

|

|

Volume 5: No.
2, April 2008
ESSAY
Development of a Federally Funded Demonstration
Colorectal Cancer Screening Program
Laura C. Seeff, MD, Amy DeGroff, MPH, Florence Tangka, PhD, Ena Wanliss, MS, Anne Major, BA, Marion Nadel, PhD, A. Blythe Ryerson, MPH, Janet Royalty, MS, Cynthia Gelb, BS, Eddie Reed, MD
Suggested citation for this article: Seeff LC, DeGroff A, Tangka F, Wanliss E, Major A, Nadel M,
et al. Development of a federally funded demonstration colorectal
cancer screening program. Prev Chronic Dis 2008;5(2).
http://www.cdc.gov/pcd/issues/2008/
apr/07_0206.htm. Accessed [date].
Abstract
Colorectal cancer is the second leading cause of cancer-related mortality among U.S. adults. In 2004,
treatment costs for colorectal cancer were $8.4 billion.
There is substantial evidence that colorectal cancer incidence and mortality are reduced with regular screening.
The natural history of this disease is also well described:
most colorectal cancers develop slowly from preexisting polyps. This slow
development provides an opportunity to intervene with screening tests, which can
either prevent colorectal cancer through the removal of polyps or detect it at
an early stage. However, much less is known about how best to implement an
effective colorectal cancer screening program. Screening rates are low, and uninsured persons, low-income persons, and persons who have not visited a physician within a year are least likely to be screened.
Although the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has 15 years of experience supporting the National Breast and Cervical Cancer Early Detection Program for the underserved population, a similar national program for colorectal cancer is not in place. To explore the feasibility of implementing a national program for the underserved U.S. population and to learn which settings and which program models are most viable and cost-effective, CDC began a 3-year colorectal cancer screening demonstration program in 2005.
This article describes briefly this demonstration program and the process CDC used to design it and to select program sites. The multiple-methods evaluation now under way to assess the program’s feasibility and describe key outcomes is also detailed. Evaluation results will be used to inform future activities related to organized screening for colorectal cancer.
Back to top
Introduction
Cancer is the second leading cause of death among U.S. adults, and colorectal
cancer is the second leading cause of cancer-related deaths among U.S. men and
women. In 2004, there were 145,083 new cases of colorectal cancer, and 53,580 people died of the
disease (1). Although colorectal cancer affects both sexes and all races, men,
African Americans, and Alaska Natives have disproportionately high incidences
and mortality rates of colorectal cancer (2). In addition, colorectal cancer is
expensive to treat: in 2004, the national cost of medical treatment for this
disease was $8.4 billion (3).
Most colorectal cancers develop slowly from pre-existing polyps. This slow development provides an opportunity to intervene with screening tests, which can either prevent colorectal cancer through the removal of polyps or detect it at an early stage (4). Substantial scientific evidence shows that the incidence and mortality are reduced by regular screening (5-10). However, screening rates have been slow to increase (11), and
it is not clear how best to implement an effective colorectal cancer
screening program that reaches the people most in need. Uninsured persons, low-income persons, or those who have not seen a physician within the previous year are least likely to be screened (11).
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has 15 years of experience supporting the National Breast and Cervical Cancer Early Detection Program (NBCCEDP) for the medically underserved population, but a similar national program for
colorectal cancer is not in place (12). The NBCCEDP uses a comprehensive approach to breast and cervical cancer control, which includes providing early detection services, educational activities, public and private partnerships, and quality assurance measures.
Clinically, screening for colorectal cancer is more complex than screening for either breast or cervical cancer because several screening tests are acceptable, each with a different recommended interval and each performed by different types of health care specialists. To understand better how to structure and implement population-level
colorectal cancer screening and to explore which settings and program models are most viable and cost-effective, CDC began a 3-year colorectal cancer screening demonstration
program in 2005. It was designed for low-income persons aged 50 to 64 years who are underinsured or uninsured for
colorectal cancer screening.
This article describes briefly the process used to establish the CDC-funded
Colorectal Cancer Screening Demonstration Program and the tools developed to implement this program. In accompanying reports in this issue of Preventing Chronic Disease (13-15), we present case-study and cost-study evaluation findings from the program start-up period, which we defined as beginning when the demonstration sites received their initial funds and ending when the screening
itself began. Future reports will include evaluation results from the implementation phase of the program.
Back to top
Program Planning Process
In the summer of 2004, CDC held two meetings with 58 invited stakeholders, including clinicians and health scientists from CDC, other federal health agencies, partner organizations such as the American Cancer Society and Prevent Cancer Foundation, state health departments,
and health systems such as managed care organizations.
Also in attendance were representatives from Australia, the United Kingdom, and Italy, many with experience in organized
colorectal cancer screening programs.
During these stakeholder meetings, we used published data, the combined
experience of meeting attendees, and consensus opinion to make key decisions
that helped define the demonstration program. These decisions included the following:
Applicants for funds to implement a screening program could be any nonprofit medical entity that offered services to low-income persons who are underinsured for
colorectal cancer screening.
When possible, screening programs would be flexible in their structure and design so they could meet the needs of the community they intended to serve.
Applicants would need to actively collaborate with their state’s CDC-funded Comprehensive Cancer Control Program.
Because the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) (16) recommends four screening tests with no one "best" test recommended, applicants proposing a screening program could choose which
colorectal cancer screening tests to offer as long as
- The selected test or tests are recommended by USPSTF.
- The applicant has the capacity to offer the selected test or tests.
Providers within each selected program would be reimbursed for screening and diagnostic tests at the Medicare rate.
The focus of the screening programs would be on people aged 50 to 64 at average risk for
colorectal cancer; younger persons would be eligible if they are at increased risk.
- Persons at increased risk for colorectal cancer because of a personal or family history of
the disease would be eligible to receive
screening services.
- Persons with colorectal cancer symptoms or at high risk of
colorectal cancer because they already have inflammatory bowel disease or certain genetic conditions would not be eligible to receive services,
because these conditions require frequent specialized care.
Programs would need to convene a local medical advisory board to address ongoing clinical issues.
As with the NBCCEDP, CDC funds would not be used for cancer treatment. To be eligible for consideration, applicants had to identify, in advance, sources that would provide treatment services for 1) cancers detected through the screening program and 2) complications that may arise during screening and diagnostic procedures.
Back to top
Site Selection and Program Features
Of the 39 applicants who competed for funds to start a demonstration project, 5 were selected and awarded a combined $2.1 million for year 1 of a 3-year program beginning in 2005. The successful applicants were the Maryland Department of Health and Mental Hygiene; Missouri Department of Health and Senior Services; Nebraska Department of Health and Human Services; Public Health – Seattle & King County, Washington; and Stony Brook University
Medical Center, New York. The program’s structure and the screening tests selected for the program are described in Figure 1.
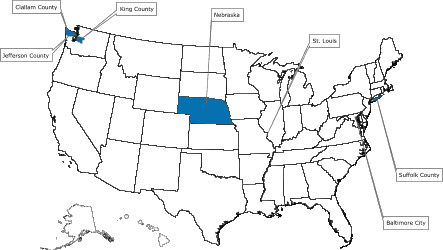
[ View enlarged image and descriptive text.
Readers who print the entire article should also print the enlarged map. ]
Figure. Colorectal Cancer Demonstration Screening Sites, 2005–2008
Note: All programs provide screening and follow-up
services to low-income persons aged 50–64 years, who are underinsured or
uninsured for colorectal cancer. In addition, some programs focus on a specific demographic subgroup.
Each of the five programs is described in this issue of Preventing Chronic Disease (14). Program components in the five selected sites include clinical services (screening, surveillance, and diagnostic services), patient support, data collection and tracking, program management, public education and outreach, quality services measures, partnerships, and evaluation of program process and effectiveness. A multidisciplinary CDC team worked closely with the five selected sites during
their start-up; the team included physicians, public health advisors, epidemiologists, program analysts, evaluators, health economists, data consultants, and health communications specialists.
Back to top
Materials Developed for the Colorectal Cancer
Screening Program
During the start-up phase, which ranged from 9 to 11 months, CDC staff and program staff at each site collaborated to develop the program’s materials and components. These include policies, a set of standard data elements (colorectal cancer clinical data elements or CCDEs), a data user’s manual, data collection forms, a readiness checklist, a cost-assessment tool, and an evaluation plan. The cost-assessment
tool and evaluation plan are described in another article in this issue of Preventing Chronic Disease
(15). The readiness checklist, program policies, CCDEs, and data users' manual
are available at http://www.cdc.gov/cancer/colorectal/what_cdc_is_doing/demonstration. Data collection forms were designed individually by each program site and are available on request.
Program policies
CDC created a policy manual for this demonstration program. Each site also created its own individual policies, which usually mirrored the policies that CDC created for the overall program. Policies were developed on the following topics: 1) patient eligibility, 2) reimbursement, 3) reporting adverse events, 4) collecting and reporting data, and 5) medical advisory committees. A series of supporting documents
to accompany the policy manual were developed by CDC in collaboration with all sites. These documents include guidelines for patient eligibility and ineligibility, reimbursable clinical services, data reporting requirements and schedules, and service quality indicators. These indicators were developed to capture data on the characteristics of the population being served by the program,
the completeness of clinical follow-up and treatment, and the timeliness of clinical follow-up and treatment.
Colorectal Cancer Clinical Data Elements
The CCDEs were developed by CDC, program sites, and two external clinical experts to ensure that information collected
about clients’ demographic characteristics, screening history, risk factors, screening and diagnostic tests, final diagnosis, and treatment would be consistent and complete. These data will be used to monitor the extent to which the five demonstration sites achieve the objectives of the demonstration project. They will also be used to guide future policy and program development.
CDC provided technical assistance on data management and reporting to each of the five sites through routine communication and
through tools that promote standard reporting, including a communication Web site for program participants, an extensive data dictionary, and software to validate the data set being submitted. Because of the short time frame and limited number of awardees participating in the program, we did not provide a standard data management system.
Quality assurance
Several measures were taken to emphasize the importance of delivering high-quality clinical services. Programs were made aware of important quality issues, including the frequent and inappropriate use of in-office rather than at-home fecal occult blood tests (FOBT) (17), wide variation in adenoma detection rates among endoscopists, and too-frequent surveillance following polyp detection (18). Teleconferences were conducted with CDC staff, endoscopists at all five sites, and a leading expert
in assessing the quality of colorectal cancer screening about issues of quality and colonoscopy reporting guidelines. Programs and their participating endoscopists were encouraged to monitor their performance and follow the new standard colonoscopy reporting system (CO-RADS) (19), which specifies which elements should be included in colonoscopy reports, provides a standard method for reporting them, and specifies the key quality indicators that endoscopists should monitor periodically. The CCDEs include
several factors that allow the quality of endoscopic services to be measured (e.g., whether the bowel preparation was adequate, whether the cecum was reached, whether polyps were completely removed).
Public education materials
CDC’s Screen for Life: National Colorectal Cancer Action Campaign (SFL)
(http://www.cdc.gov/cancer/colorectal/sfl/) is a multimedia campaign that promotes
colorectal cancer screening for adults aged 50 years or older. Programs were not required to use SFL materials, but materials that could be adapted for local use were developed by CDC staff and made available to the five programs. During start-up, two sites used the SFL materials and worked with CDC to adapt the SFL logo for their
own program’s use. Later, a third program elected to use SFL materials for patient education.
Readiness checklist
CDC developed a readiness checklist (available at
http://www.cdc.gov/cancer/colorectal/what_cdc_is_doing/demonstration) to be used during start-up to assist CDC and the five sites to monitor progress toward implementing the program. The items in the checklist corresponded to program components and include providing screening and diagnostic follow-up services, public education and outreach, data collection and tracking, patient support, partnership development and maintenance, quality assurance and professional development, and
program management.
Evaluation
A comprehensive evaluation of the colorectal cancer screening program is being conducted. It will provide information to guide our next steps. Evaluators engaged program and CDC stakeholders in developing a multisite and multiple-method evaluation to assess the program’s implementation, outcomes, and efficiencies. Qualitative and quantitative evaluation approaches will be used 1) to analyze patient screening and diagnostic services, 2) to determine cost and cost-effectiveness, and 3) to conduct a
longitudinal multiple-case study.
Back to top
State Programs
Colorectal cancer screening is rapidly becoming a priority at the local, state, and national levels. Several states (e.g., New York, Maryland) have long-standing programs; other states and cities (e.g., Colorado, New York City) recently began
colorectal cancer screening; and others (e.g., Iowa, Wyoming) are planning to allocate new resources for organized
colorectal cancer screening programs. CDC is working closely with the five demonstration program sites and communicating with other local and state partners who are taking
steps toward establishing local or state programs so that lessons learned can be disseminated widely. Several pieces of legislation have been introduced into the U.S. Congress that, if passed, would establish a national
colorectal cancer screening program.
Program activities for the demonstration sites will continue through August 2008. The evaluation findings published in this issue of Preventing
Chronic Disease (13-15) and findings to be reported from the implementation phase of the demonstration program will be used to make adjustments during the demonstration period and to guide emerging programs and larger future efforts.
Back to top
Acknowledgments
We thank the five Colorectal Cancer Screening Demonstration Program sites, Information Management Systems, Inc, and Research Triangle Institute for their invaluable time and contributions to the program described in this article.
Back to top
Author Information
Corresponding Author: Laura C. Seeff, MD, Centers for Disease Control and
Prevention, Division of Cancer Prevention and Control, 4770 Buford Hwy, Mailstop K-52, Atlanta, GA 30341-3717. Telephone: 770-488-3223. E-mail: LVS3@cdc.gov.
Author Affiliations: Amy DeGroff, Florence Tangka, Ena Wanliss, Anne Major, Marion Nadel,
A. Blythe Ryerson, Janet Royalty, Cynthia Gelb, Eddie Reed, Division of Cancer
Prevention and Control, National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and
Health Promotion, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta,
Georgia.
Back to top
References
- U.S. Cancer Statistics Working Group. United States cancer statistics: 2004
incidence and mortality. Atlanta (GA): U.S. Department of Health and Human Services,
National Cancer Institute and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; 2007.
- Jackson-Thompson J, Ahmed F, German RR, Lai SM, Friedman C.
Descriptive epidemiology of colorectal cancer in the United States, 1998-2001. Cancer 2006;107(5
suppl):1103-11.
- Brown ML, Riley GF, Schussler N, Etzioni R.
Estimating health care costs related to cancer treatment from SEER-Medicare data. Med Care 2002;40(8 Suppl):IV-104-17.
- Winawer SJ, Zauber AG, Ho MN, O’Brien MJ, Gottlieb LS, Sternberg SS,
et al.
Prevention of colorectal cancer by colonoscopic polypectomy. The National Polyp Study Workgroup.
N Engl J Med 1993;329(27):1977-81.
- Mandel JS, Church TR, Bond JH, Ederer F, Geisser MS, Mongin SJ, et al.
The effect of fecal occult-blood screening on the incidence of colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med 2000;343(22):1603-7.
- Mandel JS, Bond JH, Church TR, Snover DC, Bradley GM, Schuman LM, et al.
Reducing mortality from colorectal cancer by screening for fecal occult
blood. Minnesota Colon Cancer Control Study. [Published erratum in: N
Engl J Med 1993;329(9):672]. N Engl J Med 1993;328(19):1365-71.
- Selby JV, Friedman GD, Quesenberry CP Jr, Weiss NS.
A case-control study of screening sigmoidoscopy and mortality from colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med 1992;326(10):653-7.
- Newcomb PA, Norfleet RG, Storer BE, Surawicz TS, Marcus PM.
Screening sigmoidoscopy and colorectal cancer mortality. J Natl Cancer Inst 1992;84(20):1572-5.
- Hardcastle JD, Chamberlain JO, Robinson MH, Moss SM, Amar SS, Balfour TW, et al.
Randomised controlled trial of faecal-occult-blood screening for colorectal cancer. Lancet 1996;348(9040):1472-7.
- Kronborg O, Fenger C, Olsen J, Jorgensen OD, Sondergaard O.
Randomised study of screening for colorectal cancer with faecal-occult-blood test. Lancet 1996;348(9040):1467-71.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Increased use of colorectal cancer tests — United States, 2002 and 2004.
MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2006;55(11):308-11.
- The National Breast and Cervical Early Detection Program: 1991-2002 national
report. Atlanta (GA): Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for
Disease Control and Prevention; 2005.
- DeGroff A, Boehm J, Green SG, Holden D, Seeff LC. CDC’s Colorectal Cancer Screening Demonstration Program: facilitators and challenges to program start-up. Prev Chronic Dis 2008;5(2).
http://www.cdc.gov/pcd/issues/2008/apr/07_0205.htm.
- DeGroff A, Holden D, Green SG, Boehm J, Seeff LC, Tangka F. Starting
up the Colorectal Cancer Screening Demonstration Project. Prev Chronic Dis 2008;5(2).
http://www.cdc.gov/pcd/issues/2008/apr/07_0204.htm.
- Tangka FKL, Subramanian S, Bapat B, Seeff LC, DeGroff A, Gardner J, et al. Cost of starting colorectal cancer screening programs: results from five federally funded demonstration programs. Prev Chronic Dis 2008;5(2).
http://www.cdc.gov/pcd/issues/2008/apr/07_0202.htm.
- U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Screening for colorectal cancer: recommendations and rationale. Rockville
(MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality; 2002. http://www.ahrq.gov/clinic/3rduspstf/colorectal/colorr.htm. Accessed September 12, 2007.
- Nadel MR, Shapiro JA, Klabunde CN, Seeff LC, Uhler R, Smith RA, et al.
A national survey of primary care physicians’ methods for screening for fecal occult blood. Ann Intern Med 2005;142(2):86-94.
- Rex DK, Bond JH, Winawer S, Levin TR, Burt RW, Johnson DA, et al.
Quality in the technical performance of colonoscopy and the continuous
quality improvement process for colonoscopy: recommendations of the U.S.
Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer. Am J Gastroenterol 2002;97(6):1296-308.
- Lieberman D, Nadel M, Smith RA, Atkin W, Duggirala SB, Fletcher R, et al.
Standardized colonoscopy reporting and data system: report of the Quality
Assurance Task Force of the National Colorectal Cancer Roundtable.
Gastrointest Endosc 2007;65(6):757-66.
Back to top
*URLs for nonfederal organizations are provided solely as a
service to our users. URLs do not constitute an endorsement of any organization
by CDC or the federal government, and none should be inferred. CDC is
not responsible for the content of Web pages found at these URLs.
|
|
