Isocomène
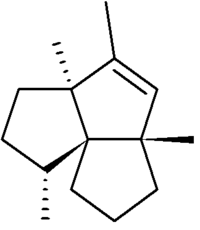
L’isocomène est un composé organique de formule C15H24, isolé pour la première fois à partir de la plante Isocoma wrightii, de la famille des astéracées, dont il tire son nom[2]. C'est un sesquiterpène dont la structure inhabituelle à trois cycles cyclopentane annélés a été décrite pour la première fois[2] par Zalkow et al. en 1977. La première synthèse totale de l'isocomène a été publiée par M.C. Pirrung[3] en 1979. Les étapes-clefs sont une réaction de cycloaddition [2 + 2] intramoléculaire photocatalysée, suivie d'un réarrangement qui forme trois centres chiraux contigus[4].
| Isocomène | |
| |
| Identification | |
|---|---|
| Nom UICPA | (2R,5S,8S)-2,5,6,8-tétraméthyltricyclo[6.3.0.01,5]undec-6-ène |
| Synonymes |
1,3a,4,5a-Tétraméthyl-1,2,3,3a,5a,6,7,8-octahydrocyclopenta[c]pentalène |
| No CAS | |
| PubChem | 188113 |
| SMILES | |
| InChI | |
| Propriétés chimiques | |
| Formule | C15H24 [Isomères] |
| Masse molaire[1] | 204,351 1 ± 0,013 7 g/mol C 88,16 %, H 11,84 %, |
| Unités du SI et CNTP, sauf indication contraire. | |
Références
- Masse molaire calculée d’après « Atomic weights of the elements 2007 », sur www.chem.qmul.ac.uk.
- (en) L. H. Zalkow, R. N. Harris, D. Van Derveer et J. A. Bertrand, « Isocomene: a novel sesquiterpene from Isocoma Wrightii. X-Ray crystal structure of the corresponding diol », Journal of the Chemical Society, Chemical Communications, no 13, , p. 456–457 (ISSN 0022-4936, DOI 10.1039/C39770000456, lire en ligne, consulté le ).
- Michael C. Pirrung, « Total synthesis of (.+-.)-isocomene », Journal of the American Chemical Society, vol. 101, no 23, , p. 7130–7131 (ISSN 0002-7863, DOI 10.1021/ja00517a087).
- Nicolaou, K. C., Classics in total synthesis I: targets, strategies, methods, VCH, (ISBN 3-527-29284-5, 978-3-527-29284-4 et 3-527-29231-4, OCLC 33971941, lire en ligne).
- Portail de la chimie
Cet article est issu de Wikipedia. Le texte est sous licence Creative Commons - Attribution - Partage dans les Mêmes. Des conditions supplémentaires peuvent s'appliquer aux fichiers multimédias.