Chapter 4
Controlling and Reporting of Cash and Receivables
By Boundless

Cash and cash equivalents are the most liquid type of company assets used by businesses to settle debts and purchase goods.

Types of cash include currency, funds in bank accounts, and non-risky financial instruments that are readily convertible to cash.
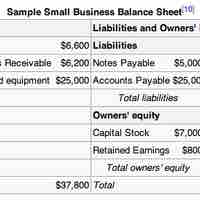
Cash and cash equivalents are reported in the current asset section of a business's balance sheet.
Cash internal controls is a system used to promote accuracy, prevent theft, and ensure a business has enough cash to pay its debts.
A bank is a good cash control because it limits employees' access to company assets and provides documentation on withdrawals and deposits.
A bank reconciliation is an internal control that ensures that the cash in its accounts equals what it has recorded in its books.

A company manages its cash primarily through the use of a voucher system and bank reconciliations.

A receivable is money owed to a business by its clients and shown on its balance sheet as an asset.

Receivables can generally be classified as accounts receivables or notes receivable, though there are other types of receivables as well.

If you are operating under the accrual basis, you record account receivable transactions irrespective of any changes in cash.

Receivables of all types are normally reported at their net realizable value, which is the amount the company expects to receive in cash.

Notes Receivable represents claims for which formal instruments of credit are issued as evidence of debt, such as a promissory note.

In accounting, notes receivables are accounts to keep track of accrued assets that have been earned but not yet received.

Companies have two methods available to them for measuring the net value of accounts receivable: the allowance method and the direct write-off method.

Companies use two methods for handling uncollectible accounts: the allowance method and the direct write-off method.

Accounts receivable represents money owed by entities to the firm on the sale of products or services on credit.

To help prevent fraudulent activities, management must implement internal controls/structure and know what situations to look for.
Receivables can be classified as accounts receivables, trade debtors, bills receivable, and other receivables.
To deal with foreign currency and bad debts, we have a "gain or loss" account and methods to measure the net value of accounts receivable.
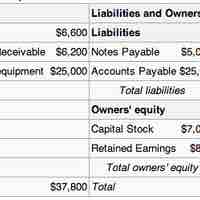
Accounts receivable are reported as a line item on the balance sheet and in a more detailed again report.
The receivables turnover ratio measures how efficiently a firm uses its assets.