Chapter 16
Civilizations in the Americas
By Boundless
The Moche culture lasted from 100 to 800 CE in what is modern-day Peru.

The Nazca lived near the southern coast of Peru from 100 BCE to 800 CE.
.jpg)
The Sicán culture inhabited what is now the north coast of Peru between about 750 and 1375 CE.
The Chimú lived in modern-day Peru from 900–1470 CE.
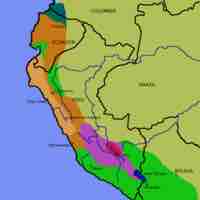
The Inca Empire was the largest of the pre-Columbian mesoamerican empires.
The Inca Empire utilized complex road systems, recording tools, and a hierarchical rule of law to oversee the administration of its vast population.

The Inca Empire worshipped the Sun god Inti, and expanded its hold on outlying areas by incorporating other deities into the religious system.
The Inca Empire already faced instability due to the Inca Civil War, European diseases, and internal revolt when explorer Francisco Pizarro began the conquest of Inca territory.
The Olmec were the first major civilization in Mexico, lasting from approximately 1500—400 BCE.
The Mixtec are a group who lived in modern-day Mexico before the Spanish conquest. People still identify as Mixtec today.
Teotihuacan was a city founded outside of modern Mexico City in 100 BCE and was known for its pyramids.
The Zapotec civilization developed in modern-day Mexico and lasted from approximately the 6th century BCE to the 16th century CE.
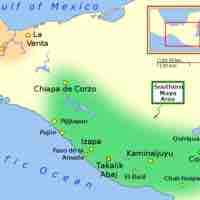
The Preclassic period lasted from 2000 BCE to 250 CE and saw the emergence of many distinctive elements of Mayan civilization.
The Classic period lasted from 250 to 900 CE and was the peak of the Maya civilization.

The period after the second collapse of the Maya Empire (900 CE–1600 CE) is called the Postclassic period.

The Toltecs were a Mesoamerican people who preceded the Aztecs and existed between 800 and 1000 CE.

The Aztecs were a pre-Columbian Mesoamerican people of Central Mexico during the 14th, 15th, and 16th centuries.
The Aztec religion focused on death, rebirth, and the renewal of the sun. The Aztecs practiced ritual sacrifice, ball games, and bloodletting in order to renew the sun each day.

The Aztec empire was defeated by an alliance between the Spanish and the Confederacy of Tlaxcala.
The peoples of the Great Basin area required ease of mobility to follow bison herds and gather seasonally available food supplies.

The mild climate and abundant natural resources along the Pacific Coast of North America allowed a complex aboriginal culture to flourish.

Eastern Woodland Culture refers to the way of life of indigenous peoples in the eastern part of North America between 1,000 BCE and 1,000 CE.

Environmental changes allowed for many cultural traditions to flourish and develop similar social structures and religious beliefs.
Mississippian cultures lived in the modern-day United States in the Mississippi valley from 800 to 1540.