Chapter 1
Introduction to Accounting
By Boundless

Accountancy is the process of communicating financial information about a business entity to users such as shareholders and managers.

Inputs into accounting include journal entries, the bookkeeping process, and the general ledger.
Accounting outputs are financial statements that detail the financial activities of a business, person, or other entity.

Financial reporting is used by owners, managers, employees, investors, institutions, government, and others to make important decisions about a business.

A conceptual framework is a system of ideas and objectives that lead to the creation of a consistent set standards.

The objective of business financial reporting is to provide information that is useful for making business and economic decisions.
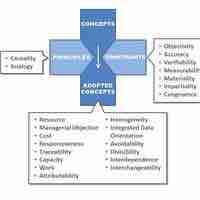
In order to prepare the financial statements, it is important to adhere to certain fundamental accounting concepts.
In accounting, recognition of revenues and expenses is based on the matching principle.
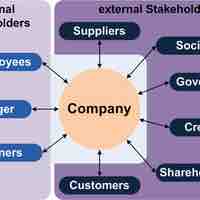
A stakeholder is an individual or group that has a legitimate interest in a company.
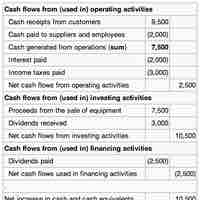
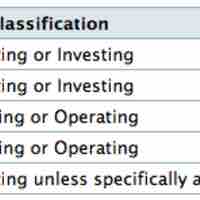
Activities of the business include operating activities and non-operating activities such as investing activities, and financing activities.

The role of accounting in business is to help internal and external stakeholders make better business decisions by providing them with financial information.

Business ethics is a form of applied ethics that examines ethical principles, moral/ethical problems that arise in a business environment.
The balance sheet is a summary of the financial balances of a company and reflects the company's solvency and financial position.
The income statement shows revenues and expenses for a specific period.

The statement of retained earnings explains the changes in a company's retained earnings over the reporting period.

The cash flow statement provides information on a firm's liquidity and solvency.

The four main financial statements provide relevant financial information for internal and external users.

Financial statement notes explain specific items in the financial statements.

When an audit is performed on a company, the auditor issues a formal opinion in the form of an auditor report.

The SEC enforces and regulates security laws, the AICPA dictates the professional conduct of accountants, and the FASB develops GAAP.
Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) is the standard framework for financial accounting used in any given jurisdiction.
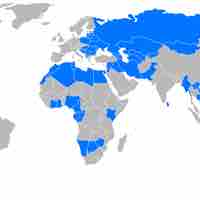
The IFRS is a common global financial language for business affairs that is understandable and comparable across international boundaries.

A major difference between GAAP and IFRS is that GAAP is rule-based, whereas IFRS is principle-based.
The full disclosure principle states information important enough to influence decisions of an informed user should be disclosed.

The process of disclosing financial statements is carried out through what is known as a Form 10-K.
Events that trigger disclosure should be based on an accountant's assessment of materiality.

Accountants must stay up to date with current issues in reporting and disclosures related to standards set by regulatory agencies.