Section 2
Vectors
Book
Version 3
By Boundless
By Boundless
Boundless Physics
Physics
by Boundless
7 concepts
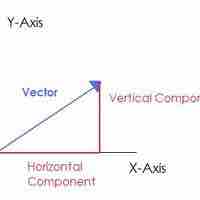
Components of a Vector
Vectors are geometric representations of magnitude and direction and can be expressed as arrows in two or three dimensions.
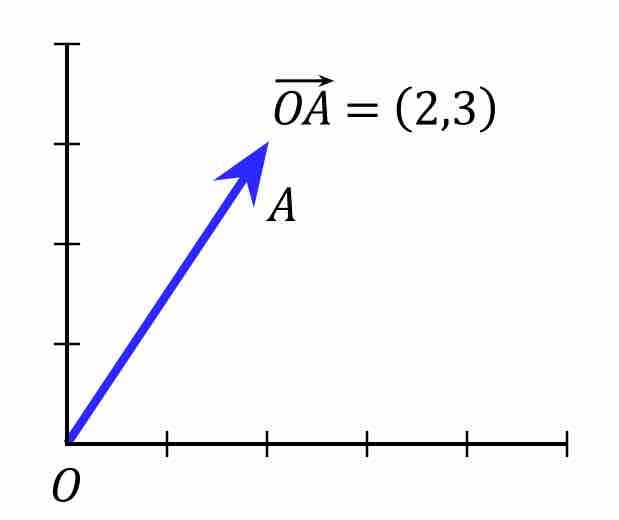
Scalars vs. Vectors
Scalars are physical quantities represented by a single number, and vectors are represented by both a number and a direction.
Adding and Subtracting Vectors Graphically
Vectors may be added or subtracted graphically by laying them end to end on a set of axes.
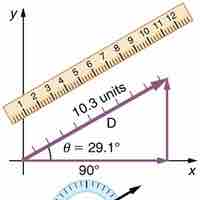
Adding and Subtracting Vectors Using Components
It is often simpler to add or subtract vectors by using their components.
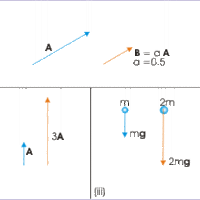
Multiplying Vectors by a Scalar
Multiplying a vector by a scalar changes the magnitude of the vector but not the direction.
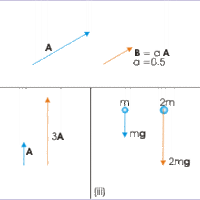
Unit Vectors and Multiplication by a Scalar
Multiplying a vector by a scalar is the same as multiplying its magnitude by a number.
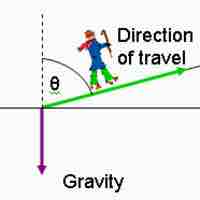
Position, Displacement, Velocity, and Acceleration as Vectors
Position, displacement, velocity, and acceleration can all be shown vectors since they are defined in terms of a magnitude and a direction.