Chapter 8
Pricing
By Boundless
Price is both the money someone charges for a good or service and what the consumer is willing to give up to receive a good or service.

Depending on whether they are describing a good or a service and the product's industry, people may use terms other than the word price.

Since pricing has a direct impact on a company's revenue, and thus profit, setting the right price is essential to a company's success.
Value is the worth of goods, and relative value is attractiveness measured in terms of utility of one good relative to another.
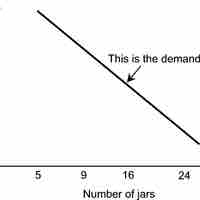
A demand curve is a graph showing the relationship between the price of a certain item and what consumers are willing to buy at the price.
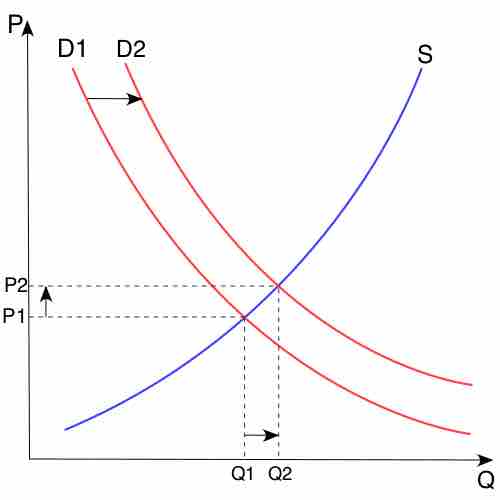
Changes in either supply or demand will move the market clearing point and change the market price for a good.
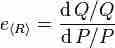
Elasticity of demand is a measure used in economics to show the responsiveness of the quantity demanded of an item to a change in its price.

Yield management systems give managers optimal control of inventory to sell it to the right customer at the right time for the right price.
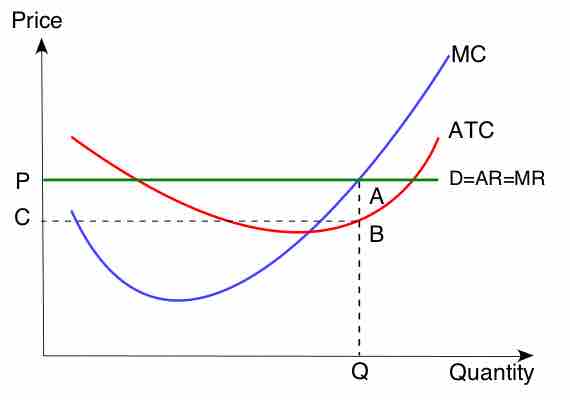
Pricing decisions tend to heavily involve analysis regarding marginal contributions to revenues and costs.
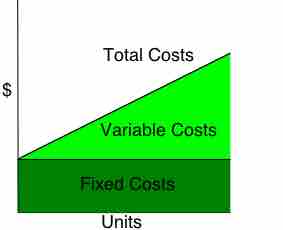
Fixed costs are business expenses that are not dependent on the level of goods or services produced by the business.

The break-even point is the point at which costs and revenues are equal.
For the vast majority of business entities, the ultimate objective should be to increase profits, often through a better pricing strategy.

Factors to consider in pricing include Economic Value added to Customers (EVC), competitor's pricing, and government regulations.

Most executives pursue strategies that align pricing with revenue generation, enabling their organizations to survive and thrive long term.
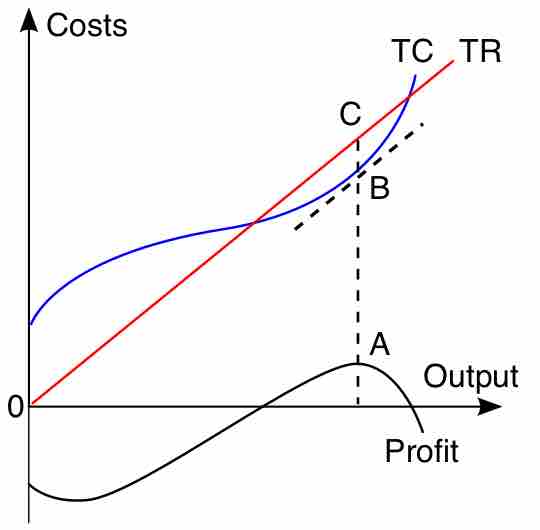
If the sole objective of a firm is to maximize profit, there are various profit maximizing pricing methods that can be used.
Marketers should understand the position of their company and the returns expected when making adjustments in prices.

Increasing market share is one of the most important objectives of business and pricing may offer a mechanism to increase share.

Cash flow is extremely important to firms as this is how they buy goods, pay employees, fund new investments, and pay dividends.

A status quo pricing objective is one that maintains current price levels or meets the price levels of the competition.

Quality refers to the ability of a product or service to consistently meet or exceed customer requirements or expectations.

Cost-based pricing is the act of pricing based on what it costs a company to make a product.
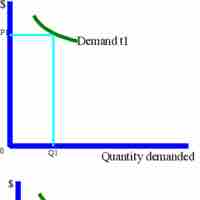
Demand-based pricing is any pricing method that uses consumer demand - based on perceived value - as the central element.
Competition-based pricing describes a situation where a firm has a pricing policy that reflects the pricing decisions of competitors.
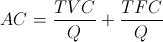
Markup pricing is a strategy in which a company first calculates the cost of the product, then adds a proportion of it as markup.
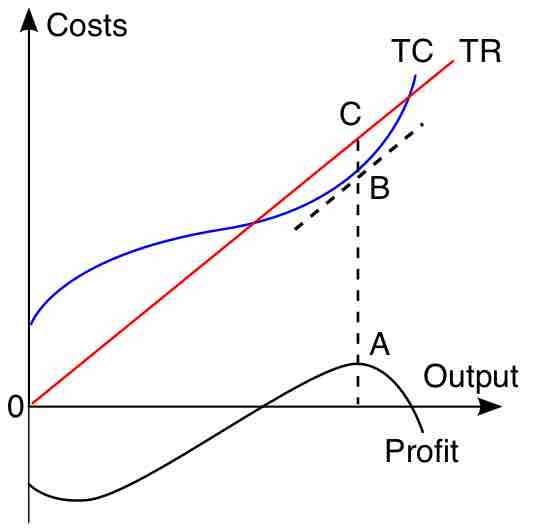
Profit maximization analysis is the process by which a firm determines the price and output level that returns the greatest profit.
With a new product, competition does not exist or is minimal, hence the general pricing strategies depend on different factors.

Line pricing is the use of a limited number of price points for all the product offerings of a vendor.

Psychological pricing is a marketing practice based on the theory that certain prices have meaning to many buyers.

During a recession, companies must consider their unique situation and what value they provide customers when devising a pricing strategy.

Everyday low price is a pricing strategy offering consumers a low price without having to wait for sale price events or comparison shopping.

High-low pricing is a strategy where most goods offered are priced higher than competitors, but lower prices are offered on other key items.

One pricing strategy does not fit all, thus adapting various pricing strategies to new scenarios is necessary for a firm to stay viable.

Discounts and allowances are reductions to a basic price of goods or services and can occur anywhere in the distribution channel.

Value-based pricing seeks to set prices primarily on the value perceived by customers rather than on the cost of the product or historical prices.
Geographical pricing is the practice of modifying a basic list price based on the location of the buyer to reflect shipping costs.
Transfer pricing describes all aspects of intracompany pricing arrangements between business entities for goods and services.

Penalties, in the form of fees and restricted user access, exist for consumers who violate terms in contracts.
Unfair business practices are oppressive or unconscionable acts by companies against consumers or other stakeholders.

Deceptive price advertising uses misleading or false statements in advertising and promotion and is usually illegal.

Predatory pricing is the practice of selling a product or service at a very low price, intending to drive competitors out of the market.
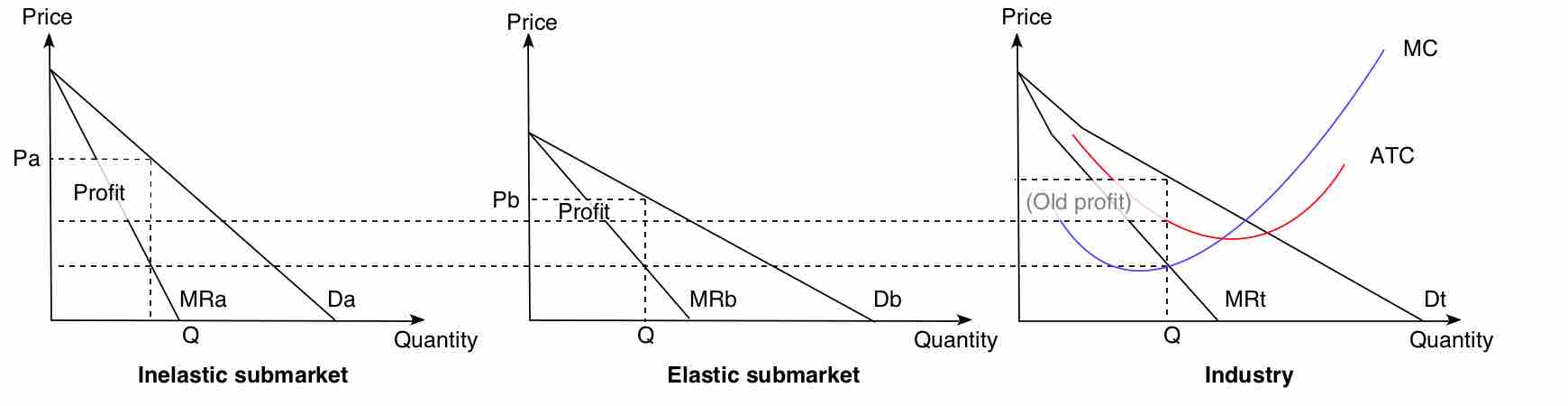
Although there are legal concerns around monopolistic practices, price discrimination is a popular tactic for capturing consumer surplus.

Price fixing is a collusion between competitors in order to raise prices of a good or service, at the expense of competitive pricing.