
DPDx is an education resource designed for health professionals and laboratory scientists. For an overview including prevention and control visit www.cdc.gov/parasites/crypto.
Cryptosporidiosis
[Cryptosporidium spp.]
Laboratory Diagnosis
Acid-fast staining methods, with or without stool concentration, are most frequently used in clinical laboratories. For greatest sensitivity and specificity, immunofluorescence microscopy is the method of choice (followed closely by enzyme immunoassays). Molecular methods are mainly a research tool.
Safety
Oocysts in stool specimens (fresh or in storage media) remain infective for extended periods. Thus stool specimens should be preserved in 10% buffered formalin or sodium acetate-acetic acid-formalin (SAF) to render oocysts nonviable. (Contact time with formalin necessary to kill oocysts is not clear; we suggest at least 18 to 24 hours). In addition, the usual safety measures for handling potentially infectious material should be adopted.
For more information on safety, visit CDD's Biosafety Guidelines or Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA).
Specimen processing
Stool specimens may be submitted fresh, preserved in 10% buffered formalin (see above, "Safety"), or suspended in a storage medium composed of aqueous potassium dichromate (2.5% w/v, final concentration). The use of mercuric chloride-containing preservatives (e.g., polyvinyl alcohol, PVA) is not recommended due to incompatibilities with some methodologies and the environmental hazards posed by the disposal of mercury-containing compounds. Oocyst numbers can be quite variable, even in liquid stools. Multiple stool samples should be tested before a negative diagnostic interpretation is reported. To maximize recovery of oocysts, stool samples should be concentrated prior to microscopic examination. Formalin-ethyl acetate sedimentation is the recommended stool concentration method for clinical laboratories. Two potential shortcomings of oocyst concentration techniques are:
- Sedimentation methods are generally performed using low speed centrifugation. Given their small size and mass, cryptosporidial oocysts may become trapped in the ether or ethyl acetate plug and fail to sediment properly. Increased centrifugation speed or time (500 x g, 10 minutes) may be warranted when attempting to recover cryptosporidial oocysts.
- Resolution of cryptosporidial infections is accompanied by increasing numbers of non-acid-fast, oocyst "ghosts." Such oocysts may not float or sediment as expected, giving rise to false-negative results.
Enzyme Immunoassays
At least four commercial EIA tests (see Table below) have been introduced for the detection of cryptosporidial antigens in stool samples. These kits are reportedly superior to conventional microscopic examination (especially acid-fast staining methods) and show good correlation with the monoclonal antibody-based immunofluorescence assays. Kit sensitivities and specificities ranged from 66.3% to 100% and 93% to 100%, respectively (see Table).
| Kit Name (Clinical specimens) |
Manufacturer/distributor | Type of test1 | Sensitivity2 | Specificity2 | Comparison test | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ProSpecT/ Cryptosporidium | Alexon, Inc. | EIA-plate | 97 98 96 94 (97) |
98 98 99.5 99 (98) |
acid-fast stain, IIF3 acid-fast stain M-DIF4 M-DIF4, acid-fast, Color Vue |
1 2 3 4 |
| IDEIA Cryptosporidium | Dako Corp. | EIA-plate | 100 (93.1) |
100 (98.7) |
auramine stain, N-DIF5 | 5 |
| MeriFluor™ Cryptosporidium/Giardia | Meridian Diagnostics, Inc. | DFA, IgG | 100 96 (100) |
100 100 (100) |
acid-fast stain acid-fast, ProSpecT, Color Vue |
6 4 |
| Color Vue Cryptosporidium | Seradyn, Inc. | EIA-plate | 93 76 94 (92) |
93 100 100 (100) |
IIF3 M-DIF4 M-DIF4, acid-fast, ProSpecT |
7 3 4 |
| Cryptosporidium Antigen Detection Microwell ELISA | LMD Laboratories | EIA-plate | 66.3 93 |
99.8 99 |
acid-fast, auramine IIF3 |
8 9 |
- 1 EIA = enzyme immunoassay; DFA = direct immunofluorescence assay, IIF = indirect immunofluorescence assay, NA = not available
- 2 Percent specificity or specificity compared to conventional methods, numbers in parentheses indicate values reported by the manufacturer
- 3 IIF = indirect immunofluorescence (MeriFluor Cryptosporidium/Giardia assay)
- 4 M-DIF = direct immunofluorescence (MeriFluor Cryptosporidium/Giardia assay)
- 5 N-DIF = direct immunofluorescence (DetectIF Cryptosporidium, Shield Diagnostics, Ltd.)
References:
- Xia Z, Sonnad S, Turner S, Marasigan M. Evaluation of a microtiter assay for detection of Cryptosporidium antigen in stool. 92nd Annual Meeting of the American Society for Microbiology, New Orleans, LA. 1992. p. 106.
- Dagan R, Fraser D, El-On J, Kassis I, Deckelbaum R, Turner S. Evaluation of an enzyme immunoassay for the detection of Cryptosporidium spp. in stool specimens from infants and young children in field studies. Am J Trop Med Hyg 1995;52:134.
- Aarnaes SL, Blanding J, Speier S, Forthal D, de la Maza LM, Peterson EM. Comparison of the ProSpecT and Color Vue enzyme-linked immunoassays for the detection of Cryptosporidium in stool specimens. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 1994;19:221.
- Kehl KSC, Cicirello H, Havens PL. Comparison of four different methods for detection of Cryptosporidium species. J. Clin Microbiol 1995;33:416.
- Siddons CA, Chapman PA, Rush BA. Evaluation of an enzyme immunoassay kit for detecting Cryptosporidium in faeces and environmental samples. J Clin Pathol 1992;45:479.
- Garcia LS, Shum AC, Bruckner DA. Evaluation of a new monoclonal antibody combination reagent for the direct fluorescent detection of Giardia cysts and Cryptosporidium oocysts in human fecal specimens. J Clin Microbiol 1992;30:3255.
- Sloan LM, Rosenblatt JE. Evaluation of an immunoassay for the detection of Cryptosporidium stool specimens. 91st Annual Meeting of the American Society for Microbiology, Dallas, TX. 1991. p. 22.
- Newman RD, Jaeger KL, Wuhib T, Lima AA, Guerrant RL, Sears CL. Evaluation of an antigen capture enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of Cryptosporidium oocysts. J Clin Microbiol 1993;31:2080.
- Rosenblatt JE, Sloan LM. Evaluation of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of Cryptosporidium spp. in stool specimens. J Clin Microbiol 1993;31:1468.
Molecular Methods
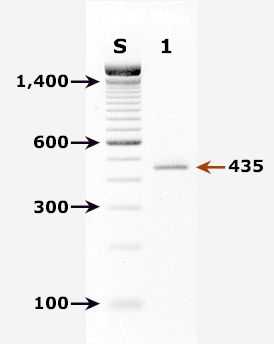
Agarose gel (2%) analysis of a PCR diagnostic test for detection of Cryptosporidium parvum DNA. PCR was performed using primers CPBDIAGF and CPBDIAGR.
Agarose gel (2%) analysis of a PCR diagnostic test for detection of Cryptosporidium parvum DNA. PCR was performed using primers CPBDIAGF and CPBDIAGR.1
- Lane S: Molecular base pair standard (100-bp ladder). Black arrows show the size of standard bands.
- Lane 1: C. parvum positive fecal specimen. The red arrow shows the diagnostic band of 435 bp for zoonotic Cryptosporidium parvum.
Real-Time PCR
A TaqMan-based real-time PCR assay for detection and identification of Cryptosporidium parvum (bovine genotype) and Cryptosporidium hominis (human genotype) has been developed and validated at CDC.2 The assay combines the detection of two genomic targets: the 18S rRNA gene to achieve a sensitive detection of Cryptosporidium spp. and a gene with unknown function to provide species differentiation. Each DNA sample is run in two parallel reactions. The first consists of the highly sensitive detection of the Cryptosporidium 18S rRNA gene and the species-specific detection of C. parvum in a duplex format. The other reaction detects C. hominis on the species level.
More on: TaqMan real-time PCR
References
- Johnson DW, Pieniazek NJ, Griffin DW, Misener L, Rose JB. Development of a PCR protocol for sensitive detection of Cryptosporidium oocysts in water samples. Appl Environ Microbiol 1995;61:3849-55.
Antibody detection: There are currently no commercially available serologic assays for the detection of Cryptosporidium-specific antibodies. However, immunoblots for detecting the 17 and 27 kDa sporozoite antigens associated with recent infection may be useful for epidemiologic investigations.
 ShareCompartir
ShareCompartir
 Laboratory Diagnosis of Cryptosporidiosis -- Cryptosporidium spp. [PDF, 294 KB, 2 Pages]
Laboratory Diagnosis of Cryptosporidiosis -- Cryptosporidium spp. [PDF, 294 KB, 2 Pages]

