
Balantidiasis
[Balantidium coli]
Causal Agents
Balantidium coli, a large ciliated protozoan parasite.
Life Cycle

Cysts are the parasite stage responsible for transmission of balantidiasis 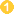 . The host most often acquires the cyst through ingestion of contaminated food or water
. The host most often acquires the cyst through ingestion of contaminated food or water  . Following ingestion, excystation occurs in the small intestine, and the trophozoites colonize the large intestine
. Following ingestion, excystation occurs in the small intestine, and the trophozoites colonize the large intestine 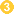 . The trophozoites reside in the lumen of the large intestine of humans and animals, where they replicate by binary fission, during which conjugation may occur
. The trophozoites reside in the lumen of the large intestine of humans and animals, where they replicate by binary fission, during which conjugation may occur 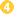 . Trophozoites undergo encystation to produce infective cysts
. Trophozoites undergo encystation to produce infective cysts 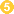 . Some trophozoites invade the wall of the colon and multiply. Some return to the lumen and disintegrate. Mature cysts are passed with feces.
. Some trophozoites invade the wall of the colon and multiply. Some return to the lumen and disintegrate. Mature cysts are passed with feces. 
Geographic Distribution
Worldwide. Because pigs are an animal reservoir, human infections occur more frequently in areas where pigs are raised. Other potential animal reservoirs include rodents and nonhuman primates.
Clinical Presentation
Most cases are asymptomatic. Clinical manifestations, when present, include persistent diarrhea, occasionally dysentery, abdominal pain, and weight loss. Symptoms can be severe in debilitated persons.
Balantidium coli cysts in wet mounts.
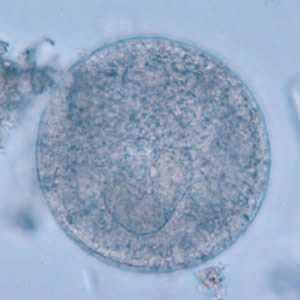
Figure A: B. coli cyst in a wet mount, unstained.
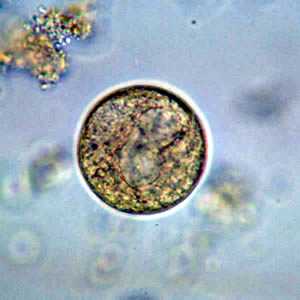
Figure B: B. coli cyst in a wet mount, unstained.
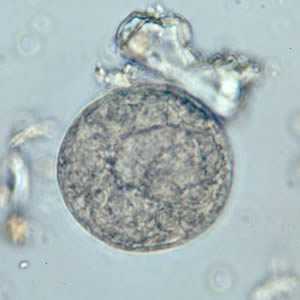
Figure C: B. coli cyst in a wet mount, unstained.
B. coli trophozoites.
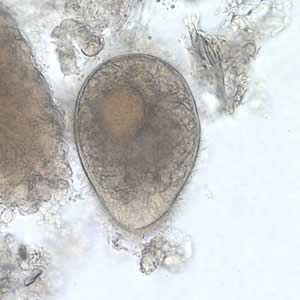
Figure A: B. coli trophozoite in a wet mount, 500× magnification. Note the visible cilia on the cell surface.
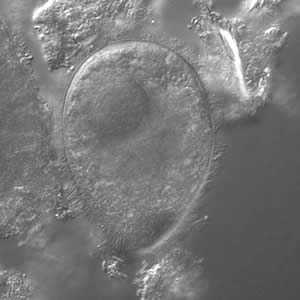
Figure B: B. coli trophozoite under differential interference contract (DIC) microscopy, 500× magnification
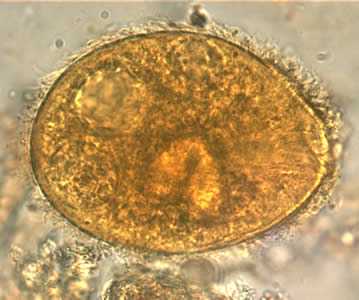
Figure C: B. coli trophozoite in a wet mount, 1000× magnification. Note the visible cilia on the cell surface. Image contributed by the Oregon Public Health Laboratory.
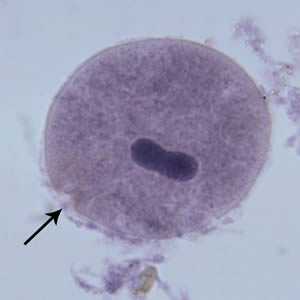
Figure D: B. coli trophozoite in a Mann's hematoxylin stained smear, 500× magnification. Note the cytosome (black arrow) and the bean shaped macronucleus.
Balantidium coli trophozoites in intestinal tissue, stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E)
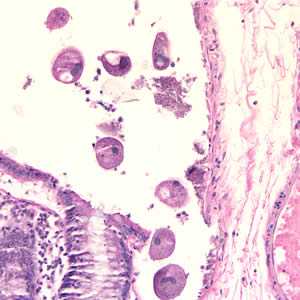
Figure A: Balantidium coli trophozoites in colon tissue stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E)at 200x magnification.
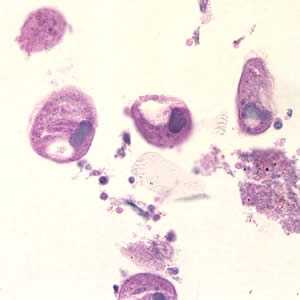
Figure B: Balantidium coli trophozoites in colon tissue stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) at 400x magnification.
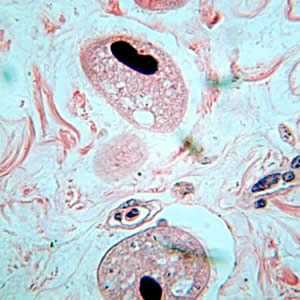
Figure C: Balantidium coli trophozoites in tissue stained with H&E.
Laboratory Diagnosis
Diagnosis is based on detection of trophozoites in stool specimens or in tissue collected during endoscopy. Cysts are less frequently encountered. Balantidium coli is passed intermittently and once outside the colon is rapidly destroyed. Thus stool specimens should be collected repeatedly, and immediately examined or preserved to enhance detection of the parasite.
More on: Morphologic comparison with other intestinal parasites
Treatment Information
Three medications are used most often to treat Balantidium coli: tetracycline, metronidazole, and iodoquinol.
Tetracycline*: adults, 500 mg orally four times daily for 10 days; children ≥ 8 years old, 40 mg/kg/day (max. 2 grams) orally in four doses for 10 days. (Note: Tetracyclines are contraindicated in pregnancy and in children < 8 years old. Tetracycline should be taken 1 hour before or 2 hours after meals or ingestion of dairy products.)
Alternatives:
Metronidazole*: adults, 500-750 mg orally three times daily for 5 days; children, 35-50 mg/kg/day orally in three doses for 5 days.
OR
Iodoquinol*: adults, 650 mg orally three times daily for 20 days; children, 30-40 mg/kg/day (max 2 g) orally in three doses for 20 days. (Note: iodoquinol should be taken after meals.)
Nitazoxanide*: has been tried in small studies, which suggest some therapeutic benefit (adults, 500 mg orally twice daily for 3 days; children age 4-11 years old 200 mg orally twice daily for 3 days; children 1-3 years old 100 mg orally twice daily for 3 days).
*Not FDA-approved for this indication
Tetracycline
Tetracycline is available for human use in the United States.
Note on Treatment in Pregnancy
Note on Treatment During Lactation
Note on Treatment in Pediatric Patients
Metronidazole
Metronidazole is available for human use in the United States.
Note on Treatment in Pregnancy
Note on Treatment During Lactation
Note on Treatment in Pediatric Patients
Iodoquinol
Iodoquinol is available for human use in the United States.
Note on Treatment in Pregnancy
Note on Treatment During Lactation
Note on Treatment in Pediatric Patients
DPDx is an education resource designed for health professionals and laboratory scientists. For an overview including prevention and control visit www.cdc.gov/parasites/.
- Page last reviewed: October 17, 2016
- Page last updated: October 17, 2016
- Content source:
- Global Health – Division of Parasitic Diseases and Malaria
- Notice: Linking to a non-federal site does not constitute an endorsement by HHS, CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the site.
- Maintained By:


 ShareCompartir
ShareCompartir