CDC Timeline 2000s
Take a minute to review many of CDC's momentous contributions to public health since it was organized in 1946 as the Communicable Disease Center.
2000s
-
2009
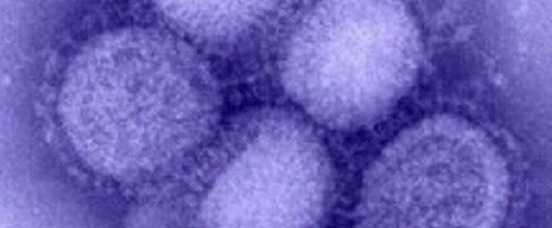
- CDC identifies the novel H1N1 influenza virus. The H1N1 flu pandemic dominates CDC activity for the year, and demonstrates CDC’s unique ability to assess and explain risk
- H1N1 flu pandemic outbreak and response.
- Widespread asbestos contamination in Libby, Montana; the ATSDR helps provide screenings and health care service for those exposed
-
2008

- Salmonella and E. coli outbreaks, large multi-state foodborne outbreaks are detected and investigated, revealing gaps in food safety and the need to improve prevention efforts
- CDC’s Emergency Operations Center (EOC) activates for Hurricane Dolly; Tropical Storm Edouard, Hurricanes Gustav, Hanna, and Ike
-
2007
- For the first time since 1963, CDC issues federal order of isolation for a Tuberculosis (TB) patient.
- NIOSH Science Blog debuts becoming a useful communication channel that provides workplace safety and health information to the public
-
2006
- Responds to a multi-state mumps outbreak involving more than 6,500 reported cases. This resurgence predominantly affects college-aged students living in the Midwest, with outbreaks occurring on many different Midwestern college campuses
- CDC’s Emergency Operations Center (EOC) activates for Tropical Storm Ernesto
- Responds to multi-state outbreak of E. coli, infections linked to fresh spinach
- Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) recommends routine immunizations for children and adolescents of rotavirus and human papillomavirus vaccines.
-
2005

- March is declared Deep-Vein Thrombosis Awareness Month
- Hurricanes Katrina and Rita response.
- The Surgeon General releases A Call to Action to Improve the Health and Wellness of Persons with Disabilities [PDF – 737 KB], and highlights disability as a major public health issue. The call to action appeals to all Americans to help improve the quality of life for people with disabilities through better health care and understanding
- Last large case of polio transmission stopped in India and Africa.
-
2004

- Rubella is eliminated in the United States
- CDC collaborates with the Office of the Surgeon General to promote the Family History Initiative, the first public campaign addressing the issue of family health history. The Initiative designates Thanksgiving Day as National Family History Day. A web-based tool, My Family Health Portrait, is created to help people collect the disease histories of their families
- An earthquake in the Indian Ocean triggers a devastating tsunami, causing an estimated 228,000 deaths in 14 countries on three continents. The Thai Ministry of Public Health responds with assistance from CDC, the Armed Forces Research Institute of Medical Sciences, and WHO
- CDC provides support for laws restricting access to over-the-counter medications used in methamphetamine production in Georgia
- Fungal meningitis from steroid injections response.
-
2003
- Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS) is first discovered in Asia. CDC responds by providing guidance for surveillance, clinical and laboratory evaluation, and reporting. SARS outbreak in Asia and Canada and response.
- MMWR reports the first identification of Bovine Spongiform Encephalopathy (BSE) in the United States
- A package containing ricin and a note threatening to poison water supplies is discovered in a South Carolina postal facility, becoming the first potential chemical terrorism event involving ricin in the U.S.
- U.S. experiences an outbreak of monkeypox, the first time human monkeypox is reported outside of Africa. CDC deploys teams of medical officers, epidemiologists, and other experts to several states to assist with the investigation
-
2002
- CDC reports that U.S. newborn HIV infections are down 80% since 1981
- Congress mandates that issues related to children’s neurobehavioral disorders, including ADHD, be included as part of NCBDDD’s research agenda
-
2001

- CDC learns of the first case of inhalational anthrax in the U.S. since 1976. The person, a 63-year-old Florida man, is the first of 22 victims of domestic terrorism infected by anthrax sent through the mail.
- World Trade Center and bioterrorist anthrax attacks and response
- The Children’s Health Act (Public Law 106-310) establishes the National Center on Birth Defects and Developmental Disabilities (NCBDDD) at CDC. The Act expands research and services for a variety of childhood health problems and authorizes the establishment of Centers of Excellence at both CDC and NIH to promote research and monitoring efforts related to autism
- National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) provides technical assistance for responder safety and health in the World Trade Center rescue and recovery
- National Center on Birth Defects and Developmental Disabilities (NCBDDD) established.
-
2000
- CDC and West Virginia University release Women and Heart Disease: An Atlas of Racial and Ethnic Disparities in Mortality, the first national atlas of heart disease death rates among U.S. women 35 and older. The new maps indicate a woman’s risk of dying from heart disease depends in part on where she lives
- CDC receives reports of Rift Valley fever (RVF) in Saudi Arabia with more than 300 people infected. This outbreak represents the first cases of RVF outside the continent of Africa
- Page last reviewed: May 12, 2015
- Page last updated: June 29, 2016
- Content Source:
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
- Page maintained by: Office of the Associate Director for Communication, Division of Public Affairs


 ShareCompartir
ShareCompartir