There are two primary accounting methods - cash basis and accrual basis. The cash basis of accounting, or cash receipts and disbursements method, records revenue when cash is received and expenses when they are paid in cash. In contrast, the accrual method records income items when they are earned and records deductions when expenses are incurred, regardless of the flow of cash. Accrual accounts include, among others, accounts payable, accounts receivable, goodwill, deferred tax liability and future interest expense.
The term accrual is also often used as an abbreviation for the terms accrued expense and accrued revenue. Accrued revenue (or accrued assets) is an asset, such as unpaid proceeds from a delivery of goods or services, when such income is earned and a related revenue item is recognized, while cash is to be received in a later period, when the amount is deducted from accrued revenues. An example of an accrued expense is a pending obligation to pay for goods or services received from a counterpart, while cash is to be paid out in a latter accounting period when the amount is deducted from accrued expenses.
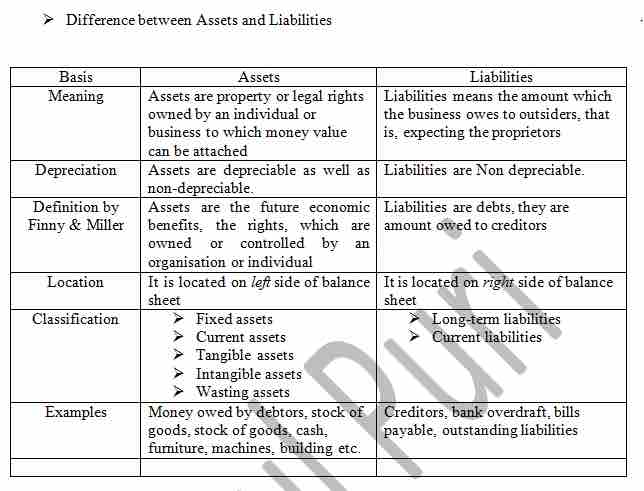
In financial accounting, assets are economic resources. Anything capable of being owned or controlled to produce value is considered an asset. Simply stated, assets represent value of ownership that can be converted into cash. Two major asset classes are intangible assets and tangible assets. Intangible assets are identifiable non-monetary assets that cannot be seen, touched or physically measured, are created through time and effort, and are identifiable as a separate asset. Tangible assets contain current assets and fixed assets. Current assets include inventory, while fixed assets include such items as buildings and equipment.
Assets and liabilities
Differences between assets and liabilities
A liability is an obligation of an entity arising from past transactions, the settlement of which may result in the transfer of assets, provision of services, or other yielding of economic benefits in the future. A liability is defined by the following characteristics:
- Any type of borrowing from persons or banks for improving a business or personal income,
- A responsibility to others that entails settlement by future transfer of assets, provision of services, or other transactions,
- A responsibility that obligates the entity to another, leaving it little or no discretion to avoid settlement, or
- A transaction or event obligating the entity that has already occurred.
In accounting and finance, equity is the residual claim or interest of the most junior class of investors in assets after all liabilities are paid. If liability exceeds assets, negative equity exists. In an accounting context, shareholders' equity represents the remaining interest in assets of a company, spread among individual shareholders in common or preferred stock.