Heptanol
L'heptanol est l'alcool simple dont la chaîne carbonée contient sept atomes de carbone, de formule C7H15OH. Il existe en de très nombreux isomères, dépendamment de la position du groupe hydroxyle et de l'état de la chaîne carbonée.
- n-heptanol :
- heptan-1-ol
- heptan-2-ol
- heptan-3-ol
- heptan-4-ol
 heptan-1-ol
heptan-1-ol heptan-2-ol
heptan-2-ol heptan-3-ol
heptan-3-ol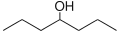 heptan-4-ol
heptan-4-ol
- méthylhexan-1-ol :
- 2-méthylhexan-1-ol
- 3-méthylhexan-1-ol
- 4-méthylhexan-1-ol
- 5-méthylhexan-1-ol
- 6-méthylhexan-1-ol
- méthylhexan-2-ol :
- 2-méthylhexan-2-ol
- 3-méthylhexan-2-ol
- 4-méthylhexan-2-ol
- 5-méthylhexan-2-ol
- 6-méthylhexan-2-ol
- méthylhexan-3-ol :
- 2-méthylhexan-3-ol
- 3-méthylhexan-3-ol
- 4-méthylhexan-3-ol
- 5-méthylhexan-3-ol
- 6-méthylhexan-3-ol
- éthylpentan-1-ol :
- 2-éthylpentan-1-ol
- 3-éthylpentan-1-ol
- éthylpentan-2-ol :
- 3-éthylpentan-2-ol
- éthylpentan-3-ol :
- 2-éthylpentan-3-ol
- 3-éthylpentan-3-ol
- Portail de la chimie
Cet article est issu de Wikipedia. Le texte est sous licence Creative Commons - Attribution - Partage dans les Mêmes. Des conditions supplémentaires peuvent s'appliquer aux fichiers multimédias.