Chapter 17
The Protestant Reformation
By Boundless
The Protestant Reformation was the schism within Western Christianity initiated by Martin Luther, John Calvin, and other early Protestants.
Martin Luther was a seminal figure in the Protestant Reformation, who strongly disputed the claim that freedom from God's punishment for sin could be purchased with money, famously argued in his Ninety-five Theses of 1517.

Calvinism is a major branch of Protestantism that follows the theological tradition and forms of Christian practice of John Calvin and is characterized by the doctrine of predestination in the salvation of souls.

The Anabaptists were a group of radical religious reformists formed in Switzerland who suffered violent persecution by both Roman Catholics and Protestants.
Beginning with Henry VIII in the 16th century, the Church of England broke away from the authority of the Pope and Catholic Church.

The French Wars of Religion (1562–98) is the name of a period of fighting between French Catholics and Protestants (Huguenots).
Between the 15th and 18th centuries in Europe, many people were accused of and put on trial for practicing witchcraft.
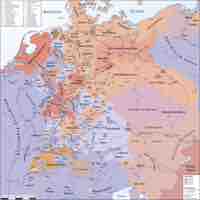
The Thirty Years' War was a series of wars between various Protestant and Catholic states in the fragmented Holy Roman Empire between 1618 and 1648.
The Bohemian Revolt (1618–1620) was an uprising of the Bohemian estates against the rule of the Habsburg dynasty, in particular Emperor Ferdinand II, which triggered the Thirty Years' War.
After the Bohemian Revolt was suppressed by Ferdinand II, the Danish King Christian IV, fearing that recent Catholic successes threatened his sovereignty as a Protestant nation, led troops against Ferdinand.
The Swedish Intervention in the Thirty Years' War was a major turning point of the war, where King Gustav II Adolf of Sweden ordered a full-scale invasion of the Catholic states.
No longer able to tolerate the encirclement of two major Habsburg powers on its borders, Catholic France entered the war on the side of the Protestants to counter the Habsburgs and bring the Thirty Years' War to an end.
The Peace of Westphalia was a series of peace treaties signed between May and October 1648 in the Westphalian cities of Osnabrück and Münster that ended the Thirty Years' War.