)
- McCormick & Company (Hunt Valley) 482
- MICROS Systems (Columbia)
- Millennial Media (Baltimore)
- Nielsen Audio (Columbia)
- Pandora Jewelry USA (Baltimore)
- T. Rowe Price (Baltimore) 447
- Transamerica Corporation (Baltimore)
- Sinclair Broadcast Group (Hunt Valley) 465
- Sourcefire (Columbia)
- Sylvan Learning (Baltimore)
- Under Armour (Baltimore)
- W.R. Grace & Co. (Columbia)
- The Whiting-Turner Contracting Co. (Towson)[16]
Washington area:
- 2U (company) (Lanham, Maryland)
- ASRC Aerospace Corporation (Greenbelt, Maryland)
- Bethesda Softworks (Rockville)
- Clark Construction (Bethesda)
- Choice Hotels (Rockville)
- Coventry Health Care (Bethesda)
- EagleBank (Bethesda)
- Enviva (Bethesda)
- Federal Realty Investment Trust (Rockville)
- GEICO (Chevy Chase)
- Host Hotels & Resorts (Bethesda) 472
- Hughes Network Systems (Germantown)
- Inovalon (Bowie, Maryland)
- JBG Smith (Chevy Chase)
- Lockheed Martin (Bethesda) 49
- Marriott International (Bethesda) 293
- MedImmune (Gaithersburg)
- New Enterprise Associates (Chevy Chase)
- Novavax (Gaithersburg)
- Radio One (Lanham)
- Ritz-Carlton (Chevy Chase)
- Travel Channel (Chevy Chase)
- TV One (Silver Spring)
- United Therapeutics (Silver Spring)
Washington, D.C.
- &pizza
- APCO Worldwide
- Atlantic Media
- Black Entertainment Television
- Blackboard Inc.
- Bluemercury
- Carlyle Group
- Chemonics
- Cogent Communications
- CoStar Group
- Danaher Corporation 239
- Fannie Mae 53
- FiscalNote
- Framebridge
- Gallup
- Mapbox
- Morning Consult
- National Geographic Society
- NGP VAN
- Pepco Holdings 279
- Social Tables
- The Advisory Board Company
- The Washington Post Company
- Vox Media
- XM Satellite Radio
Northern Virginia
- AES Corporation (Arlington) 194
- Amazon (Crystal City)
- Appian Corporation (Tysons Corner)
- AvalonBay Communities (Arlington)
- Airbus North America (Herndon)
- BAE Systems Inc. (Arlington)
- Bechtel (Reston)
- Bloomberg Industry Group (Arlington)
- Boeing Defense, Space & Security (Arlington)
- Booz Allen Hamilton (McLean) 481
- CACI (Arlington)
- Capital One (McLean) 100
- Carfax (Centreville, Virginia)
- Computer Sciences Corporation (Falls Church) 379
- Communications Satellite Corporation (Herndon)
- Comscore (Reston)
- Cvent (Tysons Corner)
- DynCorp International (Falls Church)
- Freddie Mac (McLean) 39
- FNH USA (Fredericksburg)
- FLIR Systems Government and Defense (Arlington)
- Graham Holdings (Arlington)
- Gannett Company (McLean)
- General Dynamics (Falls Church) 90
- GTT Communications (Tysons Corner)
- Hilton Hotels Corporation (McLean) 241
- ICF International (Fairfax)
- Iridium Communications (McLean)
- Stride, Inc. (Herndon)
- Kellogg Brown and Root Services (Arlington)
- Leidos (Reston) 381
- Ligado Networks (Reston)
- Mars, Incorporated (McLean)
- M.C. Dean, Inc. (Dulles)
- MicroStrategy (Tysons Corner)
- Naviance (Arlington)
- Navy Federal Credit Union (Vienna)
- NII Holdings (Reston)
- Northrop Grumman (Falls Church) 114
- NVR Incorporated (Reston) 446
- Orbital Sciences (Dulles)
- Park Hotels & Resorts (Tysons Corner)
- Parsons Corporation (Centreville)
- Rolls-Royce North America (Reston)
- Rosetta Stone (Arlington)
- Science Applications International Corporation (McLean)
- SLM Corporation (Reston) "Sallie Mae"
- Strategic Education, Inc. (Herndon)
- Space Adventures (Vienna)
- Tegna Inc. (Tysons Corner)
- The Motley Fool (Alexandria, Virginia)
- The Teaching Company (Chantilly)
- Verisign (Reston)
- Verizon Business (Ashburn)
- Volkswagen Group of America (Herndon)
- VSE Corporation (Alexandria, Virginia)
- XO Communications (Herndon)
Sports
Table of professional teams and venues
| Club | Sport | League | Founded | Venue |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Washington Capitals | Hockey | NHL | 1974 | Capital One Arena |
| Washington Nationals | Baseball | MLB | 2005[lower-alpha 1] | Nationals Park |
| Baltimore Orioles | Baseball | MLB | 1954[lower-alpha 1] | Oriole Park at Camden Yards |
| Washington Wizards | Basketball | NBA | 1973[lower-alpha 1] | Capital One Arena |
| Baltimore Ravens | Football | NFL | 1996 | M&T Bank Stadium |
| Washington Commanders | Football | NFL | 1937[lower-alpha 1] | FedExField |
| D.C. United | Soccer | MLS | 1996 | Audi Field |
| Washington Mystics | Basketball | WNBA | 1998 | St. Elizabeths East Entertainment and Sports Arena |
| Washington Spirit | Soccer | NWSL | 2011[lower-alpha 2] | Maryland SoccerPlex (primary) Audi Field (secondary) Segra Field (secondary) |
| Old Glory DC | Rugby Union | Major League Rugby | 2018 | Segra Field |
- Year team moved to current location
- Founded as D.C. United Women; rebranded as Washington Spirit in 2012 and started NWSL play in 2013.
Transportation




_from_the_overpass_for_Virginia_State_Route_796_(Oak_Street)_on_the_edge_of_Idylwood_and_Dunn_Loring_in_Fairfax_County%252C_Virginia.jpg.webp)

Major airports
| Airport | IATA code | ICAO code | County | State | Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baltimore/Washington International Airport | BWI | KBWI | Anne Arundel County | Maryland | Closest to Baltimore and busiest in region[17] Capable of handling up to Group V aircraft |
| Ronald Reagan Washington National Airport | DCA | KDCA | Arlington | Virginia | Closest to Washington, DC Capable of handling up to Group IV aircraft |
| Dulles International Airport | IAD | KIAD | Dulles | Virginia | Most international traffic in region Capable of handling Group VI aircraft |
Rail transit systems
- Amtrak
- Washington Metro
- Virginia Railway Express
- MARC Train
- Baltimore Light Rail
- Metro Subway
- DC Streetcar
- Purple Line (future light rail)
Major highways
Interstates
 Interstate 66
Interstate 66 Interstate 70
Interstate 70 Interstate 81
Interstate 81 Interstate 83
Interstate 83 Interstate 95
Interstate 95 Interstate 97
Interstate 97 Interstate 195
Interstate 195 Interstate 270
Interstate 270 Interstate 295
Interstate 295 Interstate 370
Interstate 370 Interstate 395 (District of Columbia-Virginia)
Interstate 395 (District of Columbia-Virginia) Interstate 395 (Maryland)
Interstate 395 (Maryland) Interstate 495 (Capital Beltway)
Interstate 495 (Capital Beltway) Interstate 595 (Unsigned)
Interstate 595 (Unsigned) Interstate 695 (District of Columbia)
Interstate 695 (District of Columbia) Interstate 695 (Baltimore Beltway)
Interstate 695 (Baltimore Beltway) Interstate 795
Interstate 795 Interstate 895
Interstate 895
U.S. Routes
 U.S. Route 1
U.S. Route 1 U.S. Route 11
U.S. Route 11 U.S. Route 15
U.S. Route 15 U.S. Route 29
U.S. Route 29 U.S. Route 40
U.S. Route 40 U.S. Route 50
U.S. Route 50 U.S. Route 301
U.S. Route 301 U.S. Route 340
U.S. Route 340
State Routes
 Maryland Route 2
Maryland Route 2 Maryland Route 4
Maryland Route 4 Maryland Route 5
Maryland Route 5 Maryland Route 26
Maryland Route 26 Maryland Route 32
Maryland Route 32 Maryland Route 97
Maryland Route 97 Maryland Route 100
Maryland Route 100 Maryland Route 200 (Intercounty Connector)
Maryland Route 200 (Intercounty Connector) Baltimore–Washington Parkway (Maryland Route 295)
Baltimore–Washington Parkway (Maryland Route 295) Maryland Route 355
Maryland Route 355 Virginia State Route 3
Virginia State Route 3 Virginia State Route 7
Virginia State Route 7 Virginia State Route 9
Virginia State Route 9 Virginia State Route 28
Virginia State Route 28 Virginia State Route 267
Virginia State Route 267 Virginia State Route 286 (Fairfax County Parkway)
Virginia State Route 286 (Fairfax County Parkway) Virginia State Route 289 (Franconia–Springfield Parkway)
Virginia State Route 289 (Franconia–Springfield Parkway) West Virginia Route 9
West Virginia Route 9
See also
- United States metropolitan area
- National Capital Region
- List of parks in the Baltimore–Washington metropolitan area
- Beltway Series
References
- "CSA Median household income". Greaterbaltimore.org. Archived from the original on 7 December 2012. Retrieved 16 November 2017.
- "Raleigh-Durham area ranks third in U.S. for college degrees". Triangle.bizjournals.com. Retrieved 16 November 2017.
- OMB BULLETIN NO. 18-04: Revised Delineations of Metropolitan Statistical Areas, Micropolitan Statistical Areas, and Combined Statistical Areas, and Guidance on Uses of the Delineations of These Areas . Office of Management and Budget. September 14, 2018.
- "Caroline County Economic Development". Archived from the original on 2015-07-11. Retrieved 2015-07-21.
- "- Washington DC South". washingtondcsouth.com. Retrieved 16 November 2017.
- "King George County Department of Economic Development". King George County Department of Economic Development. Retrieved 16 November 2017.
- Gardner, D'Vera Cohn and Amy (16 March 2006). "3 Virginia Exurbs Near Top of U.S. in Growth". Washingtonpost.com. Retrieved 16 November 2017.
- "FAMPO Technical Committee - FAMPO". Fampo.gwregion.org. Retrieved 16 November 2017.
- "2020 Population and Housing State Data". U.S. Census Bureau. August 12, 2021. Retrieved September 5, 2021.
- "COG & Our Region - Metropolitan Washington Council of Governments". Mwcog.org. Retrieved 16 November 2017.
- "Transportation Planning Board - Transportation - Metropolitan Washington Council of Governments". Mwcog.org. Retrieved 16 November 2017.
- O'Leary, __Sara Ann. "Home - Baltimore Metropolitan Council". Baltometro.org. Retrieved 16 November 2017.
- About BMC – Baltimore Metropolitan Council Archived 2007-05-01 at the Wayback Machine
- "U.S. Census Bureau – Principal cities of metropolitan and micropolitan statistical areas". Census.gov. Retrieved 16 November 2017.
- "Metropolitan And Micropolitan Statistical Areas And Principal Cities, November 2007, with codes". Census.gov. Retrieved 16 November 2017.
- "Whiting-Turner Contracting on the Forbes America's Largest Private Companies List". Forbes.com. Retrieved 16 November 2017.
- As according to Federal Aviation Administration CY 2011 Enplanement Data, BWI exceeded Dulles by less than 24,000 passengers. As of 2010, however, Dulles has an edge in international traffic.