Bubonic plague
| Bubonic plague | |
|---|---|
 | |
| A bubo on the upper thigh of a person infected with bubonic plague. | |
| Specialty | Infectious disease |
| Symptoms | Fever, headaches, vomiting, swollen lymph nodes[1][2] |
| Usual onset | 1–7 days after exposure[1] |
| Causes | Yersinia pestis spread by fleas[1] |
| Diagnostic method | Finding the bacterium in the blood, sputum, or lymph nodes[1] |
| Treatment | Antibiotics such as streptomycin, gentamicin, or doxycycline[3][4] |
| Frequency | 650 cases reported a year[1] |
| Deaths | 10% mortality with treatment[3] 30-90% if untreated[1][3] |
Bubonic plague is one of three types of plague caused by bacterium Yersinia pestis.[1] One to seven days after exposure to the bacteria, flu-like symptoms develop.[1] These symptoms include fever, headaches, and vomiting.[1] Swollen and painful lymph nodes occur in the area closest to where the bacteria entered the skin.[2] Occasionally, the swollen lymph nodes may break open.[1]
The three types of plague are the result of the route of infection: bubonic plague, septicemic plague, and pneumonic plague.[1] Bubonic plague is mainly spread by infected fleas from small animals.[1] It may also result from exposure to the body fluids from a dead plague-infected animal.[5] In the bubonic form of plague, the bacteria enter through the skin through a flea bite and travel via the lymphatic vessels to a lymph node, causing it to swell.[1] Diagnosis is made by finding the bacteria in the blood, sputum, or fluid from lymph nodes.[1]
Prevention is through public health measures such as not handling dead animals in areas where plague is common.[1] Vaccines have not been found to be very useful for plague prevention.[1] Several antibiotics are effective for treatment, including streptomycin, gentamicin, and doxycycline.[3][4] Without treatment, plague results in the death of 30% to 90% of those infected.[1][3] Death, if it occurs, is typically within ten days.[6] With treatment the risk of death is around 10%.[3] Globally between 2010 and 2015 there were 3248 documented cases, which resulted in 584 deaths.[1] The countries with the greatest number of cases are the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Madagascar, and Peru.[1]
The plague was the cause of the Black Death that swept through Asia, Europe, and Africa in the 14th century and killed an estimated 50 million people.[1][7] This was about 25% to 60% of the European population.[1][8] Because the plague killed so many of the working population, wages rose due to the demand for labor.[8] Some historians see this as a turning point in European economic development.[8] The disease was also responsible for the Justinian plague originating in the Eastern Roman Empire in the 6th century CE, as well as the third epidemic affecting China, Mongolia, and India originating in the Yunnan Province in 1855.[9] The term bubonic is derived from the Greek word βουβών, meaning "groin".[10] The term "buboes" is also used to refer to the swollen lymph nodes.[11]
Signs and symptoms
The best-known symptom of bubonic plague is one or more infected, enlarged, and painful lymph nodes, known as buboes. After being transmitted via the bite of an infected flea, the Y. pestis bacteria become localized in an inflamed lymph node, where they begin to colonize and reproduce. Buboes associated with the bubonic plague are commonly found in the armpits, upper femoral, groin and neck region. Bubonic plague symptoms appear suddenly a few days after exposure to the bacterium.[12][13]
Symptoms include:[13]
- Chills
- Malaise
- High fever
- Muscle cramps
- Seizures
- Smooth, painful lymph gland swelling called a buboes
- Gangrene (complication as Septicemic plague[14])
Other symptoms include heavy breathing, continuous vomiting of blood, aching limbs, coughing, and extreme pain caused by the decay or decomposition of the skin; further symptoms include extreme fatigue, gastrointestinal problems, delirium, and coma.[14][15] Additional forms of the disease include septicemic plague and pneumonic plague in which the bacterium reproduces in the persons blood and lungs respectively.[16][17]
 Symptoms of bubonic plague
Symptoms of bubonic plague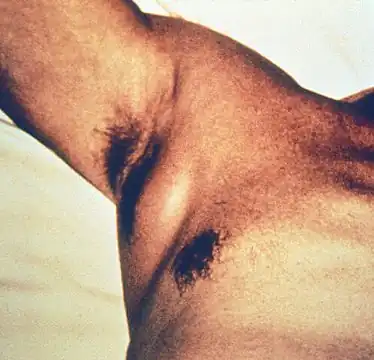 Swollen axillary lymph node
Swollen axillary lymph node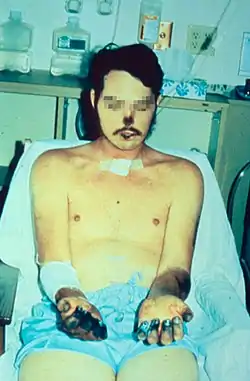 Necrosis in a person recovering from bubonic plague that disseminated to the blood and the lungs
Necrosis in a person recovering from bubonic plague that disseminated to the blood and the lungs
Cause

Bubonic plague is an infection of the lymphatic system, usually resulting from the bite of an infected flea, Xenopsylla cheopis . In very rare circumstances, as in the septicemic plague, the disease can be transmitted by direct contact with infected tissue or exposure to the cough of another human. The flea is parasitic on house and field rats, and seeks out other prey when its rodent hosts die. The bacteria remain harmless to the flea, allowing the new host to spread the bacteria. The bacteria form aggregates in the gut of infected fleas and this results in the flea regurgitating ingested blood, which is now infected, into the bite site of a rodent or human host. Once established, bacteria rapidly spread to the lymph nodes and multiply.[18][13][19][20]
Mechanism
First the vector bites a individual, the bacilli travel to lymph nodes, are phagocytosed by polymorphonuclear/mononuclear phagocytes. After this intracellular multiplication begins and then replication within macrophages. With eventual lysis of phagocytes, bacteremia begins.[21]
In its infection of the human body the Bubonic plague has many ways of circumventing the human immune system to then propagate within macrophages, afterwards, the infection causes a pro-inflammatory response.[13]
Y. pestis bacilli can resist phagocytosis and even reproduce inside phagocytes and kill them. As the disease progresses, the lymph nodes can hemorrhage and become swollen and necrotic. Bubonic plague can progress to lethal septicemic plague in some cases. The plague is also known to spread to the lungs and become the disease known as the pneumonic plague.[13][21][22]
Diagnosis

Laboratory testing is required in order to diagnose and confirm plague. Ideally, confirmation is through the identification of Y. pestis culture from a patient sample. Confirmation of infection can be done by examining serum taken during the early and late stages of infection. To quickly screen for the Y. pestis antigen in patients, rapid dipstick tests have been developed for field use.[23]
Samples taken for testing include:[24]
- Buboes- (fluid sample)
- Blood
- Lungs
Prevention
While a vaccine should be used for those who work with Y. Pestis, the plague is very rare in the majority of the world.[25][26]
Targeted chemoprophylaxis, sanitation, and vector control played a role in controlling the 2003 Oran outbreak of the bubonic plague.[27]
Treatment

Several classes of antibiotics are effective in treating bubonic plague. These include aminoglycosides such as streptomycin and gentamicin, tetracyclines (especially doxycycline), and the fluoroquinolone ciprofloxacin. Mortality associated with treated cases of bubonic plague is about 1–15%, compared to a mortality of 40–60% in untreated cases.[28]
People potentially infected with the plague need immediate treatment and should be given antibiotics within 24 hours of the first symptoms to prevent death. Other treatments include oxygen, intravenous fluids, and respiratory support. People who have had contact with anyone infected by pneumonic plague are given prophylactic antibiotics.[29]
Using the broad-based antibiotic streptomycin has proven to be dramatically successful against the bubonic plague within 12 hours of infection.[30]
Epidemiology

Globally between 2010 and 2015 there were 3248 documented cases, which resulted in 584 deaths.[1] The countries with the greatest number of cases are the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Madagascar, and Peru.[1]
For over a decade since 2001, Zambia, India, Malawi, Algeria, China, Peru, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo had the most plague cases with over 1,100 cases in the Democratic Republic of the Congo alone. From 1,000 to 2,000 cases are conservatively reported per year to the WHO.[31] From 2012 to 2017, reflecting political unrest and poor hygienic conditions, Madagascar began to host regular epidemics.[31]
Between 1900 and 2015, the United States had 1,036 human plague cases with an average of 9 cases per year. In 2015, 16 people in the Western United States developed plague, including 2 cases in Yosemite National Park.[32] These US cases usually occur in rural northern New Mexico, northern Arizona, southern Colorado, California, southern Oregon, and far western Nevada.[33]
In November 2017, the Madagascar Ministry of Health reported an outbreak to WHO (World Health Organization) with more cases and deaths than any recent outbreak in the country. Unusually most of the cases were pneumonic rather than bubonic.[34]
In June 2018, a child was confirmed to be the first person in Idaho to be infected by bubonic plague in nearly 30 years.[35]
A couple died in May 2019, in Mongolia, while hunting marmots.[36] Another two people in the province of Inner Mongolia, China were treated in November 2019 for the disease.[37]
In July 2020, in Bayannur, Inner Mongolia of China, a human case of bubonic plague was reported. Officials responded by activating a city-wide plague-prevention system for the remainder of the year.[38] Also in July 2020, in Mongolia, a teenager died from bubonic plague after consuming infected marmot meat.[39]
History
Yersinia pestis has been discovered in archaeological finds from the Late Bronze Age (~3800 BP).[40]
First pandemic
.jpg.webp)
The first recorded epidemic affected the Sassanian Empire and their arch-rivals, the Eastern Roman Empire (Byzantine Empire) and was named the Plague of Justinian after emperor Justinian I, who was infected but survived through extensive treatment.[41][42] The pandemic resulted in the deaths of an estimated 25 million (6th century outbreak) to 50 million people (two centuries of recurrence).[43][44] The historian Procopius wrote, in Volume II of History of the Wars, of his personal encounter with the plague and the effect it had on the rising empire. In the spring of 542, the plague arrived in Constantinople, working its way from port city to port city and spreading around the Mediterranean Sea, later migrating inland eastward into Asia Minor and west into Greece and Italy. Because the infectious disease spread inland by the transferring of merchandise through Justinian's efforts in acquiring luxurious goods of the time and exporting supplies, his capital became the leading exporter of the bubonic plague. Procopius, in his work Secret History, declared that Justinian was a demon of an emperor who either created the plague himself or was being punished for his sinfulness.[44]
Second pandemic
In the Late Middle Ages Europe experienced the deadliest disease outbreak in history when the Black Death, the infamous pandemic of bubonic plague, hit in 1347, killing a third of the European human population. Some historians believe that society subsequently became more violent as the mass mortality rate cheapened life and thus increased warfare, crime, popular revolt, waves of flagellants, and persecution.[45] The Black Death originated in Central Asia and spread from Italy and then throughout other European countries. Arab historians Ibn Al-Wardni and Almaqrizi believed the Black Death originated in Mongolia. Chinese records also showed a huge outbreak in Mongolia in the early 1330s.[46] Research published in 2002 suggests that it began in early 1346 in the steppe region, where a plague reservoir stretches from the northwestern shore of the Caspian Sea into southern Russia.The Mongols had cut off the trade route, the Silk Road, between China and Europe which halted the spread of the Black Death from eastern Russia to Western Europe. The epidemic began with an attack that Mongols launched on the Italian merchants' last trading station in the region, Caffa in the Crimea.[30] In late 1346, plague broke out among the besiegers and from them penetrated into the town. The Mongol forces catapulted plague infected corpses into Caffa as a form of attack one of the first known instances of biological warfare.[47] When spring arrived, the Italian merchants fled on their ships, unknowingly carrying the Black Death; carried by the fleas on rats, the plague initially spread to humans near the Black Sea and then outwards to the rest of Europe as a result of people fleeing from one area to another.[48]
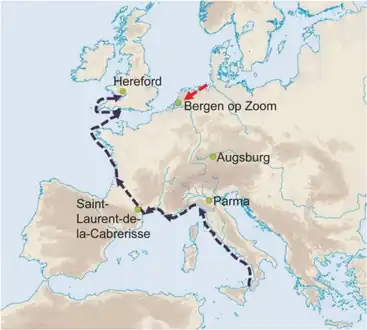 Five archaeological sites -independent infection routes black/red dotted arrows for spread of Black Death
Five archaeological sites -independent infection routes black/red dotted arrows for spread of Black Death Citizens of Tournai bury plague victims. Miniature from The Chronicles of Gilles Li Muisis (1272–1352). Bibliothèque royale de Belgique, MS 13076-77, f. 24v.
Citizens of Tournai bury plague victims. Miniature from The Chronicles of Gilles Li Muisis (1272–1352). Bibliothèque royale de Belgique, MS 13076-77, f. 24v. People who died of bubonic plague in a mass grave from 1720 to 1721 in Martigues, France
People who died of bubonic plague in a mass grave from 1720 to 1721 in Martigues, France
Third pandemic

The plague resurfaced for a third time in the mid-19th century, beginning in China and moving to India and Hong Kong, the bubonic plague killed several million victims.[49] Like the two previous outbreaks, this one also originated in Eastern Asia, most likely in Yunnan Province of China, where there are several natural plague foci.[50] The initial outbreaks occurred in the second half of the eighteenth century.[51][52] The disease remained localized in Southwest China for several years before spreading. In the city of Canton, beginning in January 1894, the disease killed 80,000 people by June. Daily water-traffic with the nearby city of Hong Kong rapidly spread the plague there, killing over 2,400 within two months.[53]
Also known as the modern pandemic, the third pandemic spread the disease to port cities throughout the world in the second half of the 19th century and early 20th century via shipping routes.[54] The plague infected people in Chinatown in San Francisco from 1900 to 1904,[55] and in the nearby locales of Oakland and the East Bay again from 1907 to 1909.[56] During the outbreak from 1900 to 1904 in San Francisco is when authorities made permanent the Chinese Exclusion Act. This law was originally signed into existence by President Chester A. Arthur in 1882. The Chinese Exclusion Act was supposed to last for ten years but was renewed in 1892 with the Geary Act and subsequently made permanent in 1902 during the outbreak of plague in Chinatown, San Francisco. The last major outbreak in the United States occurred in Los Angeles in 1924,[57] though the disease is still present in wild rodents, and can be passed to humans that come in contact with them.[58] According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention[59], in 1994, a plague outbreak in several Indian states caused an estimated 700 infections with several deaths and triggered a large migration of Indians within India as they tried to avoid the plague; though there are some who question if it was the Bubonic plague at all.[60][61][62]
Society and culture

The scale of death and social upheaval associated with plague outbreaks has made the topic prominent in a number of historical and fictional accounts since the disease was first recognized. The Black Death in particular is described and referenced in numerous contemporary sources, some of which, including works by Chaucer, Boccaccio, and Petrarch, are considered part of the Western canon. The Decameron, by Boccaccio, is notable for its use of a frame story involving individuals who have fled Florence for a secluded villa to escape the Black Death. First-person, sometimes sensationalized or fictionalized, accounts of living through plague years have also been popular across centuries and cultures. For example, Samuel Pepys's diary makes a number of references to his first-hand experiences of the Great Plague of London in 1665–1666.[63]
Later works, such as Albert Camus's novel The Plague or Ingmar Bergman's film The Seventh Seal have used bubonic plague in settings, such as quarantined cities in either medieval or modern times, as a backdrop to explore a variety of concepts. Common themes include the breakdown of society, institutions, and individuals during the plague, the cultural and psychological existential confrontation with mortality.[64][65]
Renaissance
A theory that has been advanced is that the devastation in Florence caused by the Black Death, which hit Europe between 1348 and 1350, resulted in a shift in the world view of people in 14th century Italy. Italy was particularly badly hit by the plague, and it has been speculated that the resulting familiarity with death caused thinkers to dwell more on their lives on Earth, rather than on spirituality and the afterlife.[66] It has also been argued that the Black Death prompted a new wave of piety, manifested in the sponsorship of religious works of art.[67] However, this does not fully explain why the Renaissance occurred specifically in Italy in the 14th century. The Black Death was a pandemic that affected all of Europe in the ways described, not only Italy. The Renaissance's emergence in Italy was most likely the result of the complex interaction of the above factors.[68]
Medicine
Although the Black Death highlighted the shortcomings of medical science in the medieval era, it also led to positive changes in the field of medicine. As described by David Herlihy in The Black Death and the Transformation of the West, more emphasis was placed on "anatomical investigations" following the Black Death.[69] How individuals studied the human body notably changed, becoming a process that dealt more directly with the human body in varied states of sickness and health. Further, at this time, the importance of surgeons became more evident.[69]
Biological warfare
Some of the earliest instances of biological warfare were said to have been products of the plague, as armies of the 14th century were recorded catapulting diseased corpses over the walls of towns and villages to spread the pestilence; this was done by Jani Beg when he attacked the city of Kaffa in 1343.[70]
Later, plague was used during the Second Sino-Japanese War as a bacteriological weapon by the Imperial Japanese Army. These weapons were provided by Shirō Ishii's units and used in experiments on humans before being used on the field. For example, in 1940, the Imperial Japanese Army Air Service bombed Ningbo with fleas carrying the bubonic plague.[71] During the Khabarovsk War Crime Trials, the accused, such as Major General Kiyoshi Kawashima, testified that, in 1941, 40 members of Unit 731 air-dropped plague-contaminated fleas on Changde. These operations caused epidemic plague outbreaks.[72]
See also
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 World Health Organization (November 2014). "Plague Fact sheet N°267". Archived from the original on 24 April 2015. Retrieved 10 May 2015.
- 1 2 "Plague Symptoms". 13 June 2012. Archived from the original on 19 August 2015. Retrieved 21 August 2015.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Prentice MB, Rahalison L (April 2007). "Plague". Lancet. 369 (9568): 1196–207. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(07)60566-2. PMID 17416264. S2CID 208790222.
- 1 2 "Plague Resources for Clinicians". 13 June 2012. Archived from the original on 21 August 2015. Retrieved 21 August 2015.
- ↑ "Plague Ecology and Transmission". 13 June 2012. Archived from the original on 22 August 2015. Retrieved 21 August 2015.
- ↑ Keyes, Daniel C. (2005). Medical response to terrorism : preparedness and clinical practice. Philadelphia [u.a.]: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 74. ISBN 9780781749862. Archived from the original on 27 July 2020. Retrieved 16 July 2020.
- ↑ Haensch S, Bianucci R, Signoli M, Rajerison M, Schultz M, Kacki S, Vermunt M, Weston DA, Hurst D, Achtman M, Carniel E, Bramanti B (2010). "Distinct Clones of Yersinia pestis Caused the Black Death". PLOS Pathogens. 6 (#10): e1001134. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1001134. PMC 2951374. PMID 20949072.
- 1 2 3 "Plague History". 13 June 2012. Archived from the original on 21 August 2015. Retrieved 21 August 2015.
- ↑ Cohn SK (2008). "Epidemiology of the Black Death and successive waves of plague". Medical History Supplement. 52 (27): 74–100. doi:10.1017/S0025727300072100. PMC 2630035. PMID 18575083.
- ↑ LeRoux, Neil (2007). Martin Luther As Comforter: Writings on Death Volume 133 of Studies in the History of Christian Traditions. BRILL. p. 247. ISBN 9789004158801. Archived from the original on 27 July 2020. Retrieved 16 July 2020.
- ↑ Edman, Bruce F. Eldridge, John D. (2004). Medical Entomology a Textbook on Public Health and Veterinary Problems Caused by Arthropods (Rev.. ed.). Dordrecht: Springer Netherlands. p. 390. ISBN 9789400710092. Archived from the original on 27 July 2020. Retrieved 16 July 2020.
- ↑ Sencen, Lisa. "Plague". NORD (National Organization for Rare Disorders). Archived from the original on 13 May 2022. Retrieved 25 July 2022.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Dillard, Robert L.; Juergens, Andrew L. (2022). "Plague". StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Archived from the original on 31 March 2021. Retrieved 26 July 2022.
- 1 2 "Plague". webwiser.nlm.nih.gov. Archived from the original on 19 August 2022. Retrieved 9 August 2022.
- ↑ Roussos, Dikea (1 July 2002). "Plague". Primary Care Update for OB/GYNS. 9 (4): 125–128. doi:10.1016/S1068-607X(02)00102-6. ISSN 1068-607X. Retrieved 31 July 2022.
- ↑ Gage, Kenneth L. (1 January 2012). "320 - Plague and Other Yersinia Infections". Goldman's Cecil Medicine (Twenty Fourth Edition). W.B. Saunders. pp. 1895–1900. ISBN 978-1-4377-1604-7. Retrieved 10 August 2022.
- ↑ "CDC | Facts About Plague". www.emergency.cdc.gov. 21 February 2019. Archived from the original on 23 July 2022. Retrieved 10 August 2022.
- ↑ Lawrenz, MB (2010). "Model systems to study plague pathogenesis and develop new therapeutics". Frontiers in microbiology. 1: 119. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2010.00119. PMID 21687720. Archived from the original on 11 February 2022. Retrieved 25 July 2022.
- ↑ Boyer, Sebastien; Gillespie, Thomas R.; Miarinjara, Adélaïde (1 July 2022). "Xenopsylla cheopis (rat flea)". Trends in Parasitology. 38 (7): 607–608. doi:10.1016/j.pt.2022.03.006. ISSN 1471-4922. Archived from the original on 9 August 2022. Retrieved 5 August 2022.
- ↑ "Plague Ecology and transmission". CDC. Archived from the original on 22 August 2015. Retrieved 7 August 2022.
- 1 2 "Plague: Background, Pathophysiology, Epidemiology". emedicine (registration required). 16 October 2021. Archived from the original on 24 June 2022. Retrieved 28 July 2022.
- ↑ "Bubonic and Pneumonic Plague --- Uganda, 2006". www.cdc.gov. Archived from the original on 4 November 2021. Retrieved 7 August 2022.
- ↑ "Diagnosis and treatment of plague | CDC". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 26 November 2019. Archived from the original on 5 April 2022. Retrieved 28 July 2022.
- ↑ "Plague – Diagnosis and treatment – Mayo Clinic". www.mayoclinic.org. Archived from the original on 27 July 2020. Retrieved 1 December 2017.
- ↑ "Plague Vaccine". www.cdc.gov. Archived from the original on 14 July 2018. Retrieved 2 August 2022.
- ↑ "Prevention of Plague: Recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP)". www.cdc.gov. Archived from the original on 29 May 2022. Retrieved 3 August 2022.update
- ↑ Bertherat, Eric; Bekhoucha, Souad; Chougrani, Saada; Razik, Fathia; Duchemin, Jean B.; Houti, Leila; Deharib, Larbi; Fayolle, Corinne; Makrerougrass, Banaouda; Dali-Yahia, Radia; Bellal, Ramdan; Belhabri, Leila; Chaieb, Amina; Tikhomirov, Evgueni; Carniel, Elisabeth (2007). "Plague Reappearance in Algeria after 50 Years, 2003". Emerging Infectious Diseases. 13 (10): 1459–1462. doi:10.3201/eid1310.070284. PMC 2851531. PMID 18257987.
- ↑ "Plague". Archived from the original on 5 March 2010. Retrieved 25 February 2010.
- ↑ "Plague". Healthagen, LLC. Archived from the original on 6 June 2011. Retrieved 4 April 2011.
- 1 2 Echenberg, Myron (2002). Pestis Redux: The Initial Years of the Third Bubonic Plague Pandemic, 1894–1901. Journal of World History, vol 13,2
- 1 2 Filip, Julia (11 April 2014). "Avoiding the Black Plague Today". The Atlantic. Archived from the original on 27 July 2020. Retrieved 11 April 2014.
- ↑ Regan, Michael (January 2017). "Human Plague Cases Drop in the US". PBS. Archived from the original on 16 July 2020. Retrieved 1 January 2017.
- ↑ "Plague in the United States | Plague | CDC". www.cdc.gov. 23 October 2017. Archived from the original on 8 April 2020. Retrieved 1 December 2017.
- ↑ "Emergencies Preparedness, Response, Plague, Madagascar, Disease Outbreak News | Plague | CDC". www.who.int. 15 November 2017. Archived from the original on 29 July 2020. Retrieved 15 November 2017.
- ↑ "Child in Idaho Confirmed To Have The Bubonic Plague". iflscience.com. Archived from the original on 29 July 2020. Retrieved 16 July 2020.
- ↑ Schriber, Melody; Bichelle, Rae Ellen (7 May 2019). "Bubonic Plague Strikes in Mongolia: Why Is It Still A Threat?". NPR. NPR. Archived from the original on 7 May 2019. Retrieved 8 May 2019.
- ↑ CNN, Jessie Yeung. "Two people got the plague in China. Why is it still a thing?". CNN. Archived from the original on 14 November 2019. Retrieved 14 November 2019.
- ↑ CNN, Jessie Yeung. "The bubonic plague is back again in China's Inner Mongolia". CNN. Archived from the original on 16 July 2020. Retrieved 6 July 2020.
- ↑ "Teenager dies of Black Death in Mongolia amid fears of new outbreak". The Independent. 14 July 2020. Archived from the original on 16 July 2020. Retrieved 14 July 2020.
- ↑ Spyrou MA, Tukhbatova RI, Wang CC, Valtueña AA, Lankapalli AK, Kondrashin VV, Tsybin VA, Khokhlov A, Kühnert D, Herbig A, Bos KI, Krause J (June 2018). "Analysis of 3800-year-old Yersinia pestis genomes suggests Bronze Age origin for bubonic plague". Nature Communications. 9 (1): 2234. Bibcode:2018NatCo...9.2234S. doi:10.1038/s41467-018-04550-9. PMC 5993720. PMID 29884871.
- ↑ Little, Lester K. (2007). "Life and Afterlife of the First Plague Pandemic." In: Little, Lester K. editor. (2007), Plague and the End of Antiquity: The Pandemic of 541–750. Cambridge University Press. (2007). ISBN 978-0-521-84639-4 pp. 8–15
- ↑ McCormick, Michael (2007). "Toward a Molecular History of the Justinian Pandemic." In: Little, Lester K. editor. (2007), Plague and the End of Antiquity: The Pandemic of 541–750. Cambridge University Press. (2007). ISBN 978-0-521-84639-4 pp. 290–312.
- ↑ Rosen, William (2007), Justinian's Flea: Plague, Empire, and the Birth of Europe Archived 25 January 2010 at the Wayback Machine. Viking Adult; pg 3; ISBN 978-0-670-03855-8.
- 1 2 Moorshead Magazines, Limited. "The Plague of Justinian." History Magazine 11.1 (2009): 9–12. History Reference Center
- ↑ Cohn, Samuel K.(2002). The Black Death: End of a Paradigm. American Historical Review, vol 107, 3, pg. 703–737
- ↑ Sean Martin (2001). Black Death:Chapter One. Harpenden, GBR:Pocket Essentials. p. 14.
- ↑ Wheelis, Mark (2002). "Archive copy". Emerging Infectious Diseases. 8 (9): 971–975. doi:10.3201/eid0809.010536. PMC 2732530. PMID 12194776. Archived from the original on 7 March 2018. Retrieved 16 July 2020.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ↑ Glatter, Kathryn A.; Finkelman, Paul (February 2021). "History of the Plague: An Ancient Pandemic for the Age of COVID-19". The American Journal of Medicine. 134 (2): 176–181. doi:10.1016/j.amjmed.2020.08.019. Archived from the original on 18 June 2022. Retrieved 29 July 2022.
- ↑ "Pandemics That Changed History". HISTORY. Archived from the original on 3 March 2020. Retrieved 2 August 2022.
- ↑ Nicholas Wade (31 October 2010). "Europe's Plagues Came From China, Study Finds". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 4 November 2010. Retrieved 1 November 2010.
The great waves of plague that twice devastated Europe and changed the course of history had their origins in China, a team of medical geneticists reported Sunday, as did a third plague outbreak that struck less harmfully in the 19th century.
- ↑ Benedict, Carol (1996). Bubonic plague in nineteenth-century China. Modern China. Vol. 14. Stanford, Calif.: Stanford Univ. Press. pp. 107–155. doi:10.1177/009770048801400201. ISBN 978-0804726610. PMID 11620272. S2CID 33772946.
- ↑ Cohn, Samuel K. (2003). The Black Death Transformed: Disease and Culture in Early Renaissance Europe. A Hodder Arnold. p. 336. ISBN 978-0-340-70646-6.
- ↑ Pryor, E. G. (1975). "The Great Plague OF Hong Kong" (PDF). Journal of the Royal Asiatic Society Hong Kong Branch. 15: 69. ISSN 1991-7295. PMID 11614750. Archived (PDF) from the original on 16 January 2020. Retrieved 2 June 2014.
- ↑ "History | Plague | CDC". www.cdc.gov. Archived from the original on 21 August 2015. Retrieved 26 November 2017.
- ↑ Porter, Dorothy (11 September 2003). "Book Review". New England Journal of Medicine. 349 (11): 1098–1099. doi:10.1056/NEJM200309113491124. ISSN 0028-4793.
- ↑ "On This Day: San Francisco Bubonic Plague Outbreak Begins". www.findingdulcinea.com. Archived from the original on 1 December 2017. Retrieved 25 November 2017.
- ↑ Griggs, Mary Beth. "30,000 People in Quarantine After Bubonic Plague Kills One in China". Smithsonian. Archived from the original on 27 July 2020. Retrieved 25 November 2017.
- ↑ "Maps and Statistics | Plague | CDC". www.cdc.gov. 23 October 2017. Archived from the original on 8 April 2020. Retrieved 1 December 2017.
- ↑ "Update: Human Plague -- India, 1994". wonder.cdc.gov. Archived from the original on 16 July 2022. Retrieved 30 July 2022.
- ↑ "Plague Manual: Epidemiology, Distribution, Surveillance and Control" (PDF). WHO. Archived from the original on 16 July 2020. Retrieved 6 August 2022.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link) - ↑ Saxena, Vijay K., and T. Verghese. "Ecology of Flea-Transmitted Zoonotic Infection in Village Mamla, District Beed". Current Science, vol. 71, no. 10, 1996, pp. 800–802. JSTOR, www.jstor.org/stable/24098741. Accessed 1 July 2020.
- ↑ Deodhar, N. S.; Yemul, Vishwanath L.; Banerjee, Kalyan (1998). "Plague That Never Was: A Review of the Alleged Plague Outbreaks in India in 1994". Journal of Public Health Policy. 19 (2): 184–199. doi:10.2307/3343297. ISSN 0197-5897. Retrieved 30 July 2022.
- ↑ Pepys, Samuel. "Samuel Pepys Diary - Plague extracts". Samuel Pepys Diary. Archived from the original on 7 April 2020. Retrieved 31 August 2019.
- ↑ Aronson, Ronald (27 October 2011). Zalta, Edward N. (ed.). "Albert Camus". The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy. Summer 2017 Edition. Archived from the original on 26 January 2022. Retrieved 29 July 2022.
- ↑ Giddins, Gary. "The Seventh Seal: There Go the Clowns". The Criterion Collection. Archived from the original on 5 July 2022. Retrieved 29 July 2022.
- ↑ Barbara Tuchman (1978) A Distant Mirror, Knopf ISBN 0-394-40026-7.
- ↑ The End of Europe's Middle Ages: The Black Death Archived March 9, 2013, at the Wayback Machine University of Calgary website. (Retrieved April 5, 2007)
- ↑ Brotton, J., The Renaissance: A Very Short Introduction, OUP, 2006 ISBN 0-19-280163-5.
- 1 2 David Herlihy, The Black Death and the Transformation of the West (Cambridge, Mass.: Harvard University Press, 1997), 72.
- ↑ Wheelis, Mark (September 2002). "Biological Warfare at the 1346 Siege of Caffa". Emerging Infectious Diseases. 8 (9): 971–975. doi:10.3201/eid0809.010536. Archived from the original on 3 May 2022. Retrieved 1 August 2022.
- ↑ "The Independent – 404". The Independent. Archived from the original on 12 September 2011.
- ↑ Daniel Barenblatt, A Plague upon Humanity., 2004, pages 220–221.
Further reading
- Alexander, John T. (2003) [First published 1980]. Bubonic Plague in Early Modern Russia: Public Health and Urban Disaster. Oxford, UK; New York, NY: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-515818-2. OCLC 50253204.
- Carol, Benedict (1996). Bubonic Plague in Nineteenth-Century China. Stanford, CA: Stanford University Press. ISBN 978-0-8047-2661-0. OCLC 34191853.
- Biddle, Wayne (2002). A Field Guide to Germs (2nd Anchor Books ed.). New York: Anchor Books. ISBN 978-1-4000-3051-4. OCLC 50154403.
- Little, Lester K. (2007). Plague and the End of Antiquity: The Pandemic of 541–750. New York, NY: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-84639-4. OCLC 65361042.
- Rosen, William (2007). Justinian's Flea: Plague, Empire and the Birth of Europe. London, England: Viking Penguin. ISBN 978-0-670-03855-8.
- Scott, Susan, and C. J. Duncan (2001). Biology of Plagues: Evidence from Historical Populations. Cambridge, UK; New York, NY: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-80150-8. OCLC 44811929.
- Batten-Hill, David (2011). This Son of York. Kendal, England: David Batten-Hill. ISBN 978-1-78176-094-9. Archived from the original on 20 May 2013. Retrieved 27 August 2018.
- Kool JL (April 2005). "Risk of person-to-person transmission of pneumonic plague". Clinical Infectious Diseases. 40 (8): 1166–72. doi:10.1086/428617. PMID 15791518.
External links
| Wikisource has original text related to this article: |
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |