Section 5
Endocrine Glands
By Boundless
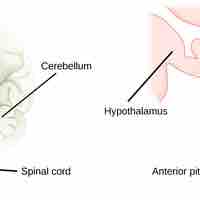
The hypothalamus, an endocrine organ, regulates the anterior pituitary gland and transports hormones along the posterior pituitary gland.
The thyroid gland, the largest endocrine gland, is responsible for the production of the hormones T3, T4, and calcitonin.
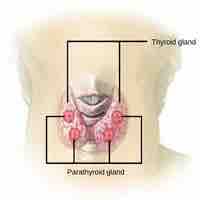
Parathyroid glands produce parathyroid hormone, which is responsible for specific physiological responses in the body related to calcium.
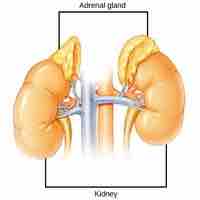
Adrenal glands are composed of the adrenal cortex and medulla; both produce hormones that control essential body functions and responses.
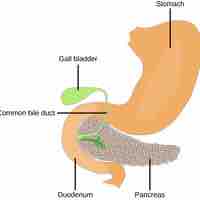
The pancreas produces digestive enzymes and hormones, which are important in blood sugar regulation and other body functions.
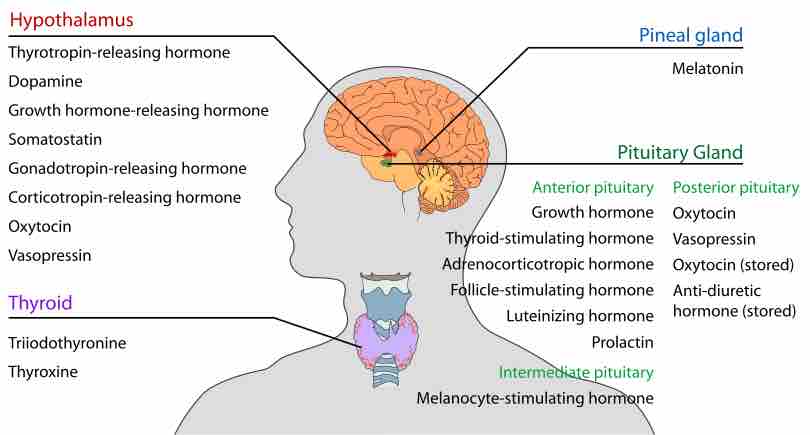
The pineal gland is responsible for melatonin production, while the gonads secrete hormones relating to sexual characteristic development.
Several organs with specialized non-endocrine functions possess endocrine roles, such as hormone production and release.