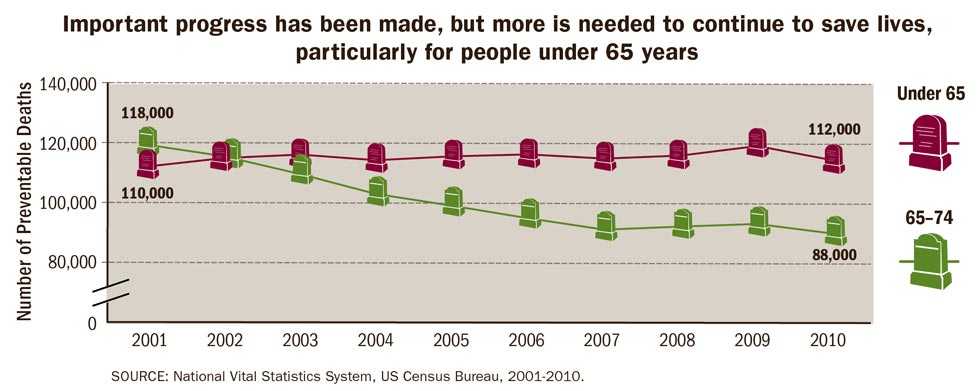
Important progress has been made, but more is needed to continue to save lives, particularly for people under 65 years
| Year |
Under 65 years | 65- 74 years |
|---|---|---|
| 2001 | 110,299 | 117,662 |
| 2002 | 113,094 | 113,777 |
| 2003 | 114,280 | 107,822 |
| 2004 | 112,377 | 101,139 |
| 2005 | 113,714 | 97,110 |
| 2006 | 114,353 | 92,916 |
| 2007 | 112,918 | 89,080 |
| 2008 | 113,993 | 90,091 |
| 2009 | 117,139 | 90,996 |
| 2010 | 112,329 | 87,741 |
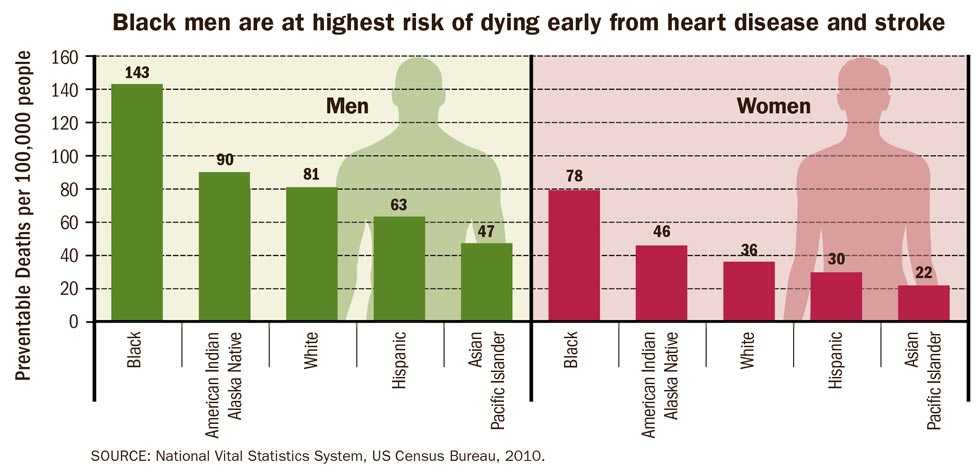
Black men are at highest risk of dying early from heart disease and stroke.
Preventable deaths per 100,000 people:
Men:
- Black: 143
- American Indian/Alaska Native: 90
- White: 81
- Hispanic: 63
- Asian Pacific Islander: 47
Women:
- Black: 78
- American Indian/Alaska Native: 46
- White: 36
- Hispanic: 30
- Asian Pacific Islander: 22
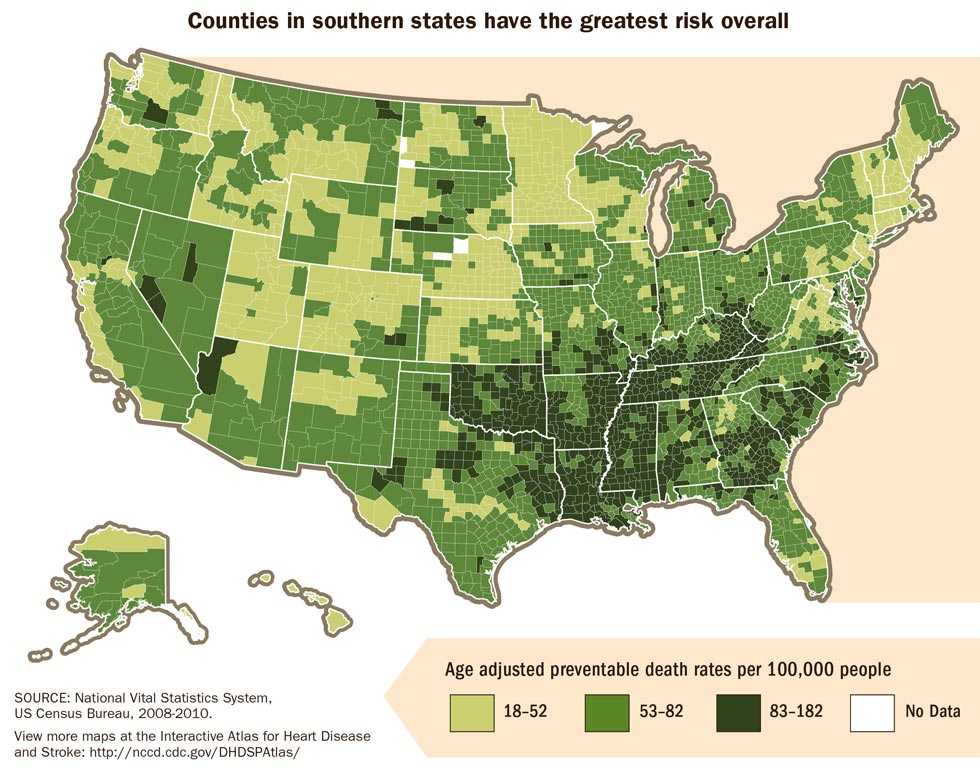
Counties with the highest risk of preventable heart disease and stroke deaths from 2008-2010 are located primarily in the southern Appalachian region and much of Tennessee, Arkansas, Mississippi, Louisiana, and Oklahoma, whereas the lowest risk counties are located in the West, Midwest, and Northeast census regions. States with the greatest difference in county rates include Colorado, Virginia, Kentucky, and Maryland.
SOURCE: National Vital Statistics System, US Census Bureau, 2008-2010.
View more maps at the Interactive Atlas for Heart Disease and Stroke.
Nearly 800,000 Americans die each year from heart disease and stroke. Most of the major risk factors can be managed or prevented
Risk factors and solutions for managing them
- High blood pressure – Make control your goal.
- High cholesterol – Work with your doctor on a treatment plan to manage your cholesterol.
- Diabetes – Work with your doctor on a treatment plan to manage your diabetes.
- Tobacco use – If you don't smoke, don’t start. If you do smoke get help to quit.
- Unhealthy diet – Eat a healthy diet, low in sodium and trans fats and high in fresh fruits and vegetables.
- Physical inactivity – The Surgeon General recommends adults engage in moderateintensity exercise for 2 hours and 30 minutes every week.
- Obesity – Work to maintain a healthy weight.