Chapter 16
Economic Policy
By Boundless
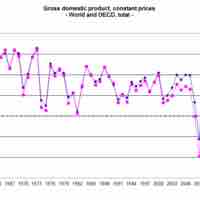
There are four major goals of economic policy: stable markets, economic prosperity, business development and protecting employment.

Mainstream modern economics can be broken down into four schools of economic thought: classical, Marxian, Keynesian, and the Chicago School.

Associated with industrialism and capitalism, the 19th century looms large in the history of economic policy and economic thought.

The Progressive Era was one of general prosperity after the Panic of 1893; a severe depression that ended in 1897.
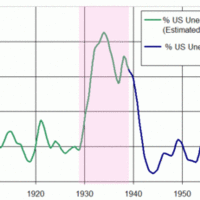
The New Deal was a series of economic programs enacted in the United States between 1933 and 1936 in response to the Great Depression.

Social policy refers to guidelines, principles, legislation and activities that affect the living conditions conducive to human welfare.

Deregulation is the act or process of removing or reducing state regulations.

Monetary policy is the process by which the monetary authority of a country controls the supply of money.

Fiscal policy is the use of government revenue collection or taxation, and expenditure (spending) to influence the economy.

Fiscal policy is considered to be any change the government makes to the national budget in order to influence a nation's economy.

Antitrust laws are a form of marketplace regulation intended to prohibit monopolization and unfair business practices.
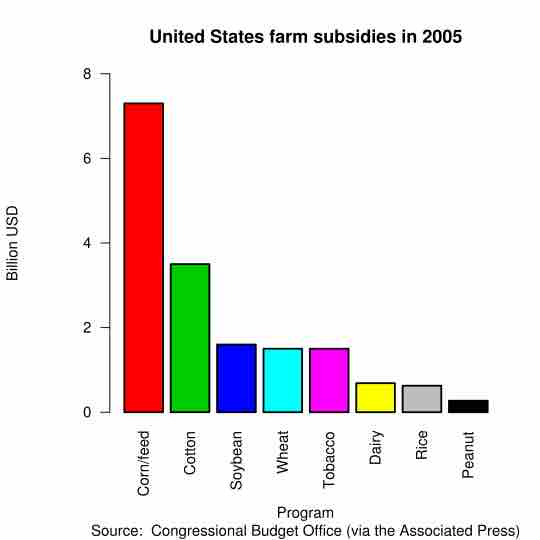
A subsidy is assistance paid to business, economic sectors, or producers; a contract is an agreement between two or more parties.
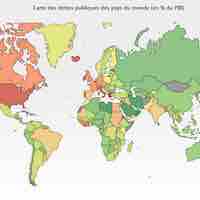
Government debt, also known as public debt, or national debt, is the debt owed by a central government.
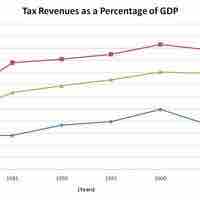
The United States is a federal republic with autonomous state and local governments with taxes imposed at each level.
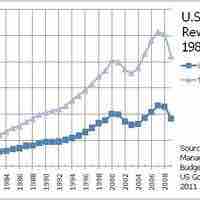
Federal income tax is levied on the income of individuals or businesses, which is the total income minus allowable deductions.
Tax evasion is the term for efforts by individuals, corporations, trusts and other entities to evade taxes by illegal means.
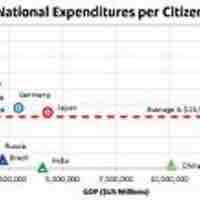
Fiscal policy is the use of government revenue collection (taxation) and expenditure (spending) to influence the economy.

Deficit spending and public debt are controversial issues within economic policy debates.

Monetary policy is the process by which a country controls the supply of money in order to promote economic growth and stability.
Income security policy is designed to provide a population with income at times when they are unable to care for themselves.

The role of the federal government in the economy has been a central debate among economists and political scientists for two centuries.
Global political instability is rising fast due to the global financial crisis and is creating new challenges that need to be managed.

The relationship between business and labor has been at the center of economic and political theory for the last two centuries.
- The Policy-Making Process
- Health Care Policy
- Energy and Environmental Policy
- Education Policy
- Immigration Policy