Chapter 8
Photosynthesis
By Boundless

The process of photosynthesis converts light energy to chemical energy, which can be used by organisms for different metabolic processes.
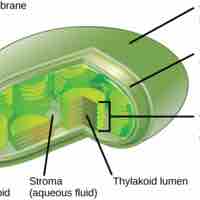
In multicellular autotrophs, the main cellular structures that allow photosynthesis to take place include chloroplasts, thylakoids, and chlorophyll.
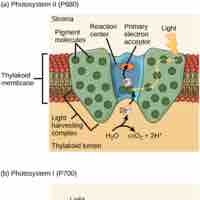
Light-dependent and light-independent reactions are two successive reactions that occur during photosynthesis.
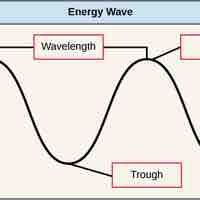
All electromagnetic radiation, or light energy, travels at a particular wavelength and carries a certain amount of energy.

Pigments, like chlorophyll and carotenoids, absorb and reflect light at a certain region of the electromagnetic spectrum.
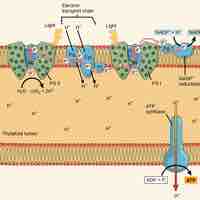
Light-dependent reactions, which take place in photosystem I and II, convert solar energy into NADPH and ATP.
Some plants have evolved mechanisms to increase the CO2 concentration in their leaves under hot and dry conditions.
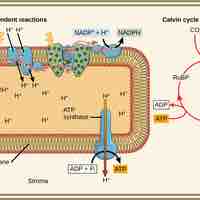
The Calvin cycle is organized into three basic stages: fixation, reduction, and regeneration.
All organisms need energy to perform life functions, and energy that is released is reused in other ways.