A major organ of the endocrine system, the anterior pituitary (also called the adenohypophysis) is the glandular, anterior lobe of the pituitary gland. The anterior pituitary regulates several physiological processes including stress, growth, reproduction, and lactation.
Its regulatory functions are achieved through the secretion of various peptide hormones that act on target organs including the adrenal gland, liver, bone, thyroid gland, and gonads. The anterior pituitary itself is regulated by the hypothalamus and by negative feedback from these target organs.
Anatomy of the Anterior Pituitary Gland
The fleshy, glandular anterior pituitary is distinct from the neural composition of the posterior pituitary. The anterior pituitary is composed of multiple parts:
- Pars distalis: This is the distal part that comprises the majority of the anterior pituitary; it is where most pituitary hormone production occurs.
- Pars tuberalis: This is the tubular part that forms a sheath that extends up from the pars distalis and wraps around the pituitary stalk. Its function is poorly understood.
- Pars intermedia: This is the intermediate part that sits between the pars distalis and the posterior pituitary and is often very small in humans.
Major Hormones Secreted by the Anterior Pituitary Gland
- Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), is a polypeptide whose target is the adrenal gland. The effects of ACTH are upon secretion of glucocorticoid, mineralocorticoids, and sex corticoids.
- Beta-endorphin is a polypeptide that effects the opioid receptor, whose effects include the inhibition of the perception of pain.
- Thyroid-stimulating hormone is a glycoprotein hormone that affects the thyroid gland and the secretion of thyroid hormones.
- Follicle-stimulating hormone is a glycoprotein hormone that targets the gonads and effects the growth of the reproductive system.
- Luteinizing hormone is a glycoprotein hormone that targets the gonads to effect sex-hormone production.
- Growth hormone is a polypeptide hormone that targets the liver and adipose tissue and promotes growth through lipid and carbohydrate metabolism.
- Prolactin is a polypeptide hormone whose target is the ovaries and mammary glands. Prolactin influences the secretion of estrogen/progesterone and milk production.
Regulation
Hormone secretion from the anterior pituitary gland is regulated by hormones secreted by the hypothalamus. Neuroendocrine neurons in the hypothalamus project axons to the median eminence, at the base of the brain. At this site, these neurons can release substances into the small blood vessels that travel directly to the anterior pituitary gland (the hypothalamo-hypophysial portal vessels).
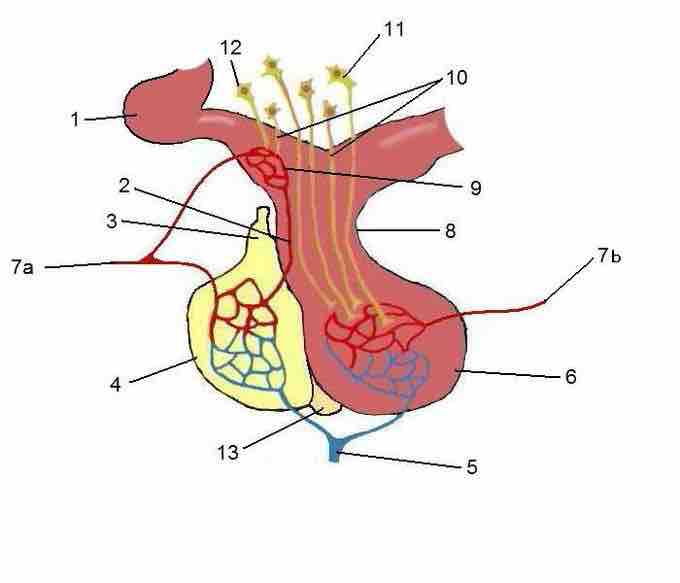
The anterior pituitary
The anterior pituitary, in yellow, is linked to the hypothalamus by a portal system. The hypothalamus releases signaling molecules that incite the anterior pituitary to produce hormones.