Chapter 19
Measuring Output and Income
By Boundless
Gross domestic product is the market value of all final goods and services produced within the national borders of a country for a given period of time.

GDP is a measure of national income and output that can be used as a comparison tool.
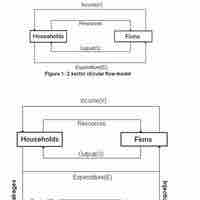
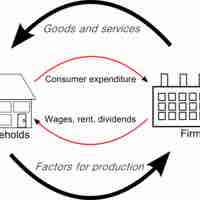
In economics, the "circular flow" diagram is a simple explanatory tool of how the major elements in an economy interact with one another.

GDP is the sum of Consumption (C), Investment (I), Government Spending (G) and Net Exports (X – M): Y = C + I + G + (X - M).

GDP can be calculated through the expenditures, income, or output approach.
The income approach evaluates GDP from the perspective of the final income to economic participants.
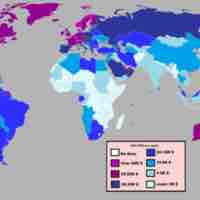
The value of GDP as a measure of the quality of life for a given country may be limited.
A variety of measures of national income and output are used in economics to estimate total economic activity in a country or region.

Personal income is an individual's total earnings from wages, investment interest, and other sources.
Disposable income is the income left after paying taxes.

Gross domestic product (GDP) per capita is the mean income of people in an economic unit.
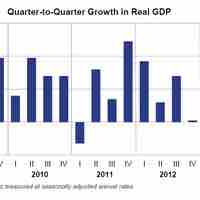
Real GDP growth is the value of all goods produced in a given year; nominal GDP is value of all the goods taking price changes into account.
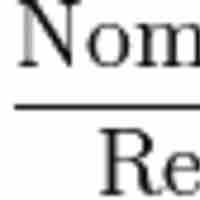
The GDP deflator is a price index that measures inflation or deflation in an economy by calculating a ratio of nominal GDP to real GDP.

Inflation is a persistent increase in the general price level, and has three varieties: demand-pull, cost-push, and built-in.

The consumer price index (CPI) is a statistical estimate of the change in prices of goods and services bought for consumption.