Chapter 13
Education
By Boundless

In today's world, some degree of education is necessary for people in most countries.

It has been argued that high rates of education are essential for countries to be able to achieve high levels of economic growth.

A lack of access to education is one of the primary limits on human development.
Savage inequalities, written by Jonathan Kozol, is a book that examines inequality in education.

In 1966, the Coleman Report launched a debate about "school effects," desegregation and busing, and cultural bias in standardized tests.

Tracking separates students within a school into different tracks based on their skills and abilities.
Conflict theorists argue that the democratic mission of education has failed because it has reproduced social and economic inequalities.

Educational capital can produce or reproduce inequality and also serve as a leveling mechanism that fosters equal opportunity.

The bureaucratization of schools has some advantages but has also led to the perpetuation of discrimination and an aversion to change.

A teacher is a person who provides education for pupils and students.

A youth subculture is a group characterized by distinct styles, behaviors and interests that offer an identity outside the mainstream.

Homeschooling is the education of children at home, rather than in other formal settings of public or private school.

According to functionalists, the socialization process is coercive, forcing us to accept to the values and norms of society.
Cultural transmission is the way a group of people within a society or culture tend to learn and pass on new information.

In academia, an individual's educational level and other academic experience can be used to gain a place in society.
Innovation is the creation of better or more effective products, processes, services, technologies, or ideas.
Child care involves caring for and supervising a child or children, usually from infancy to age thirteen.

Job hunting is the act of looking for employment, due to unemployment or discontent with a current position.
Gatekeeping is the process through which information in publications, broadcasting, and the Internet is filtered for dissemination.

Family types that are replacing the traditional nuclear family include single parent families, cohabitation, and gay and lesbian families.

The conflict theory perspective towards education focuses on the role school systems may play in implementing social control.

Tracking sorts students into different groups depending on academic ability; however, other factors often influence placement.

Credentialism refers to the common practice of relying on earned credentials when hiring staff or assigning social status.

To succeed in college, students must learn a second, hidden curriculum to meet unstated academic and social norms.

IQ is meant to measure intelligence but its validity as a measure of intelligence has been debated.

Because schools are funded by property taxes, schools in poor areas receive less funding then schools in wealthier areas.
Student achievement is highly correlated with family characteristics, including household income and parental educational attainment.
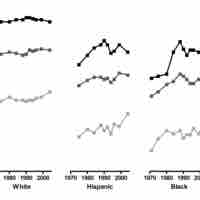
Access to education varies by geographic location, race, gender, and class.

English as a second language (ESL) refers to the use or study of English by speakers with different native languages.

While education can improve life chances, not everyone has equal access to education.
School violence is a serious problem in the United States, and attempts to explain it identify both individual and social risk factors.
Home schooling is the education of children at home rather than in the setting of a school.

A standardized test is a test that is administered and scored in a consistent manner.

Gender-based achievement gaps suggest the existence of gender bias in the classroom.

There is no standard definition of "gifted," nor a standard way of implementing gifted education.
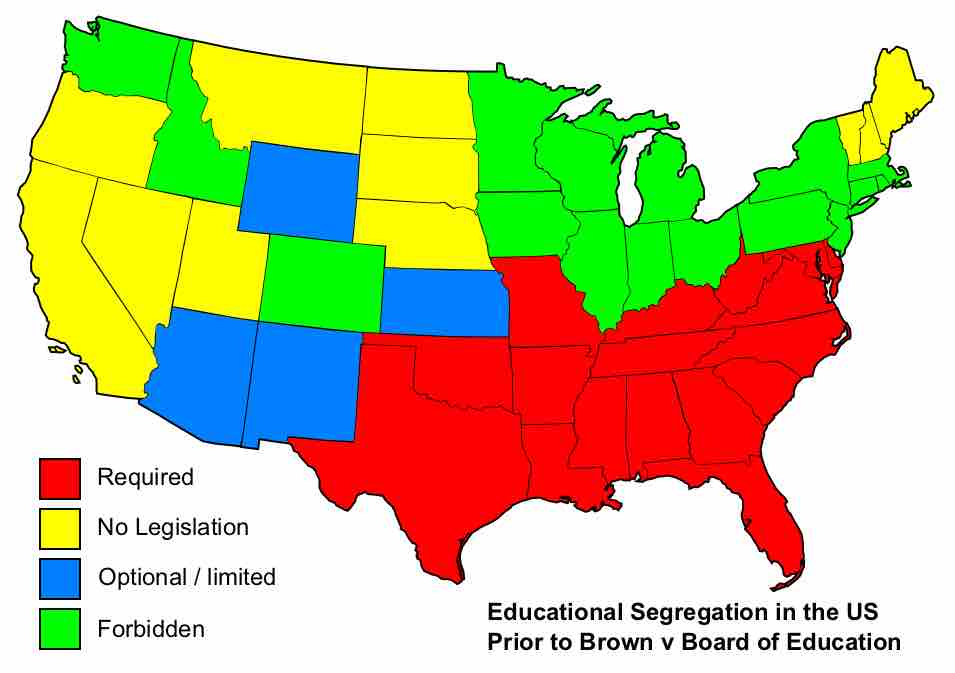
Education reforms aim at redressing some societal ills, such as gender-, and class-based inequities, or instructional ineffectiveness.

