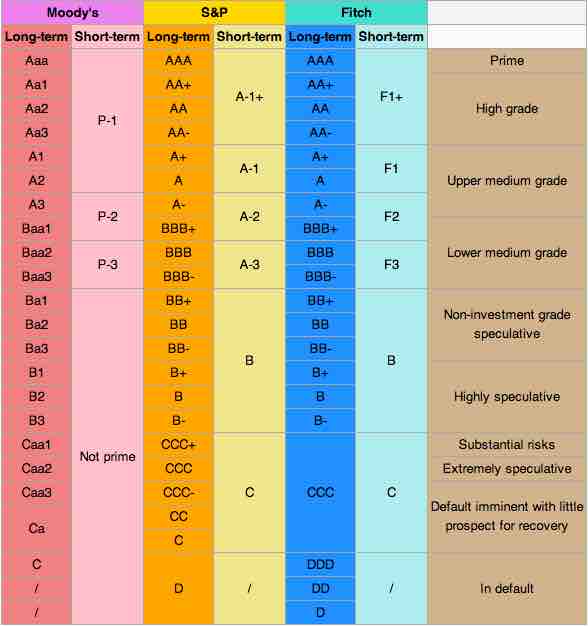
In investment, the bond credit rating assesses the credit worthiness of a corporation's or government's debt issues. It is analogous to credit ratings for individuals.The credit rating is a financial indicator to potential investors of debt securities, such as bonds. These are assigned by credit rating agencies such as Moody's, Standard & Poor's, and Fitch Ratings to have letter designations (such as AAA, B, CC), which represent the quality of a bond. Bond ratings below BBB-/Baa are considered to be not investment grade and are colloquially called "junk bonds. "
Bond rating
Bond ratings below BBB-/Baa are considered to be not investment grade and are colloquially called "junk bonds. "
Credit rating agencies registered as such with the SEC are "Nationally recognized statistical rating organizations. " The following firms are currently registered as NRSROs: A.M. Best Company, Inc.; DBRS Ltd.; Egan-Jones Rating Company; Fitch, Inc.; Japan Credit Rating Agency, Ltd.; LACE Financial Corp.; Moody's Investors Service, Inc.; Rating and Investment Information, Inc.; and Standard & Poor's Ratings Services.
Under the Credit Rating Agency Reform Act, an NRSRO may be registered with respect to up to five classes of credit ratings: (1) financial institutions, brokers, or dealers; (2) insurance companies; (3) corporate issuers; (4) issuers of asset-backed securities; and (5) issuers of government securities, municipal securities, or securities issued by a foreign government. S&P, Moody's, and Fitch dominate the market with approximately 90-95% of world market share.
Moody's assigns bond credit ratings of Aaa, Aa, A, Baa, Ba, B, Caa, Ca, C, with WR and NR as withdrawn and not rated. Standard & Poor's and Fitch assign bond credit ratings of AAA, AA, A, BBB, BB, B, CCC, CC, C, and D.
A bond is considered investment grade or IG if its credit rating is BBB- or higher by Standard & Poor's or Baa3 or higher by Moody's or BBB (low) or higher by DBRS. Generally, they are bonds that are judged by the rating agency as likely enough to meet payment obligations that banks are allowed to invest in them. Ratings play a critical role in determining how much companies and other entities that issue debt, including sovereign governments, have to pay to access credit markets (i.e., the amount of interest they pay on their issued debt). The threshold between investment-grade and speculative-grade ratings has important market implications for issuers' borrowing costs. Bonds that are not rated as investment-grade bonds are known as high-yield bonds or more derisively as junk bonds. The risks associated with investment-grade bonds (or investment-grade corporate debt) are considered significantly higher than those associated with first-class government bonds.