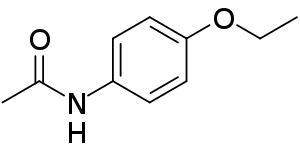
Phenacetin
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.485 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C10H13NO2 |
| Molar mass | 179.219 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Density | 1.24 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 134 °C (273 °F) (decomposes) |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (verify) | |
Phenacetin (acetophenetidin, N-(4-ethoxyphenyl)acetamide[1]) is a pain-relieving and fever-reducing drug, which was widely used following its introduction in 1887. It was withdrawn from medicinal use as dangerous from the 1970s (e.g., withdrawn in Canada in 1973,[2] and by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration in 1983[3]).
History
Phenacetin was introduced in 1887 in Elberfeld, Germany by German company Bayer, and was used principally as an analgesic; it was one of the first synthetic fever reducers to go on the market. It is also known historically to be one of the first non-opioid analgesics without anti-inflammatory properties.
Prior to World War One, Britain imported phenacetin from Germany.[4] During the war, a team including Jocelyn Field Thorpe and Martha Annie Whiteley developed a synthesis in Britain.[4]
Known mechanism of action
Phenacetin's analgesic effects are due to its actions on the sensory tracts of the spinal cord. In addition, phenacetin has a depressant action on the heart, where it acts as a negative inotrope. It is an antipyretic, acting on the brain to decrease the temperature set point. It is also used to treat rheumatoid arthritis (subacute type) and intercostal neuralgia.
In vivo, one of two reactions occur. Usually phenacitin's ether is cleaved to leave paracetamol (acetaminophen), which is the clinically relevant analgesic. A minority of the time the acetyl group is removed from the amine, producing carcinogenic P-Phenetidine. This reaction is quite rare, however, as evidenced by the fact that the drug was on the market for almost 100 years before a statistical link was established, when Canada, followed by the United States, withdrew it from the market.
Preparation
The first synthesis was reported in 1878 by Harmon Northrop Morse.[5]
Phenacetin may be synthesized as an example of the Williamson ether synthesis: ethyl iodide, paracetamol, and anhydrous potassium carbonate are heated in 2-butanone to give the crude product, which is recrystallized from water.[6]
Uses

Phenacetin was widely used until the third quarter of the twentieth century, often in the form of an A.P.C., or "aspirin-phenacetin-caffeine" compound analgesic, as a remedy for fever and pain. An early formulation (1919) was Vincent's APC in Australia.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration ordered the withdrawal of drugs containing phenacetin in November 1983, due to its carcinogenic and kidney-damaging properties.[7] It was also banned in India.[8] As a result, some branded, and previously phenacetin-based, preparations continued to be sold, but with the phenacetin replaced by safer alternatives. A popular brand of phenacetin was Roche's Saridon, which was reformulated in 1983 to contain propyphenazone, paracetamol and caffeine. Coricidin was also reformulated without phenacetin. Paracetamol is a metabolite of phenacetin with similar analgesic and antipyretic effects, but the new formulation has not been found to have phenacetin's carcinogenicity.
Phenacetin has been used as a cutting agent to adulterate cocaine in the UK and Canada, due to the similar physical properties.[9]
Due to its low cost, phenacetin is used for research into the physical and refractive properties of crystals. It is an ideal compound for this type of research.[1][10]
In Canada phenacetin is used as a laboratory reagent, and in a few hair dye preparations (as a stabilizer for hydrogen peroxide). While it is considered a prescription drug, no marketed drugs contain phenacetin.[11]
Safety
Phenacetin, and products containing phenacetin, have been shown in an animal model to have the side effect and after-effect of carcinogenesis. In humans, many case reports have implicated products containing phenacetin in urothelial neoplasms, especially urothelial carcinoma of the renal pelvis. Phenacetin is classified by the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) as carcinogenic to humans.[1] In one prospective series, phenacetin was associated with an increased risk of death due to urologic or renal diseases, death due to cancers, and death due to cardiovascular diseases.[12] In addition, people with glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency may experience acute hemolysis, or dissolution of blood cells, while taking this drug. Acute hemolysis is possible in the case of patients who develop an IgM response to phenacetin leading to immune complexes that bind to erythrocytes in blood. The erythrocytes are then lysed when the complexes activate the complement system.
Chronic use of phenacetin is known to lead to analgesic nephropathy characterized by renal papillary necrosis.[13][14][15] This is a condition which results in destruction of some or all of the renal papillae in the kidneys. It is believed that the metabolite p-phenetidine is at least partly responsible for these effects.[16]
One notable death that can possibly be attributed to the use of this drug was that of the aviation pioneer Howard Hughes. He had been using phenacetin extensively for the treatment of chronic pain; it was stated during his autopsy that phenacetin use may have been the cause of his kidney failure.[17]
See also
References
- 1 2 3 Gralak, Boris; Enoch, Stefan; Tayeb, Gérard (2000). "Anomalous refractive properties of photonic crystals". Journal of the Optical Society of America A. 17 (6): 1012–20. Bibcode:2000JOSAA..17.1012G. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.462.8012. doi:10.1364/JOSAA.17.001012. PMID 10850471.
- ↑ "Phenacetin". DrugBank. Retrieved 28 April 2020.
- ↑ "Drugs withdrawn from the market containing phenacetin" (PDF). Department of Health and Human Services - FDA. 5 October 1983. Archived from the original (PDF) on 30 October 2014.
- 1 2 Creese, Mary RS (1997). "Martha Annie Whiteley (1866-1956): Chemist and Editor" (PDF). Bulletin for the History of Chemistry. 8: 42–45.
- ↑ H. N. Morse (1878). "Ueber eine neue Darstellungsmethode der Acetylamidophenole". Berichte der deutschen chemischen Gesellschaft. 11 (1): 232–233. doi:10.1002/cber.18780110151.
- ↑ "Conversion of Acetaminophen into Phenacetin". Chemistry Department Master Experiment Archive. California State University Stanislaus. Archived from the original on 2008-12-02.
- ↑ Federal Register of October 5, 1983 (48 FR 45466)
- ↑ "Drugs banned in India". Central Drugs Standard Control Organization, Dte.GHS, Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Government of India. Archived from the original on 2015-02-21. Retrieved 2013-09-17.
- ↑ "Cancer chemical in street cocaine". BBC News. 23 November 2006.
- ↑ Studenikin, P. A.; Zagumennyi, A. I.; Zavartsev, Yu D.; Popov, P. A.; Shcherbakov, Ivan A. (1995). "GdVO4as a new medium for solid-state lasers: Some optical and thermal properties of crystals doped with Cd3+, Tm3+, and Er3+ions". Quantum Electronics. 25 (12): 1162–1165. doi:10.1070/QE1995v025n12ABEH000556.
- ↑ "Health - Product safety - Chemical substances - Phenacetin information sheet". Government of Canada -. Retrieved 29 April 2020.
- ↑ Dubach U, Rosner B, Stürmer T (1991). "An epidemiologic study of abuse of analgesic drugs. Effects of phenacetin and salicylate on mortality and cardiovascular morbidity (1968 to 1987)". N Engl J Med. 324 (3): 155–60. doi:10.1056/NEJM199101173240304. PMID 1984193.
- ↑ Cochran A, Lawson D, Linton A (1967). "Renal papillary necrosis following phenacetin excess". Scott Med J. 12 (7): 246–50. doi:10.1177/003693306701200702. PMID 6036245. S2CID 33774826.
- ↑ Tan G, Rabbino M, Hopper J (1964). "Is Phenacetin a Nephrotoxin?: A Report on Twenty-three Users of the Drug". Calif Med. 101 (2): 73–7. PMC 1515485. PMID 14180501.
- ↑ Brix A (2002). "Renal papillary necrosis". Toxicol Pathol. 30 (6): 672–4. doi:10.1080/01926230290166760. PMID 12512867.
- ↑ Kankuri, Esko; Solatunturi, Erkka; Vapaatalo, Heikki (2003). "Effects of phenacetin and its metabolite p-phenetidine on COX-1 and COX-2 activities and expression in vitro". Thrombosis Research. 110 (5–6): 299–303. doi:10.1016/S0049-3848(03)00416-X. PMID 14592552.
- ↑ Tennant, Forest (July–August 2007). "Howard Hughes & Pseudoaddiction" (PDF). Practical Pain Management. 7 (6): 20. Archived from the original (PDF) on 24 September 2015. Retrieved 2 November 2015.
The phenacetin in the codeine compound produced, over time, kidney failure and death.
External links
| Look up phenacetin in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |