Collagenous spherulosis
| Collagenous spherulosis | |
|---|---|
| Other names: Mucinous spherulosis, spherulosis | |
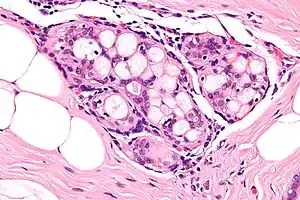 | |
| Micrograph of collagenous spherulosis with the characteristic histomorphology - intratubular eosinophilic material with a spoke-like arrangement. H&E stain. | |
| Specialty | Pathology |
Collagenous spherulosis, or simple spherulosis, is a benign finding in breast pathology. It is almost always an incidental finding, though it is occasionally associated with calcifications, which may lead to a biopsy.
It is important to correctly identify, as it can be confused with atypical ductal hyperplasia, cribriform ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS), and adenoid cystic carcinoma.[1]
Collagenous spherulosis is characterized by a tubular/cribriform architecture with intratubular eosinophilic material that classically is arranged like the spokes of a wheel ("radial spikes"). There is usually no mitotic activity, and two cells populations (epithelial & myoepithelial) are present, like in benign breast glands.
The lesions are typically small (less than 50 spherules per lesion, less than 100 micrometers in size) and may be multifocal.
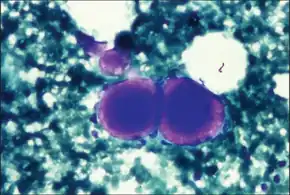 Cytological diagnosis of collagenous spherulosis of breast
Cytological diagnosis of collagenous spherulosis of breast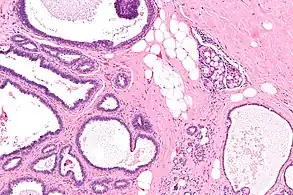 Intermed. mag.
Intermed. mag.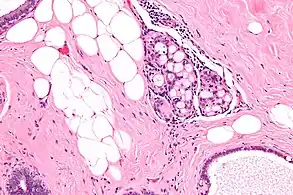 High mag.
High mag.
See also
References
- ↑ Resetkova, E.; Albarracin, C.; Sneige, N. (Jan 2006). "Collagenous spherulosis of breast: morphologic study of 59 cases and review of the literature". Am J Surg Pathol. 30 (1): 20–7. doi:10.1097/01.pas.0000179237.91515.81. PMID 16330938. S2CID 1021118.
External links
- Histomorphologic criteria for collagenous spherulosis (Stanford School of Medicine) Archived 2022-05-20 at the Wayback Machine