Reproduction
Reproduction in prokaryotes is asexual and usually takes place by binary fission. The DNA of a prokaryote exists as as a single, circular chromosome. Prokaryotes do not undergo mitosis; rather the chromosome is replicated and the two resulting copies separate from one another, due to the growth of the cell. The prokaryote, now enlarged, is pinched inward at its equator and the two resulting cells, which are clones, separate. Binary fission does not provide an opportunity for genetic recombination or genetic diversity, but prokaryotes can share genes by three other mechanisms .
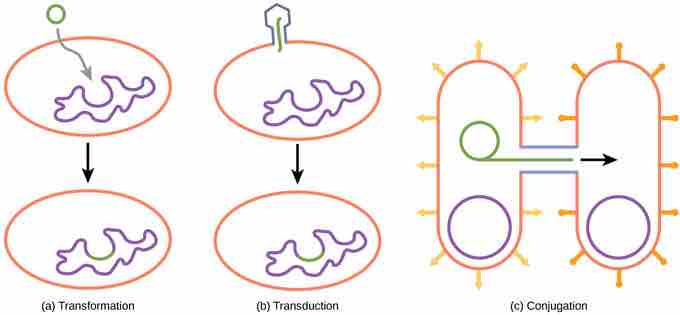
Modes of prokaryote reproduction
Besides binary fission, there are three other mechanisms by which prokaryotes can exchange DNA. In (a) transformation, the cell takes up prokaryotic DNA directly from the environment. The DNA may remain separate as plasmid DNA or be incorporated into the host genome. In (b) transduction, a bacteriophage injects DNA into the cell that contains a small fragment of DNA from a different prokaryote. In (c) conjugation, DNA is transferred from one cell to another via a mating bridge that connects the two cells after the pilus draws the two bacteria close enough to form the bridge.
In transformation, the prokaryote takes in DNA found in its environment that is shed by other prokaryotes. If a nonpathogenic bacterium takes up DNA for a toxin gene from a pathogen and incorporates the new DNA into its own chromosome, it, too, may become pathogenic. In transduction, bacteriophages, the viruses that infect bacteria, sometimes also move short pieces of chromosomal DNA from one bacterium to another. Transduction results in a recombinant organism. Archaea are not affected by bacteriophages, but instead have their own viruses that translocate genetic material from one individual to another. In conjugation, DNA is transferred from one prokaryote to another by means of a pilus, which brings the organisms into contact with one another. The DNA transferred can be in the form of a plasmid or as a hybrid, containing both plasmid and chromosomal DNA.
Reproduction can be very rapid: a few minutes for some species. This short generation time, coupled with mechanisms of genetic recombination and high rates of mutation, result in the rapid evolution of prokaryotes, allowing them to respond to environmental changes (such as the introduction of an antibiotic) very rapidly.