Causes
Autoimmune heart diseases result when the body's own immune defense system mistakes cardiac antigens as foreign, and attacks them, leading to inflammation of the heart as a whole, or in parts. The most common form of autoimmune heart disease is rheumatic heart disease, or rheumatic fever.
A typical mechanism of autoimmunity is autoantibodies, or auto-toxic T-lymphocyte mediated tissue destruction. The process is aided by neutrophils, the complement system, and tumor necrosis factor alpha.
Aetiologically, autoimmune heart disease is most commonly seen in children with a history of sore throat caused by a streptococcal infection. This is similar to the post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis. Here, the anti-bacterial antibodies cross react with the heart antigens causing inflammation.
Pericarditis, Myocarditis, and Endocarditis
Inflammatory damage can lead to pericarditis, myocarditis, and endocarditis.
Pericarditis: Here the pericardium gets inflamed. Acutely, it can cause pericardial effusion leading to cardiac tamponade and death. After healing, there may be fibrosis and adhesion of the pericardium with the heart, leading to constriction of the heart and reduced cardiac function.
Myocarditis: Here the muscle bulk of the heart gets inflamed. Inflamed muscles have reduced functional capacity. This may be fatal if left untreated, as is in a case of pancarditis. On healing, there will be fibrosis and reduced functional capacity .
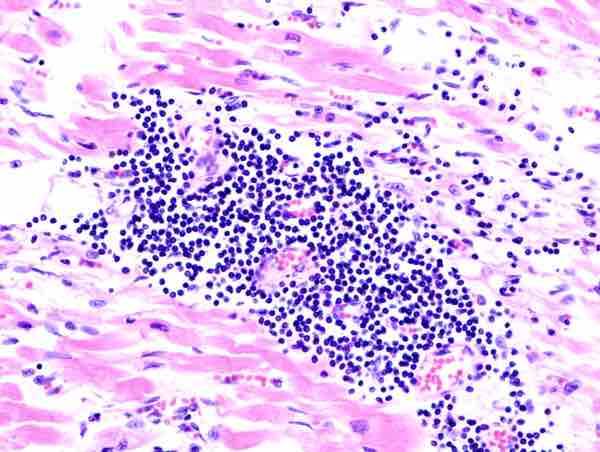
Viral myocarditis
Histopathological image of myocarditis at autopsy in a patient with acute onset of congestive heart failure
Endocarditis: Here the inner lining of the heart is inflamed, including the heart valves. This may cause a valve prolapse, adhesion of the adjacent cusps, of these valves, and occlusion of the flow tracts of blood through the heart, which causes disease known as valve stenosis.
Treatment
Specific clinical manifestations depend on the amount of inflammation. Therapy will involve intensive cardiac care and immunosuppressives, including corticosteroids, which are helpful in the acute stage of the disease. The chronic phase consists of mainly debility control and supportive care options.