Evaluation Results and Lessons Learned
Learn about CDC-funded program evaluations and evaluations of local and state organizations selected for their work in heart disease and stroke prevention.
Program/Project Evaluations
CDC funds a variety of programs nationwide for heart disease and stroke prevention. You can use the program evaluations listed below to help you in your heart disease and stroke prevention efforts.
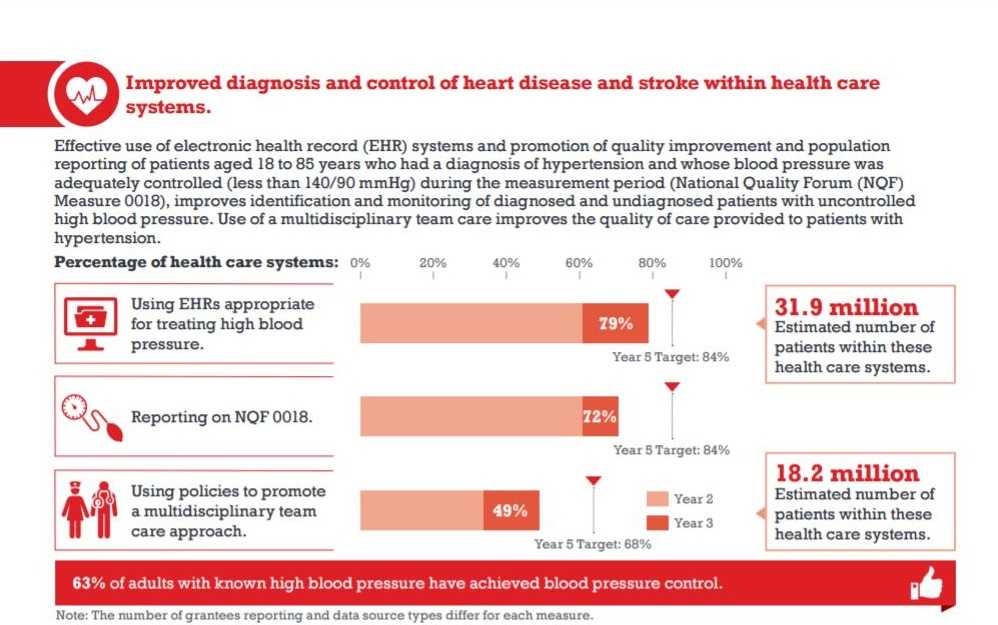
Paul Coverdell National Acute Stroke Registry Program: Summary Report 2007–2012 [PDF-651K]
The Paul Coverdell National Acute Stroke Program funds states to improve the quality of care for stroke patients. This report summarizes the programmatic strategies and activities used by grantees during the 2007–2012 funding period. The information can be used by states and public health departments interested in starting a stroke registry and improving stroke care and access to care.
Early Outcomes for Sodium Reduction in Communities Program infographic [PDF-478K]
The Sodium Reduction in Communities Program funds communities across the country to implement strategies to reduce sodium intake to no more than the recommended maximum amount as defined in the Dietary Guidelines for Americans. The infographic and the Sodium Reduction in Communities Program Outcome Evaluation Toolkit [PDF-1.7M] highlight awardees’ work in their communities during the 2013–2016 award cycle. Examples include making recipe modifications and replacing products with lower sodium options in hospitals, schools, and other local organizations.
State Cardiovascular Health Examination Survey
CDC funded three states to develop and implement a state cardiovascular health examination survey to guide strategies and evaluation of cardiovascular health promotion.
State Public Health Actions (1305) Evaluation Approach [PDF – 840 KB]
State Public Health Actions (1305) funds states to prevent, manage, and reduce the risk factors associated with chronic diseases—including childhood and adult obesity, diabetes, heart disease, and stroke. CDC developed a comprehensive approach to evaluating 1305 to assess the relevance, quality and impact of 1305 over the course of the cooperative agreement. This document provides a brief overview of the purpose and primary components of the evaluation approach.
State and Local Public Health Actions (1422) Evaluation Approach [PDF – 214 KB]
State and Local Public Health Actions (1422) funds states and large cities to prevent obesity, diabetes, heart disease, and stroke among general and priority populations with the aim of reducing health disparities and improving health equity among adults. CDC’s 1422 comprehensive evaluation approach describes and assesses the implementation of, and outcomes related to, the use of the Dual Approach [PDF – 124 KB] and mutually reinforcing strategies [PDF – 199 KB]. This document provides a brief overview of the evaluation approach and its primary components.
Evaluation Snapshots
State and Local Public Health Actions
Four distinct CDC chronic disease prevention programs work together to strengthen state and local actions to address health risk behaviors, environments, and systems associated with diabetes, heart disease, obesity, and school health. These snapshots show the work grantees are doing in the program and progress to date.
Evaluation Summaries
CDC identified the following programs as promising practices for preventing heart disease and stroke. The evaluation summaries briefly describe the program’s rigorous evaluation process, including methods and key findings. You can use the lessons learned from these cardiovascular disease prevention programs to guide strategies in your setting.
- Aggressively Treating Global Cardiometabolic Risk Factors to Reduce Cardiovascular Events (AT GOAL) Program Evaluation Summary [PDF-375K]
Established by the Consortium for Southeastern Hypertension Control (COSEHC), the AT GOAL program was selected for evaluation as a potentially promising practice to address cardiovascular disease (CVD). AT GOAL is a practice-level quality improvement (QI) initiative that uses performance metrics, offers monitoring and feedback to practices, and provides physician education. The evaluation was conducted to describe the program’s core components, identify lessons that other programs might consider, and determine its impact on intended outcomes. - The Shands Jacksonville Patient-Centered Medical Home Diabetes and Hypertension Self-Management Education Model: Evaluation Summary [PDF-1.8M]
Shands Jacksonville Patient-Centered Medical Home was selected as a promising practice because its diabetes and hypertension self-management education (DHSME) model addresses health disparities, reduces barriers to care, and improves treatment. In collaboration with staff from Shands Jacksonville and a contractor, CDC evaluated the implementation processes, clinical outcomes, and costs of the Shands Jacksonville model. - The Shands Jacksonville Patient-Centered Medical Home Diabetes and Hypertension Self-Management Education Model: Program Costs Summary [PDF-421K]
As part of the comprehensive evaluation of the Shands Jacksonville Patient-Centered Medical Home diabetes and hypertension self-management education (DHSME) model, CDC and a contractor conducted a cost study of the model in three clinics. - Residency Program Collaborative and Community Health Center Collaboration: Evaluation Summary [PDF-333K]
The Residency Program Collaborative and Community Health Center Collaborative (RPC/CHCC) was selected as a potentially promising practice to prevent and control chronic conditions, such as hypertension. - St. Johnsbury Vermont Community Health Team: Evaluation Summary [PDF-292K]
The Community Health Team (CHT) model was selected as a promising practice to prevent and control chronic conditions, such as hypertension. A mixed-methods evaluation aimed to describe the program, identify practices and lessons that other programs might consider using, and determine the effect the CHT model has on patient outcomes related to quality of life, hypertension, and health care use. - The Maryland Learning Collaborative: Evaluation Summary [PDF-466K]
CDC selected the Maryland Department of Health and Mental Hygiene (MDHMH) and specifically the Maryland Learning Collaborative (MLC) to participate in a 15-month enhanced evaluability assessment (EEA) of its strategies to reduce the effect of heart disease on population-level health outcomes. The EEA is an expedited evaluation that fulfills an important gap for reportable and actionable findings in a relatively short time frame.
- Page last reviewed: August 31, 2017
- Page last updated: August 31, 2017
- Content source:



 ShareCompartir
ShareCompartir