Chapter 6
Types of Business Ownership
By Boundless

A sole proprietorship is owned and run by one individual who receives all profits and has unlimited responsibility for all losses and debts.

The advantages of a sole proprietorship versus other forms of organizations is the relative ease of set-up and the lower start-up costs.

Sole proprietorships face a number of difficulties in the longer terms compared to limited liability companies.
A partnership, of which various forms exist, is an arrangement where parties agree to cooperate to advance their mutual interests.
Partnership agreements govern the relationship between the various individuals who are collaborating on a given venture.
Partnerships are easy to establish and carry many advantages, however there are risks due to the concentrated ownership structure.
Various partnerships need to file different tax forms; it is important to understand the IRS codes before embarking on a partnership.

Four main types of corporations are designated as C, S, limited liability companies, and nonprofit organizations.
Incorporating a business is the formation of a new corporation.

A corporation is typically owned and controlled by its shareholders.

Corporate structure consists of various departments and divisions that contribute to the company's overall mission and goals.

Shareholders of a modern business corporation have limited liability for the corporation's debts and obligations.

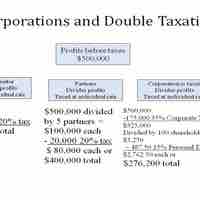
In many countries, corporate profits are taxed at a corporate tax rate, and dividends paid to shareholders are taxed at a separate rate -- double taxation.

S corporations elect to pass corporate income, losses, deductions, and credit through to their shareholders for federal tax purposes.

An LLC is a hybrid business entity which has characteristics of both a corporation and a partnership, or sole proprietorship in some cases.

Government-owned companies are either partially or fully owned by a government and have both a distinct legal form and commercial presence.

A nonprofit organization is an organization that uses surplus revenues to achieve goals rather than to distribute them as profit or dividends.

There are three major types of franchises - business format, product, and manufacturing - and each operates in a different way.

A franchise agreement can have many benefits for both the franchisor and the franchisee.

A franchise agreement can also have disadvantages for both the franchisor and the franchisee.

Home franchise operations have made franchising more accessible and affordable than ever, but still require knowledge and expertise.
Advances in technology benefits franchisors, franchisees, and the end customers.

Franchising grew greatly in 2001 to 2005, before stagnating and following the growth trend of the rest of the economy in the years that followed.
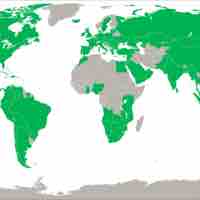
Franchises can be a powerful strategic tool in expanding globally, which has resulted in various trends in international adoption

A Franchise Agreement is a legal, binding contract between a franchisor and franchisee, enforced in the United States at the State level.
Cooperatives are independent and democratic organizations where each member has equal control.

A joint venture is when two or more parties are both invested in an original concept/project in terms of money, time, and effort.

A syndicate is a self-organizing group of individuals or entities formed to transact specific business or to promote a common interest.

Organic growth is the process of businesses expansion due to increasing the customer base, output per customer, and/or through new sales.

M&A refers to the aspect of corporate strategy, corporate finance, and management dealing with the buying and selling of companies.
Modern trends in M&A largely revolve around the acquisition of up-and-coming firms to enable technological advantage and global competencies for larger firms.