Chapter 24
Urinary System
By Boundless
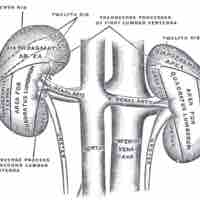
The kidneys are located at the rear wall of the abdominal cavity and they are protected by the ribcage.
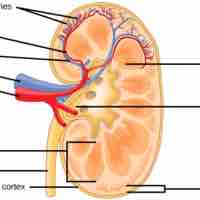
The cortex and medulla make up two of the internal layers of a kidney and are composed of individual filtering units known as nephrons.
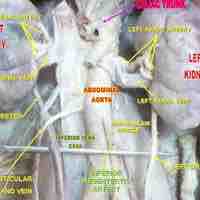
The renal veins drain the kidney and the renal arteries supply blood to the kidney.
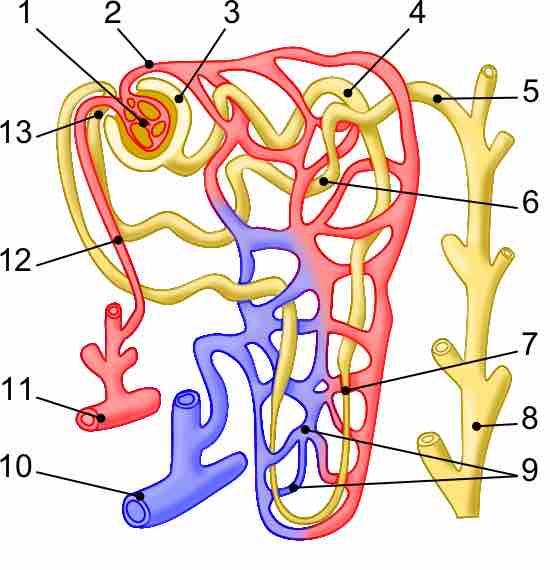
The nephron of the kidney is involved in the regulation of water and soluble substances in blood.
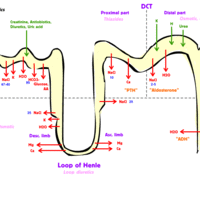
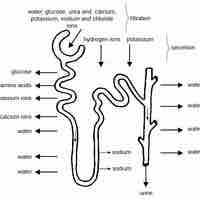
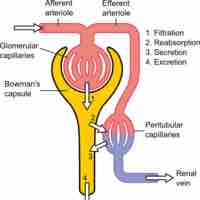
Urine is formed in three steps: filtration, reabsorption, and secretion.
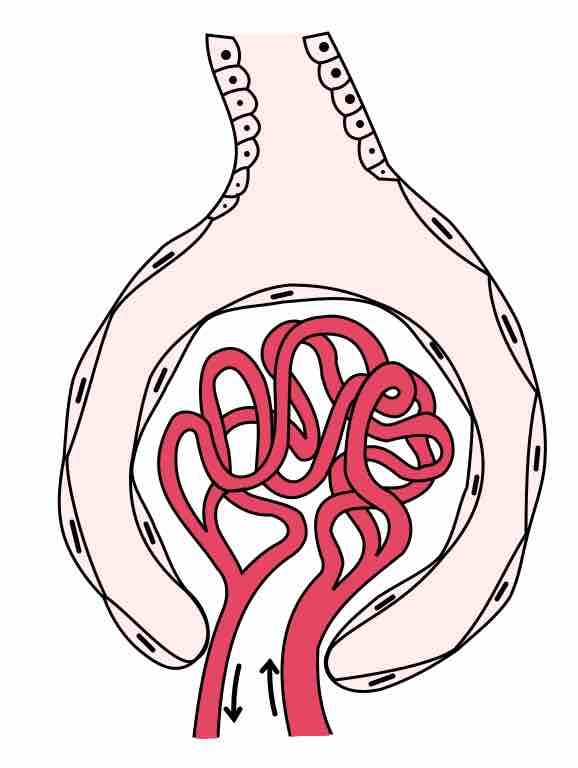
Glomerular filtration is the renal process whereby fluid in the blood is filtered across the capillaries of the glomerulus.
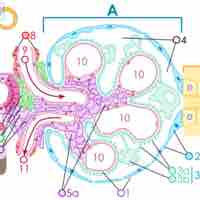
Regulation of GFR requires both a mechanism of detecting an inappropriate GFR as well as an effector mechanism that corrects it.
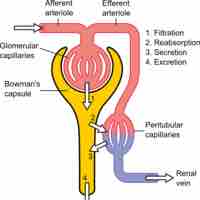
Tubular reabsorption is the process by which solutes and water are removed from the tubular fluid and transported into the blood.
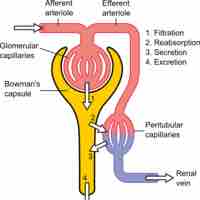
Hydrogen, creatinine, and drugs are removed from the blood and into the collecting duct through the peritubular capillary network.
Urine is a sterile waste product composed of water soluble nitrogen products.
Normal urine consists of water, urea, salts, and pigments.
Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) is produced by the pituitary gland to control the amount of water that is reabsorbed through the collecting ducts.

Urinalysis is the process of analyzing urine for target parameters of health and disease.
Clearance is a measurement of the renal excretion ability.
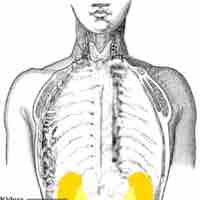
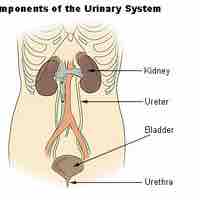
The urinary organs include the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra.
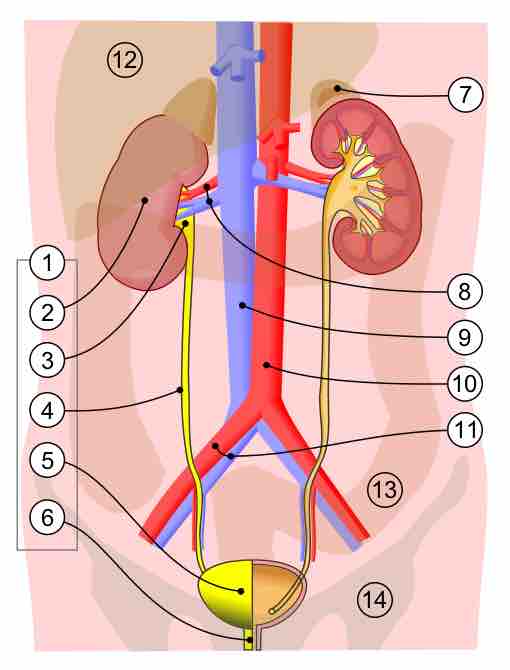
The ureters are two tubes that drain urine from each of the kidneys into the bladder.
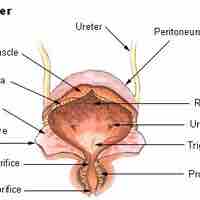
The urinary bladder is a hollow, muscular, and distendible or elastic organ that sits on the pelvic floor.
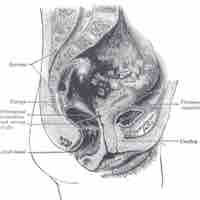
The urethra is a muscular tube that connects the bladder with the outside of the body and removes urine from the body.
Micturition is the ejection of urine from the urinary bladder through the urethra to the outside of the body.
In addition to the kidneys, the liver, skin, and lungs also have important roles in the excretion of waste from the body.