Sources of the United States' Economic Prosperity
In the two hundred and thirty years since the independence of the United States, the country has grown to be a huge, integrated, industrialized economy that makes up nearly a quarter of the world economy. The main policies that contributed to this economic prosperity were a large unified market, a supportive political-legal system, vast areas of highly productive farmlands, vast natural resources (especially timber, coal, iron, and oil) , and an entrepreneurial spirit and commitment to investing in material and human capital. The United States' economy has maintained high wages, attracting immigrants by the millions from all over the world. Technological and industrial factors have also played a major role in the United States' economic prosperity .

Advanced Technology
The United States has been able to grow into a world economic power in part due to the rapid advances of technology and industry.

Trans-Alaska Pipeline
One of the reasons for the United State's economic prosperity is the abundance of natural resources, such as oil. This picture shows the trans-Alaska oil pipeline, which carries oil from northern Alaska to the rest of the United States.
Economic Prosperity and Foreign Policy
The United States is highly influential in the world, primarily because the United States's foreign policy is backed by a $15 trillion economy, which is approximately a quarter of the global gross domestic product (GDP). Economic prosperity is a central component of any states' foreign policy. Without substantial economic means, a state cannot expect to have influence on the world stage. Similarly, economic prosperity is tied to the maintenance of a global military presence. Without a strong military, the pursuit of national interests becomes more difficult.
Continued Economic Prosperity?
In 2008, a perfect storm of economic disasters hit the United States and indeed the entire world. The most serious began with the collapse of housing bubbles in California and Florida, along with the collapse of housing prices and the construction industry. A series of the largest banks in the United States and Europe also collapsed; some went bankrupt, others were bailed out by the government. The United States government voted 700 billion in bailout money, committed trillions of dollars to shoring up the financial system, but the measures did not reverse the declines. Banks drastically tightened their lending policies, despite infusions of federal money. The stock market plunged 40%, wiping out tens of trillions of dollars in wealth; housing prices fell 20% nationwide wiping out trillions more. By late 2008, distress was spreading beyond the financial and housing sectors. President Barack Obama signed the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009 in February 2009; the bill provides 787 billion in stimulus through a combination of spending and tax cuts.
Due to the close relationship between economic prosperity and foreign policy, the recession has impacted all elements of the United States' foreign policy. Cuts to the military and defense spending have been threatened, and this economic crisis will undoubtedly take a toll on the United State's position as a global superpower. However, despite the economic recession, the sheer size of the United State's economy ensures that it will remain an important actor in the world economy .
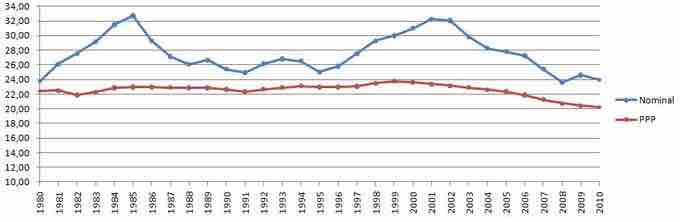
The United States' Share of World GDP
The United States' share of world GDP (nominal) peaked in 1985 with 32.74% of global GDP (nominal). The second highest share was 32.24% in 2001. Note that it is been declining since then.