

/en/word2013/creating-and-opening-documents/content/
When you create a new document in Word, you'll need to know how to save it so you can access and edit it later. As with previous versions of Word, you can save files to your computer. If you prefer, you can also save files to the cloud using OneDrive. You can even export and share documents directly from Word.
Word offers two ways to save a file: Save and Save As. These options work in similar ways, with a few important differences:
It's important to save your document whenever you start a new project or make changes to an existing one. Saving early and often can prevent your work from being lost. You'll also need to pay close attention to where you save the document so it will be easy to find later.
 Clicking the Save command
Clicking the Save command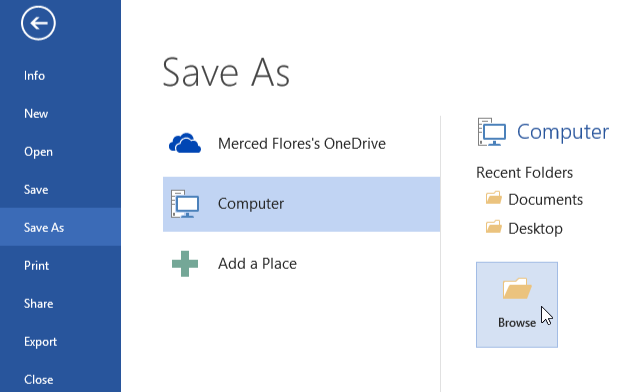 Clicking Browse
Clicking Browse Saving a document
Saving a documentIf you want to save a different version of a document while keeping the original, you can create a copy. For example, if you have a file named Sales Report, you could save it as Sales Report 2 so you'll be able to edit the new file and still refer back to the original version.
To do this, you'll click the Save As command in Backstage view. Just like when saving a file for the first time, you'll need to choose where to save the file and give it a new file name.
 Clicking Save As
Clicking Save AsIf you don't want to use OneDrive, you may be frustrated that OneDrive is selected as the default location when saving. If you find it inconvenient to select Computer each time, you can change the default save location so Computer is selected by default.
 Clicking the File tab
Clicking the File tab Clicking Options
Clicking Options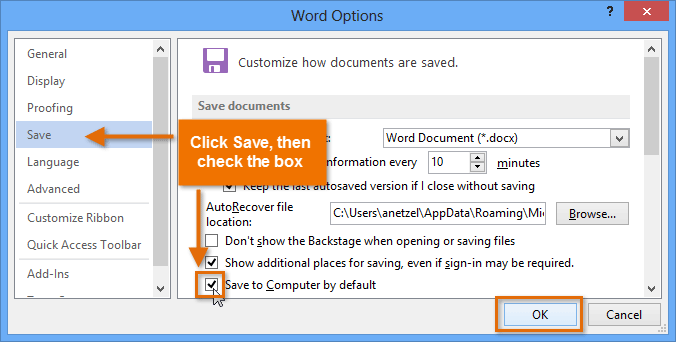 Changing the default save location
Changing the default save locationWord automatically saves your documents to a temporary folder while you are working on them. If you forget to save your changes or if Word crashes, you can restore the file using AutoRecover.
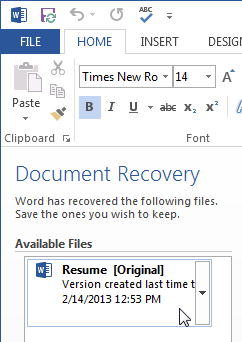 The Document Recovery pane
The Document Recovery paneBy default, Word autosaves every 10 minutes. If you are editing a document for less than 10 minutes, Word may not create an autosaved version.
If you don't see the file you need, you can browse all autosaved files from Backstage view. Select the File tab, click Manage Versions, then choose Recover Unsaved Documents.
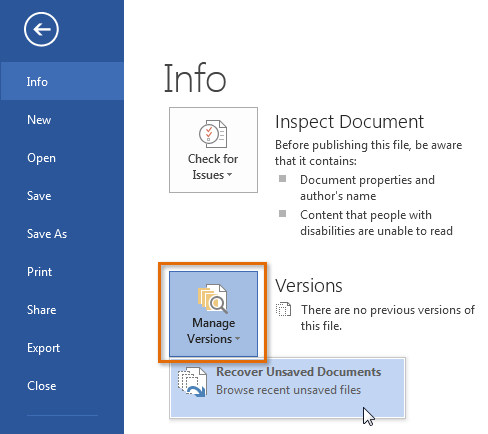 Accessing all auto-saved files
Accessing all auto-saved filesBe default, Word documents are saved in the .docx file type. However, there may be times when you need to use another file type, such as a PDF or Word 97-2003 document. It's easy to export your document from Word in a variety of file types.
Exporting your document as an Adobe Acrobat document, commonly known as a PDF file, can be especially useful if you're sharing a document with someone who does not have Word. A PDF file will make it possible for recipients to view—but not edit—the content of your document.
 Exporting a PDF file
Exporting a PDF file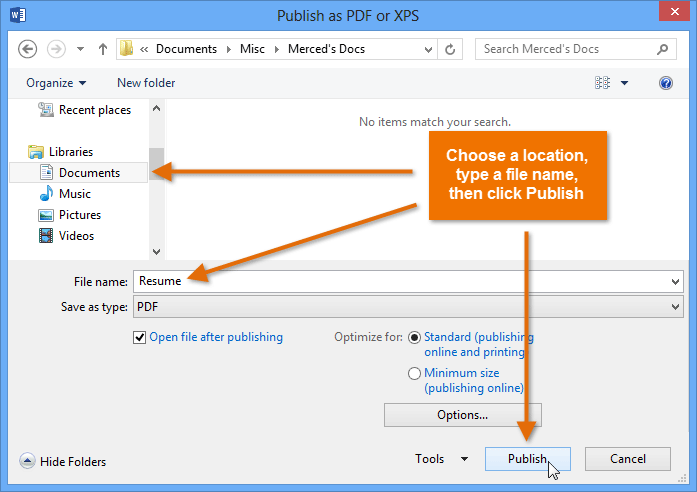 Exporting a PDF file
Exporting a PDF fileBy default, Word will export all of the pages in the document. If you want to export only the current page, click Options in the Save as dialog box. The Options dialog box will appear. Select Current page, then click OK.
 Exporting the current page
Exporting the current pageIf you need to edit a PDF file, Word allows you to convert a PDF file into an editable document. Read our guide on Editing PDF Files for more information.
You may also find it helpful to export your document in other file types, such as a Word 97-2003 Document if you need to share with people using an older version of Word, or a .txt file if you need a plain text version of your document.
 Clicking Change File Type
Clicking Change File Type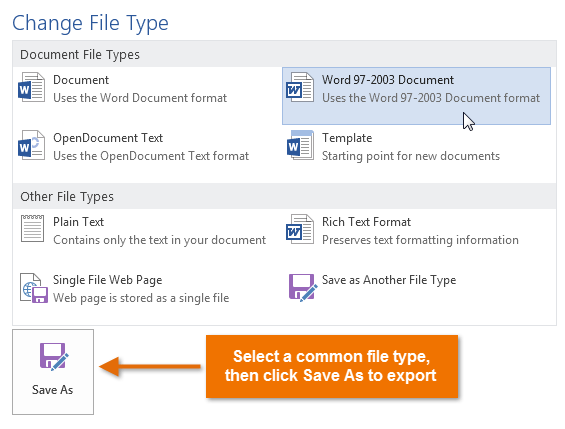 Choosing another file type
Choosing another file type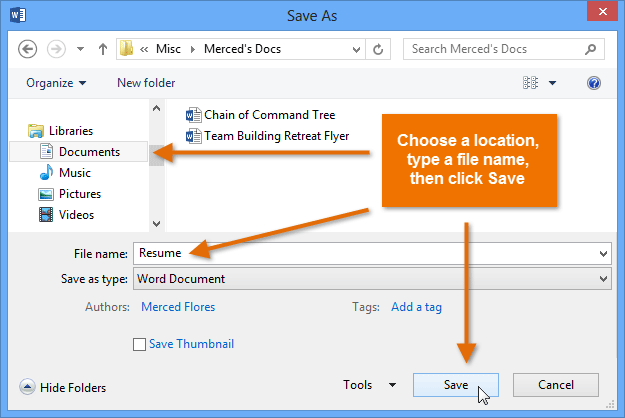 Saving as a Word 97-2003 document
Saving as a Word 97-2003 documentYou can also use the Save as type: drop-down menu in the Save As dialog box to save documents in a variety of file types.
 Using the Save As type menu to choose a file type
Using the Save As type menu to choose a file typeWord 2013 makes it easy to share and collaborate on documents using OneDrive. In the past, if you wanted to share a file with someone you could send it as an email attachment. While convenient, this system also creates multiple versions of the same file, which can be difficult to organize.
When you share a document from Word 2013, you're actually giving others access to the exact same file. This lets you and the people you share with edit the same document without having to keep track of multiple versions.
In order to share a document, it must first be saved to your OneDrive.
 Clicking Share
Clicking ShareClick the buttons in the interactive below to learn more about different ways to share a document.

/en/word2013/text-basics/content/