Chapter 35
The Nervous System
By Boundless
Neurons and glia coordinate actions and transmit signals in the CNS and PNS.
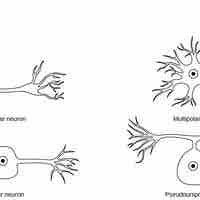
Four major types of neurons transmit signals through the body via specialized structures such as dendrites, axons, and synapses.
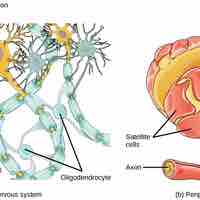
The seven types of glia have specific functions that play a role in supporting neuron function.
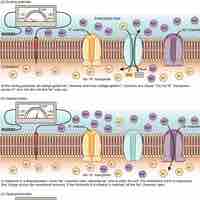
The resting potential of a neuron is controlled by the difference in total charge between the inside and outside of the cell.
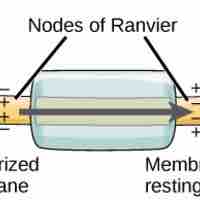
Signals are transmitted from neuron to neuron via an action potential, when the axon membrane rapidly depolarizes and repolarizes.
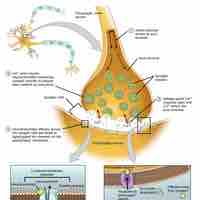
Synaptic transmission is a chemical event which is involved in the transmission of the impulse via release, diffusion, receptor binding of neurotransmitter molecules and unidirectional communication between neurons.
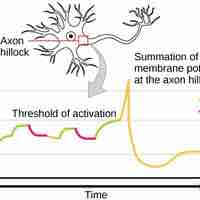
Signal summation occurs when impulses add together to reach the threshold of excitation to fire a neuron.
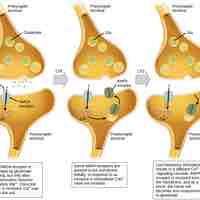
Synapses experience plasticity by strengthening or weakening over time.
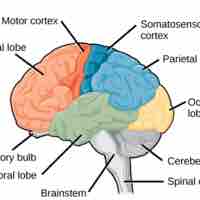
The cerebral cortex of the brain is divided into four lobes responsible for distinct functions: frontal, parietal, temporal, and occipital.
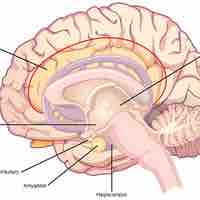
Regions of the brain other than the cerebral cortex include those involved in sleep, memory, attention, motor coordination, and motivation.
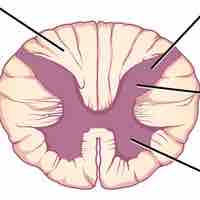
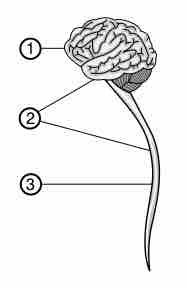
The spinal cord is a bundle of nerves that is connected to the brain and relays information from the brain to the body and vice versa.
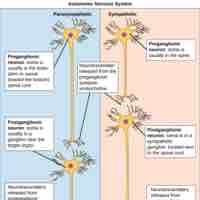
The autonomic nervous system, the relay between the CNS and internal organs, is divided into the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems.
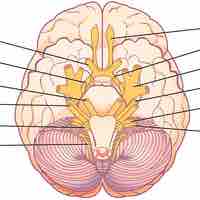
The sensory-somatic nervous system transmits sensory information from the body to the brain and motor movements from the brain to the body.
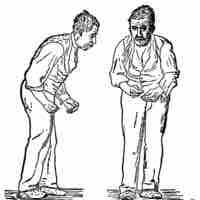
Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease are both neurodegenerative disorders characterized by loss of nervous system functioning.

Autism and ADHD are neurodevelopmental disorders that arise when nervous system development is disrupted.
Schizophrenia and depression are just two examples of mental illnesses caused by a disorder of the nervous system.
Epilepsy and stroke are examples of neurological disorders that arise from malfunctions in the nervous system.