Gross Domestic Product
The Gross domestic Product (GDP) is the market value of all final goods and services produced within a country in a given period of time. The GDP is the officially recognized totals. The following equation is used to calculate the GDP:
Written out, the equation for calculating GDP is:
GDP = private consumption + gross investment + government investment + government spending + (exports - imports).
For the gross domestic product, "gross" means that the GDP measures production regardless of the various uses to which the product can be put. Production can be used for immediate consumption, for investment into fixed assets or inventories, or for replacing fixed assets that have depreciated. "Domestic" means that the measurement of GDP contains only products from within its borders.
Nominal GDP
The nominal GDP is the value of all the final goods and services that an economy produced during a given year. It is calculated by using the prices that are current in the year in which the output is produced . In economics, a nominal value is expressed in monetary terms. For example, a nominal value can change due to shifts in quantity and price. The nominal GDP takes into account all of the changes that occurred for all goods and services produced during a given year. If prices change from one period to the next and the output does not change, the nominal GDP would change even though the output remained constant.
Nominal GDP
This image shows the nominal GDP for a given year in the United States.
Real GDP
The real GDP is the total value of all of the final goods and services that an economy produces during a given year, accounting for inflation . It is calculated using the prices of a selected base year. To calculate Real GDP, you must determine how much GDP has been changed by inflation since the base year, and divide out the inflation each year. Real GDP, therefore, accounts for the fact that if prices change but output doesn't, nominal GDP would change.
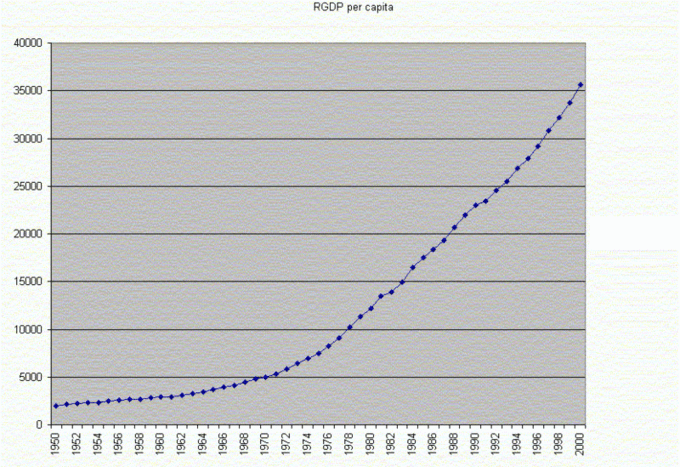
Real GDP Growth
This graph shows the real GDP growth over a specific period of time.
In economics, real value is not influenced by changes in price, it is only impacted by changes in quantity. Real values measure the purchasing power net of any price changes over time. The real GDP determines the purchasing power net of price changes for a given year. Real GDP accounts for inflation and deflation. It transforms the money-value measure, nominal GDP, into an index for quantity of total output.