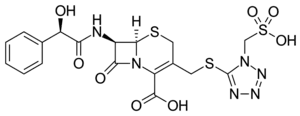
Cefonicid
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
IUPAC name
| |
| External links | |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Micromedex Detailed Consumer Information |
| US NLM | Cefonicid |
| MedlinePlus | a601206 |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ATC code | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C18H18N6O8S3 |
| Molar mass | 542.56 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
Cefonicide (or cefonicid) is an antibiotic.[1]
It is in the second-generation cephalosporin family of medications.[2]
It has a density of 1.92g/cm3.
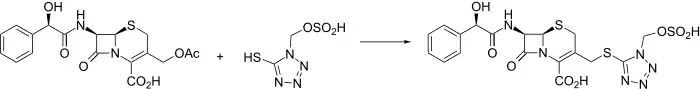
Synthesis
Injectable semi-synthetic cephalosporin antibiotic related to cefamandole, q.v.
Cefonicid is synthesized conveniently by nucleophilic displacement of the 3-acetoxy moiety of 1 with the appropriately substituted tetrazole thiole 2. The mandelic acid amide C-7 side chain is reminiscent of cefamandole.
See also
References
- ↑ Saltiel E, Brogden RN (September 1986). "Cefonicid. A review of its antibacterial activity, pharmacological properties and therapeutic use". Drugs. 32 (3): 222–59. doi:10.2165/00003495-198632030-00002. PMID 3530703.
- ↑ Beauduy, Camille E.; Winston, Lisa G. (2020). "43. Beta-lactam and other cell wall - & membrane - active antibiotics". In Katzung, Bertram G.; Trevor, Anthony J. (eds.). Basic and Clinical Pharmacology (15th ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill. p. 832. ISBN 978-1-260-45231-0. Archived from the original on 2021-10-10. Retrieved 2021-11-30.
- ↑ D. A. Berges, DE 2611270; idem, U.S. Patent 4,048,311 (1976, 1977 both to Smith Kline).
- ↑ U.S. Patent 4,093,723, U.S. Patent 4,159,373 (1978, 1979 both to Smith Kline).
This article is issued from Offline. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.