Chapter 2
The Constitution and the Founding of America
By Boundless
The way the British government was run in the colonies inspired what the Americans would write in their Constitution.

The expenses from the French and Indian War caused the British to impose taxes on the American colonies.
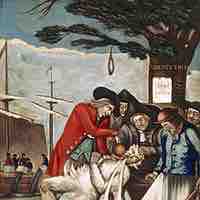
"No Taxation without Representation" was the rallying cry of the colonists who were forced to pay the stamp, sugar, and tea taxes.

The first Continental Congress was held between 1774 and 1775 to discuss the future of the American colonies.

The Second Continental Congress was ushered in at the beginning of the Revolution and eventually decided American independence.

The new congress faced many roadblocks in establishing the new nation.

The Declaration of Independence was a letter to the king explaining why the colonies were separating from Britain.

The Articles of Confederation established a confederacy-type government among the new American states.
The Articles of confederation gave few but important powers of diplomacy to the American government.
The Articles of Confederation, while riddled with problems, did have lasting effects.

Shays' rebellion prompted the Boston elite and members of the central government to question the strength of the American government.

The Annapolis Convention, led by Alexander Hamilton, was one of two conventions that met to amend the Articles of Confederation.
The Constitutional Convention was established in 1787 to replace the Articles of Confederation with a national constitution for all states.

The Framers of the Constitution were delegates to the Constitutional Convention who took part in drafting the proposed U.S. Constitution.
At the Constitutional Convention, the Virginia, Pinckney, New Jersey, and Hamilton plans gave way to the Connecticut Compromise.
In the Constitutional Convention, the Virginia Plan favored large states while the New Jersey Plan favored small states.
During the Constitutional Convention, the most contentious disputes revolved around the composition of the Presidency and the Judiciary.
The report from the Committee on Detail at the Constitutional Convention constituted the first draft of the United States Constitution.

Adopted on September 17, 1787, the Constitution is the supreme law of the United States of America.

The Bill of Rights is a series of limitations on the power of the U.S. government, protecting the natural rights of liberty and property.

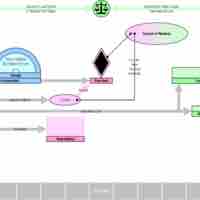
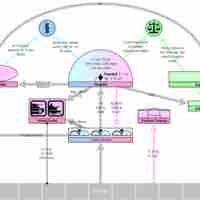
The legislative branch is represented by Congress, a bicameral chamber consisting of the House of Representatives and the Senate.
The executive power in the government is vested in the President and Vice-President of the United States, the Cabinet and federal agencies.

Organized under the U.S. Constitution, the Supreme Court and federal courts make up the judiciary branch of the United States.
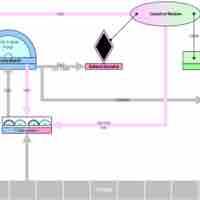
Federalism in the United States is the evolving relationship between U.S. state governments and the federal government of the United States.
The United States adheres to the principles of a constitutionally limited government in the three branches of government.

In a limited government, the power of government to intervene in the exercise of civil liberties is restricted by constitutional law.

Separation of powers is a doctrine in which each of the three branches of government have defined powers independent of each other.

To get the three branches of government to cooperate, a system of checks and balances was created to achieve a fair separation of powers.

While the Constitutional Convention was held to revise the Articles of Confederation, an entirely new constitution was drafted.
The Federalist Papers were written between 1788-9 and encouraged people to ask their representatives to ratify the Constitution.
In order for all states to ratify, a compromise over a bill of rights had to be made.

To protect the Constitution from hasty alteration, the framers of the Constitution wrote Article V.

The formal amendment processes are enumerated in Article V of the Constitution.

The formal amendment process is one of two major ways to amend the constitution.
The twenty-seven amendments serve two purposes: to protect the liberties of the people and to change original codes from the constitution.