Debt utilization ratios provide a comprehensive picture of the company's solvency or long-term financial health. The debt ratio is a financial ratio that indicates the percentage of a company's assets that are provided via debt. It is the ratio of total debt (the sum of current liabilities and long-term liabilities) and total assets (the sum of current assets, fixed assets, and other assets such as "goodwill").
Debt Ratio = Total Debt / Total Assets
For example, a company with $2 million in total assets and $500,000 in total liabilities would have a debt ratio of 25%. The higher the ratio, the greater the risk associated with the firm's operation. In addition, high debt to assets ratio may indicate low borrowing capacity of a firm, which in turn will lower the firm's financial flexibility. Like all financial ratios, a company's debt ratio should be compared with their industry average or other competing firms.
The debt-to-equity ratio (D/E) is a financial ratio indicating the relative proportion of shareholders' equity and debt used to finance a company's assets. When used to calculate a company's financial leverage, the debt usually includes only the Long Term Debt (LTD). D/E = Debt(liabilities)/Equity.
The debt service coverage ratio (DSCR), also known as debt coverage ratio (DCR), is the ratio of cash available for debt servicing to interest, principal, and lease payments. It is a popular benchmark used in the measurement of an entity's ability to produce enough cash to cover its debt (including lease) payments. The higher this ratio is, the easier it is to obtain a loan. In general, it is calculated as:
DSCR = (Annual Net Income + Amortization / Depreciation + Interest Expense + other non-cash and discretionary items (such as non-contractual management bonuses)) / (Principal Repayment + Interest payments + Lease payments)
A similar debt utilization ratio is the times interest earned (TIE), or interest coverage ratio. It is a measure of a company's ability to honor its debt payments. It may be calculated as either EBIT or EBITDA, divided by the total interest payable. EBIT is earnings before interest and taxes, and EBITDA is earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization.
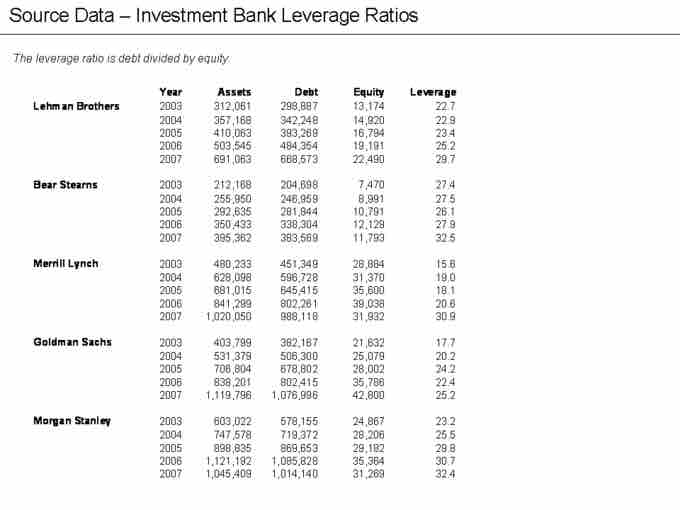
Leverage Ratios
Leverage ratios for some investment banks