Trifluridine
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Viroptic; Lonsurf (+tipiracil) |
| Other names | α,α,α-trifluorothymidine; 5-trifluromethyl-2′-deoxyuridine; FTD5-trifluoro-2′-deoxythymidine; TFT; CF3dUrd; FTD; F3TDR; F3Thd |
IUPAC name
| |
| Clinical data | |
| Drug class | Antiviral[1] |
| Main uses | Herpes simplex infections of the eye[1] |
| Side effects | Irrigation, eyelid swelling, redness of the eyes[1] |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of use | Eye drops; tablets (+tipiracil) |
| External links | |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| US NLM | Trifluridine |
| Legal | |
| License data | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetics | |
| Bioavailability | Negligible (eye drops); ≥57% (by mouth) |
| Protein binding | >96% |
| Metabolism | Thymidine phosphorylase |
| Elimination half-life | 12 minutes (eye drops); 1.4–2.1 hrs (combination with tipiracil) |
| Excretion | Mostly via urine |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C10H11F3N2O5 |
| Molar mass | 296.202 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
Trifluridine, also called trifluorothymidine (TFT) is an antiviral medication used to treat herpes simplex infections of the eye.[1] It may also be used for vaccinia infections of the eye that can occur following smallpox vaccination.[1] It is used as an eye drop.[1]
Common side effects include irrigation, eyelid swelling, and redness of the eyes.[1] It is believed to work by stopping the creation of viral DNA.[1]
Trifluridine was approved for medical use in the United States in 1980.[1][2] It is available as a generic medication and is also sold under the trade name Viroptic.[3][1] In the United States a 7.5 ml container costs about 74 USD.[3] It is also a component of the anti-cancer medication trifluridine/tipiracil.[4]
Medical uses
Trifluridine eye drops are used for the treatment of keratitis and keratoconjunctivitis caused by the herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2, as well as for prevention and treatment of vaccinia virus infections of the eye.[5]
A Cochrane review showed that trifluridine and aciclovir were a more effective treatment than idoxuridine or vidarabine,[6] significantly increasing the relative number of successfully healed eyes in one to two weeks.[7]
For cancer treatment, the combination trifluridine/tipiracil is used.
Dosage
It is used as a 1% drop every two to four hours up to 9 drops per day.[1]
Side effects
Common side effects of trifluridine eye drops include transient burning, stinging, local irritation, and edema of the eyelids.[5]
Adverse effects of the anti-cancer formulation have only been evaluated for the combination trifluridine/tipiracil, not for the individual components.
Interactions
Only in vitro interaction studies are available. In these, trifluridine used the concentrative nucleoside transporter 1 (CNT1) and equilibrative nucleoside transporters 1 (ENT1) and 2 (ENT2). Drugs that interact with these transporters could influence blood plasma concentrations of trifluridine. Being a thymidine phosphorylase inhibitor, trifluridine could also interact with substrates of this enzyme such as zidovudine.[8]
For the eye drops, trifluridine absorption is negligible,[5] rendering interactions basically irrelevant.
Pharmacology
Mechanism of action (eye drops)
It is a nucleoside analogue, a modified form of deoxyuridine, similar enough to be incorporated into viral DNA replication, but the –CF3 group added to the uracil component blocks base pairing, thus interfering with viral DNA replication.
Pharmacokinetics (eye drops)
Trifluridine passes the cornea and is found in the aqueous humour. Systemic absorption is negligible.[5]
Pharmacokinetics (oral)
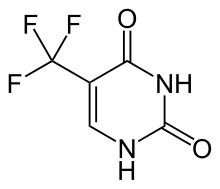
Pharmacokinetic data of oral trifluridine have only been evaluated in combination with tipiracil, which significantly affects biotransformation of the former. At least 57% of trifluridine are absorbed from the gut, and highest blood plasma concentrations are reached after two hours in cancer patients. The substance has no tendency to accumulate in the body. Plasma protein binding is over 96%. Trifluridine is metabolised by the enzyme thymidine phosphorylase to 5-trifluoromethyl-2,4(1H,3H)-pyrimidinedione (FTY), and also by glucuronidation. Elimination half-life is 1.4 hours on the first day and increases to 2.1 hours on the twelfth day. It is mainly excreted via the kidneys.[8]
Tipiracil causes Cmax (highest blood plasma concentrations) of trifluridine to increase 22-fold, and its area under the curve 37-fold, by inhibiting thymidine phosphorylase.[8]
Chemistry
The substance is a white crystalline powder. It is freely soluble in methanol and acetone; soluble in water, ethanol, 0.01 M hydrochloric acid, and 0.01 M sodium hydroxide; sparingly soluble in isopropyl alcohol and acetonitrile; slightly soluble in diethyl ether; and very slightly soluble in isopropyl ether.[9]
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 "Trifluridine Monograph for Professionals". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 21 September 2021. Retrieved 19 September 2021.
- ↑ Long, Sarah S.; Pickering, Larry K.; Prober, Charles G. (2012). Principles and Practice of Pediatric Infectious Disease. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 1502. ISBN 978-1437727029. Archived from the original on 2019-12-29. Retrieved 2020-09-20.
- 1 2 "Viroptic Prices, Coupons & Savings Tips - GoodRx". GoodRx. Archived from the original on 13 October 2016. Retrieved 19 September 2021.
- ↑ BNF (80 ed.). BMJ Group and the Pharmaceutical Press. September 2020 – March 2021. p. 969. ISBN 978-0-85711-369-6.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: date format (link) - 1 2 3 4 Drugs.com: Monograph for Trifluridine.
- ↑ Wilhelmus, Kirk R (2015-01-09). "Antiviral treatment and other therapeutic interventions for herpes simplex virus epithelial keratitis". Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd. 1: CD002898. doi:10.1002/14651858.cd002898.pub5. PMC 4443501. PMID 25879115. Archived from the original on 2018-08-31. Retrieved 2020-09-20.
- ↑ Wilhelmus, Kirk R (2015-01-09). Cochrane Eyes and Vision Group (ed.). "Antiviral treatment and other therapeutic interventions for herpes simplex virus epithelial keratitis". Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 1: CD002898. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD002898.pub5. PMC 4443501. PMID 25879115.
- 1 2 3 Haberfeld, H, ed. (2015). Austria-Codex (in German). Vienna: Österreichischer Apothekerverlag.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: unrecognized language (link) - ↑ FDA Professional Drug Information on Lonsurf.
External links
| Identifiers: |
|---|
- Costin D, Dogaru M, Popa A, Cijevschi I (2004). "Trifluridine therapy in herpetic in keratitis". Rev Med Chir Soc Med Nat Iasi. 108 (2): 409–12. PMID 15688823.
- Kuster P, Taravella M, Gelinas M, Stepp P (1998). "Delivery of trifluridine to human cornea and aqueous using collagen shields". CLAO J. 24 (2): 122–4. PMID 9571274.
- O'Brien W, Taylor J (1991). "Therapeutic response of herpes simplex virus-induced corneal edema to trifluridine in combination with immunosuppressive agents". Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 32 (9): 2455–61. PMID 1907950.
- "Trifluridine Ophthalmic Solution, 1%" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2009-09-20. Retrieved 2007-03-24.