Chapter 4
Socialization
By Boundless

Socialization prepares people for social life by teaching them a group's shared norms, values, beliefs, and behaviors.

Is nature (an individual's innate qualities) or nurture (personal experience) more important in determining physical and behavioral traits?

Sociobiology examines and explains social behavior based on biological evolution.

Social deprivation, or prevention from culturally normal interaction with society, affects mental health and impairs child development.

Social isolation refers to a complete or near-complete lack of contact with society, which can affect all aspects of a person's life.

A feral child is a human child who has lived isolated from human contact from a very young age.

Institutionalized children may develop institutional syndrome, which refers to deficits or disabilities in social and life skills.
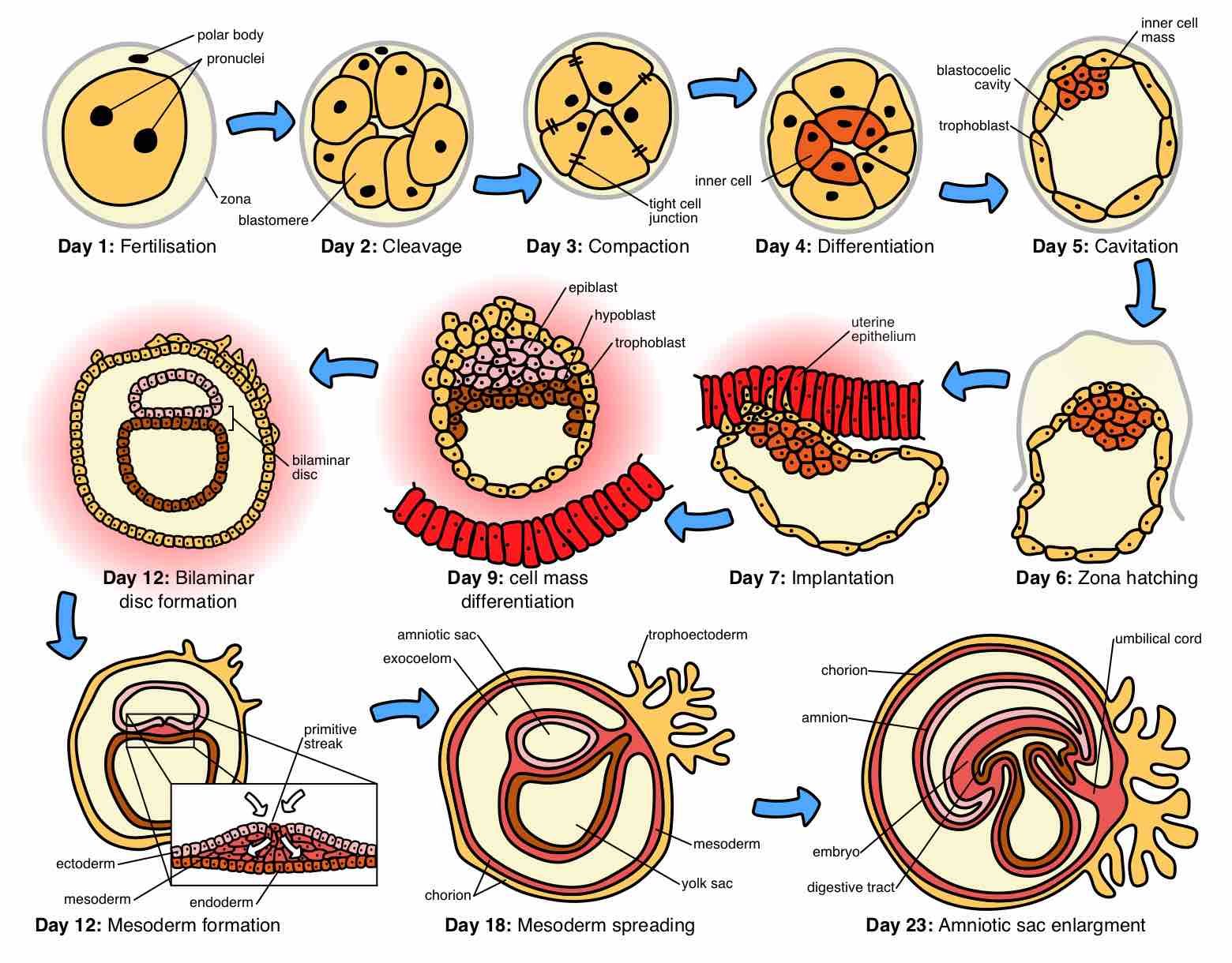
The dimensions of human development are divided into separate, consecutive stages of life from birth to old age.
Sociological theories of the self attempt to explain how social processes such as socialization influence the development of the self.

The psychology of self is the study of either the cognitive or affective representation of one's identity.
Socialization is the means by which human infants begin to acquire the skills necessary to perform as functioning members of their society.
In 1902, Charles Horton Cooley created the concept of the looking-glass self, which explored how identity is formed.
For Mead, the self arises out of the social act of communication, which is the basis for socialization.
According to Freud, human behavior, experience, and cognition are largely determined by unconscious drives and events in early childhood.

Piaget's theory of cognitive development is a comprehensive theory about the nature and development of human intelligence.

Daniel J. Levinson was one of the founders of the field of positive adult development.
A family serves to reproduce society biologically, through procreation, and socially, through the socialization of children.

A neighborhood is a geographically localized community within a larger city, town, or suburb.

Education is the process by which society transmits its accumulated knowledge, skills, customs and values from one generation to another.

Day care, in which children are cared for by a person other than their legal guardians, contributes to their socialization.
A peer group, whose members have interests, social positions, and age in common, have an influence on the socialization of group members.

Since mass media has enormous effects on our attitudes and behavior, it contributes to the socialization process.
The workplace performs its socialization process through onboarding, through which employees acquire skills to adjust to their new role.

Religion is a collection of cultural systems, belief systems, and worldviews that relate humanity to spirituality and moral values.

Division of labor is the specialization of cooperative labor in specific, circumscribed tasks and similar roles.

An incest taboo is any cultural rule or norm that prohibits sexual relations between relatives.
Ideology is a coherent system of ideas that constitutes one's goals, expectations, and actions.

A total institution is a place where a group of people is cut off from the wider community and their needs are under bureaucratic control.

Gender socialization is the process of teaching people how to behave as men or women.
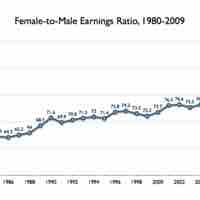
The gender pay gap, or the difference between male and female earnings, is primarily due to discriminatory social processes.
Gender role theory posits that boys and girls learn the appropriate behavior and attitudes from the family with which they grow up.

Peer groups can serve as a venue for teaching gender roles, especially if conventional gender social norms are strongly held.

In mass media, women tend to have less significant roles than men, and are often portrayed in stereotypical roles, such as wives or mothers.

Socialization is the lifelong process of preparing an individual to live within his or her own society.

The life course approach analyzes people's lives within structural, social, and cultural contexts.

Anticipatory socialization comes from an individual's desire to join a group while resocialization is imposed upon an individual by a group.
The socialization process can be separated into two main stages: primary socialization and secondary socialization.

Childhood has been constructed in different ways over time, though modern childhood is often defined by play, learning and socializing.

Adolescence is a period of significant cognitive, physical and social development, including changes in family and peer relationships.

Coming of age traditions, while different across the world, are seen in almost every society.

People marry for love, for socioeconomic stability, to start a family, and to create obligations between one another.

Middle adulthood is generally accompanied by a decline in physical health and fertility, and an increase in ability to cope with stress.

Parenting is the process of supporting the physical, emotional, social, and intellectual development of a child from infancy to adulthood.

A vocation is an occupation to which an individual is particularly drawn.
Old age cannot be exactly defined, but it is often associated with certain activities, such as becoming a grandparent or entering retirement.

Who we are as people is determined by both our genes (nature) and our socialization (nurture).

Primary and secondary socialization are two forms of socialization that are particularly important for children.

Theories of childhood socialization and development study the elements of the cognitive and social development that occur in childhood.

Identity formation is the development of an individual's distinct personality by which he or she is recognized or known.

