Origins
The Germanic peoples (also called Teutonic, Suebian, or Gothic in older literature) are an ethno-linguistic Indo-European group of northern European origin. They are identified by their use of Germanic languages, which diversified out of Proto-Germanic during the Pre-Roman Iron Age.
The term "Germanic" originated in classical times when groups of tribes living in Lower, Upper, and Greater Germania were referred to using this label by Roman scribes. These tribes generally lived to the north and east of the Gauls. They were chronicled by Rome's historians as having had a critical impact on the course of European history during the Roman-Germanic wars, particularly at the historic Battle of the Teutoburg Forest, where the vanquishment of three Roman legions at the hands of Germanic tribal warriors precipitated the Roman Empire's strategic withdrawal from Magna Germania.
As a linguistic group, modern Germanic peoples include the Afrikaners, Austrians, Danes, Dutch, English, Flemish, Frisians, Germans, Icelanders, Lowland Scots, Norwegians, Swedes, and others (including diaspora populations, such as some groups of European Americans).
Northernmost Europe, in what now constitutes the European plains of Denmark and southern Scandinavia, is where the Germanic peoples most likely originated. This is a region that was "remarkably stable" as far back as the Neolithic Age, when humans first began controlling their environment through the use of agriculture and the domestication of animals. Archeological evidence gives the impression that the Germanic people were becoming more uniform in their culture as early as 750 BCE. As their population grew, the Germanic people migrated westwards into coastal floodplains due to the exhaustion of the soil in their original settlements.
Germanic Tribes
By approximately 250 BCE, additional expansion further southwards into central Europe took place, and five general groups of Germanic people emerged, each employing distinct linguistic dialects but sharing similar language innovations. These five dialects are distinguished as North Germanic in southern Scandinavia; North Sea Germanic in the regions along the North Sea and in the Jutland peninsula, which forms the mainland of Denmark together with the north German state of Schleswig-Holstein; Rhine-Weser Germanic along the middle Rhine and Weser river, which empties into the North Sea near Bremerhaven; Elbe Germanic directly along the middle Elbe river; and East Germanic between the middle of the Oder and Vistula rivers.
Some recognizable trends in the archaeological records exist, as it is known that, generally speaking, western Germanic people, while still migratory, were more geographically settled, whereas the eastern Germanics remained transitory for a longer period. Three settlement patterns and solutions come to the fore; the first being the establishment of an agricultural base in a region that allowed them to support larger populations; the second being that the Germanic peoples periodically cleared forests to extend the range of their pasturage; and the third (and the most frequent occurrence) being that they often emigrated to other areas as they exhausted the immediately available resources.
War and conquest followed as the Germanic people migrated, bringing them into direct conflict with the Celts who were forced to either Germanize or migrate elsewhere as a result. West Germanic people eventually settled in central Europe and became more accustomed to agriculture, and it is the various western Germanic people that are described by Caesar and Tacitus. Meanwhile, the eastern Germanic people continued their migratory habits. Roman writers characteristically organized and classified people, and it may very well have been deliberate on their part to recognize the tribal distinctions of the various Germanic people so as to pick out known leaders and exploit these differences for their benefit. For the most part however, these early Germanic people shared a basic culture, operated similarly from an economic perspective, and were not nearly as differentiated as the Romans implied. In fact, the Germanic tribes are hard to distinguish from the Celts on many accounts simply based on archaeological records.
Migration Period
During the 5th century, as the Western Roman Empire lost military strength and political cohesion, numerous nomadic Germanic peoples, under pressure from population growth and invading Asian groups, began migrating en masse in various directions, taking them to Great Britain and far south through present-day Continental Europe to the Mediterranean and Northern Africa.
Over time this wandering meant intrusions into other tribal territories, and the ensuing wars for land escalated with the dwindling amount of unoccupied territory. Wandering tribes then began staking out permanent homes as a means of protection. This resulted in fixed settlements from which many tribes, under a powerful leader, expanded outwards.
Ostrogoths, Visigoths, and Lombards made their way into Italy; Vandals, Burgundians, Franks, and Visigoths conquered much of Gaul; Vandals and Visigoths also pushed into Spain, with the Vandals additionally making it into North Africa; and the Alamanni established a strong presence in the middle Rhine and Alps. In Denmark, the Jutes merged with the Danes; and in Sweden, the Geats and Gutes merged with the Swedes. In England, the Angles merged with the Saxons and other groups (notably the Jutes), and absorbed some natives, to form the Anglo-Saxons (later known as the English). Essentially, Roman civilization was overrun by these variants of Germanic peoples during the 5th century.
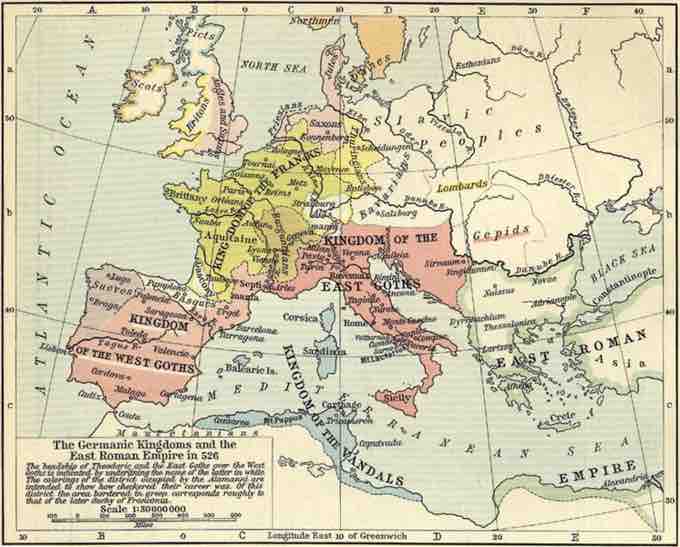
The Germanic Kingdoms and the Eastern Roman Empire in 526 CE
Military
Germanic people were fierce in battle, creating a strong military. Their love of battle was linked to their religious practices and two of their most important gods, Wodan and his son, Thor, both believed to be gods of war. The Germanic idea of warfare was quite different from the pitched battles fought by Rome and Greece, and the Germanic tribes focused on raids to capture resources and secure prestige.
Warriors were strong in battle and had great fighting abilities, making the tribes almost unbeatable. Men began battle training at a young age and were given a shield and a spear upon manhood, illustrating the importance of combat in Germanic life. The loss of the shield or spear meant a loss of honor. The Germanic warrior's intense devotion to his tribe and his chieftain led to many important military victories.
Chieftains were the leaders of clans, and clans were divided into groups by family ties. The earlier Germans elected chieftains, but as time went on it became hereditary. One of the chieftain's jobs was to keep peace in the clans, and he did this by keeping the warriors together and united.
Military chieftains relied upon retinues, a body of followers "retained" by the chieftain. A chieftain's retinue might include, but was not limited to, close relatives. The followers depended on the retinue for military and other services, and in return provided for the retinue's needs and divided with them the spoils of battle. This relationship between a chieftain and his followers became the basis for the more complicated feudal system that developed in medieval Europe.
Major Historical Figures
Political and diplomatic leaders, such as Odoacer and Theoderic the Great, changed the course of history in the late 400s CE and paved the way for later kings and conquerors. Odoacer, a German general, took over the Western Roman Empire in his own name, becoming the first barbarian king of Italy. Theoderic the Great became a barbarian king of Italy after he killed Odoacer. He initiated three decades of peace between the Ostrogoths and the Romans and united the two Germanic tribes.
Theoderic the Great lived as a hostage at the court of Constantinople for many years and learned a great deal about Roman government and military tactics, which served him well when he became the Gothic ruler of a mixed but largely Romanized "barbarian people."
.jpg)
Theoderic the Great
Bronze statue of Theoderic the Great, king of the Ostrogoths, by Peter Vischer the Elder (1512-13) at the tomb of Emperor Maximilian I in the Court Church in Innsbruck, Austria.