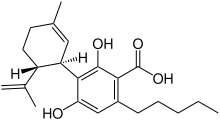
Cannabidiolic acid
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
(1′R,2′R)-2,6-Dihydroxy-5′-methyl-4-pentyl-2′-(prop-1-en-2-yl)-1′,2′,3′,4′-tetrahydro[1,1′-biphenyl]-3-carboxylic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number |
|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| 3DMet | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula |
C22H30O4 |
| Molar mass | 358.478 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Cannabidiolic acid (CBDA), is a cannabinoid found in cannabis plants.[1] It is most abundant in the glandular trichomes on the female seedless flowers or more accurately infructescence often colloquially referred to as buds.[2] CBDA is the chemical precursor to cannabidiol (CBD). Through the process of decarboxylation cannabidiol is derived via a loss of a carbon and two oxygen atoms from the 1 position of the benzoic acid ring. Cannabinoids are a class of compounds that are essentially unique to the cannabis genus. Both marijuana and hemp belong to this genus.
Chemical composition
Cannabidiolic acid is biosynthesized by Cannabidiolic acid synthase from the conjugation of olivetolic acid and cannabigerolic acid.[3] CBDA is not produced by man, but it is naturally occurs in hemp. It is a raw compound which is found in the flowering buds of the female cannabis plant.[4]
References
- ↑ Takeda, Shuso (2013). "[Medicinal chemistry and pharmacology focused on cannabidiol, a major component of the fiber-type cannabis]". Yakugaku Zasshi: Journal of the Pharmaceutical Society of Japan. 133 (10): 1093–1101. doi:10.1248/yakushi.13-00196. ISSN 1347-5231. PMID 24088353.
- ↑ Livingston, Samuel J.; Quilichini, Teagen D.; Booth, Judith K.; Wong, Darren C. J.; Rensing, Kim H.; Laflamme‐Yonkman, Jessica; Castellarin, Simone D.; Bohlmann, Joerg; Page, Jonathan E.; Samuels, A. Lacey (2020). "Cannabis glandular trichomes alter morphology and metabolite content during flower maturation". The Plant Journal. 101 (1): 37–56. doi:10.1111/tpj.14516. ISSN 1365-313X. PMID 31469934.
- ↑ PubChem. "Cannabidiolic acid". pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 2019-12-23.
- ↑ Nadel, David (2020-10-02). "Hemp Compound Spotlight: CBDA". Pure CBD Now. Retrieved 2022-12-18.