Economic Growth
Economic growth is defined as the increase in the market value of goods and services produced by an economy over time. It is usually measured as a percentage rate of increase in the real gross domestic product. In economics, economic growth refers to the growth of potential output. It shows how a country is developing its economy. Economic growth is directly impacted by human capital, which is the level of school or knowledge attainment in a country. The cognitive skills of a population directly impact economic growth. In general, economic growth is recorded and studied over the short-run and long-run.
Short-run Economic Growth
The business cycle refers to economy-wide fluctuations in production, trade, and economic activity over several months or years. The short-run variation in economic growth is called the business cycle. Economists use it to distinguish between short-run variations in economic growth and long-run economic growth. The cycle is made up of increases and decreases in production that occur over months and years. The changes in the business cycle are a result of fluctuations in aggregate demand .
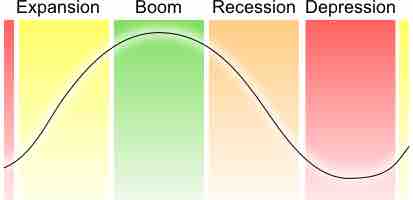
The Business Cycle
The business cycle is used to determine the short-run variation in economic growth. Variations in the business cycle fluctuation over months and years and are attributed to fluctuations in aggregate demand.
Long-run Economic Growth
Long-run economic growth is measured as the percentage rate increase in the real gross domestic product. The GDP is defined as the market value of all officially recognized final goods and services produced within a country in a given period of time. There are three approaches used to determine the GDP:
- Product (output) approach: adds together the outputs of every class of enterprise to provide the total.
- Income approach: calculates the sum of all the producers' incomes.
- Expenditure approach: the value of the total product must be equal to the people's total expenditures.
In principle, all of the approaches should yield the same result for the GDP of a country.
For example, the equation for the expenditure approach is: GDP = C + I + G + (X - M).
Written out in full, the gross domestic product (GDP) equals private consumption (C) plus, gross investment (I), government spending (G), and the exports minus the imports (X - M).
For economic purposes, the economic growth is calculated and compared to the population, also know as per capita income (indicator of a country's standard of living). When the per capita income increases it is called intensive growth. When the GDP growth is only caused by increases in population or territory it is called extensive growth.