Chapter 1
Introduction to Chemistry
By Boundless
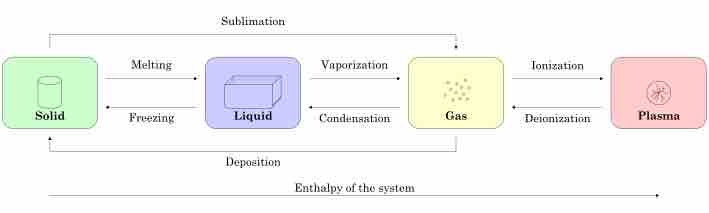
The three states of matter are the distinct physical forms that matter can take: solid, liquid, and gas.

Substances are composed of pure elements or chemically bonded elements, whereas mixtures are composed of non-bonded substances.
An element is a material that consists of a single type of atom, while a compound consists of two or more types of atoms.
The International System of Units (abbreviated SI) is the metric system used in science, industry, and medicine.
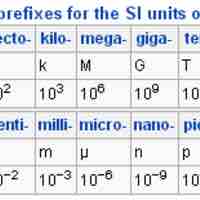
The basic SI units can be expressed as fractions and multiples of basic units by using a set of simple prefixes.
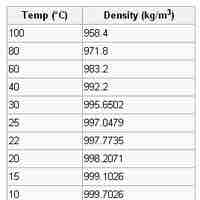
Density and volume are two common measurements in chemistry.
The ability to measure temperature accurately was a major scientific advancement, putting absolute numbers on an observable phenomenon.

Scientific notation is a more convenient way to write very large or very small numbers and follows the equation: a x 10b .

Significant figures are digits which contribute to the precision of a number.

Exact numbers are defined numbers or result from a count, unlike measured numbers.

Accuracy is how closely the measured value is to the true value, whereas precision expresses reproducibility.
Converting units using dimensional analysis makes working with large and small measurements more convenient.
To convert a measured quantity to a different unit of measure without changing the relative amount, use a conversion factor.



