Infographic: Decoding GHSA
Download Infographic PDF [904 KB]
Infographic Details
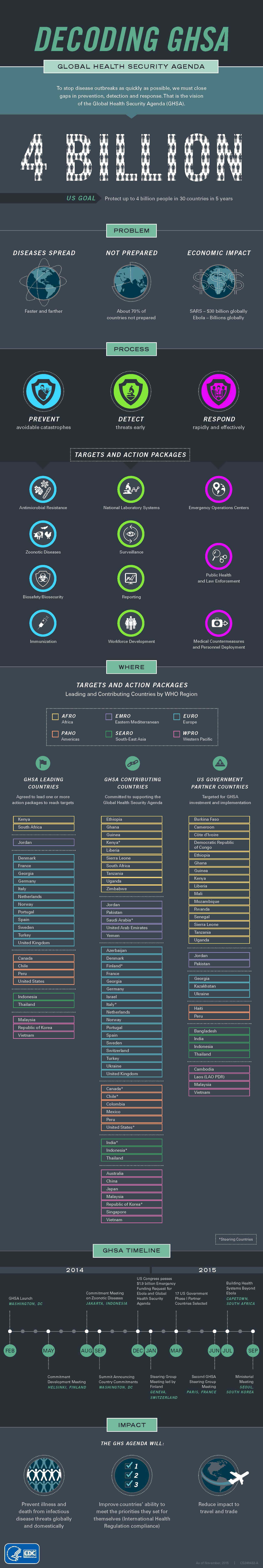
Decoding GHSA: Global Health Security Agenda
To stop disease outbreaks as quickly as possible, we must close gaps in prevention, detection and response. That is the vision of the Global Health Security Agenda (GHSA).
US Goal: Protect up to 4 billion people in 30 countries in 5 years
Problem
- Disease spread faster and farther
- Not prepared: About 70% of countries not prepared
- Economic impact:
- SARS - $30 billions globally
- Ebola - Billions globally
Process
Targets and Action Packages:
Prevent Avoidable Catastrophes
- Antimicrobial Resistance
- Zoonotic Diseases
- Biosafety/Biosecurity
- Immunization
Detect Threats Early
- National Laboratory Systems
- Surveillance
- Reporting
- Workforce Development
Respond Rapidly and Effectively
- Emergency Operations Centers
- Public Health and Law Enforcement
- Medical Countermeasures and Personnel Deployment
Where
Targets and action packages leading and contributing countries by WHO Region
GHSA Leading Countries: Agreed to lead one or more action packages to reach targets
AFRO: African countries
- Kenya
- South Africa
EMRO: Eastern Mediterranean
- Jordan
EURO: Europe
- Denmark
- France
- Georgia
- Germany
- Italy
- Netherlands
- Norway
- Portugal
- Spain
- Sweden
- Turkey
- United Kingdom
PAHO: Americas
- Canada
- Chile
- Peru
- United States
SEARO: South-East Asia
- Indonesia
- Thailand
WPRO: Western Pacific
- Malaysia
- Republic of Korea
- Vietnam
GHSA Contributing Countries: Committed to supporting the Global Health Security Agenda
AFRO: African
- Ethiopia
- Ghana
- Guinea
- Kenya*
- Liberia
- Sierra Leone
- South Africa
- Tanzania
- Uganda
- Zimbabwe
EMRO: Eastern Mediterranean
- Jordan
- Pakistan
- Saudi Arabia*
- United Arab Emirates
- Yemen
EURO: Europe
- Azerbaijan
- Denmark
- Finland*
- France
- Georgia
- Germany
- Israel
- Italy*
- Netherlands
- Norway
- Portugal
- Spain
- Sweden
- Switzerland
- Turkey
- Ukraine
- United Kingdom
PAHO: Americas
- Canada*
- Chile*
- Colombia
- Mexico
- Peru
- United States*
SEARO: South-East Asia
- India*
- Indonesia*
- Thailand
WPRO: Western Pacific
- Australia
- China
- Japan
- Malaysia
- Republic of Korea*
- Singapore
- Vietnam
US Government Partner Countries: Targeted for GHSA investment and implementation
AFRO: African
- Burkina Faso
- Cameroon
- Côte d’Ivoire
- Democratic Republic of Congo
- Ethiopia
- Ghana
- Guinea
- Kenya
- Liberia
- Mali
- Mozambique
- Rwanda
- Senegal
- Sierra Leone
- Tanzania
- Uganda
EMRO: Eastern Mediterranean
- Jordan
- Pakistan
EURO: Europe
- Georgia
- Kazakhstan
- Ukraine
PAHO: Americas
- Haiti
- Peru
SEARO: South-East Asia
- Bangladesh
- India
- Indonesia
- Thailand
WPRO: Western Pacific
- Cambodia
- Laos (LAO PDR)
- Vietnam
*Steering Countries.
GHSA Timeline
2014
- Feb: GHSA Launch in Washington, DC
- May: Commitment Development Meeting in Helsinki, Finland
- Aug: Commitment Meeting on Zoonotic Diseases in Jakarta, Indonesia
- Sep: Summit Announcing Country Commitments in Washington, DC
- Dec: US Congress passes $1.9 billion Emergency Funding Request for Ebola and Global Health Security Agenda
2015
- Jan: Steering Group Meeting led by Finland in Geneva, Switzerland
- Mar: 17 US Government Phase I Partner Countries Selected
- June: Second GHSA Steering Group Meeting in Paris, France
- July: Building Health Systems Beyond Ebola in Capetown, South Africa
- Sep: Ministerial Meeting in Seoul, South Korea
Impact
The GHS Agenda will:
- Prevent illness and death from infectious disease threats globally and domestically
- Improve countries’ ability to meet the priorities they set for themselves (International Health Regulation compliance)
- Reduce impact to travel and trade
As of November, 2015
- Page last reviewed: November 23, 2015
- Page last updated: November 23, 2015
- Content source:
Global Health
Notice: Linking to a non-federal site does not constitute an endorsement by HHS, CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the site.


 ShareCompartir
ShareCompartir