Dantron
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | Oral, rectal (enema) |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| NIAID ChemDB | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.794 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
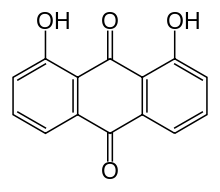
| Formula | C14H8O4 |
| Molar mass | 240.214 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
Dantron (INN), also known as chrysazin or 1,8-dihydroxyanthraquinone, is an organic substance, formally derived from anthraquinone by the replacement of two hydrogen atoms by hydroxyl groups (–OH). It is used in some countries as a stimulant laxative.
It should not be confused with ondansetron, an unrelated drug that was marketed in South Africa under the trade name "Dantron".
Medical uses
In the USA, dantron is not used because it is considered to be a carcinogen.[1]
In the UK it is considered a possible carcinogen and so its use is restricted to patients who already have a diagnosis of terminal cancer. It is mainly used in palliative care to counteract the constipating effects of opioids. Its British Approved Name was danthron, but it has now been changed to "dantron", the recommended International Nonproprietary Name.[2]
Dantron can be administered orally, or can be administered rectally as an enema either in combination with other laxatives or alone.[3]
Side effects
Dantron has the notable side-effect of causing red-colored urine.
See also
- Hydroxyanthraquinone
- Rhein (molecule)
References
- ↑ Danthron substance profile at the National Toxicology Program website
- ↑ British National Formulary website (requires free registration)
- ↑ "A06AG Enemas". WHO Collaborating Centre for Drug Statistics Methodology. World Health Organization. 13 December 2018. Retrieved 17 March 2019.