Aggressive fibromatosis
| Aggressive fibromatosis | |
|---|---|
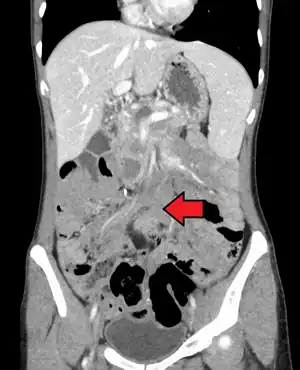 | |
| Desmoid tumor as seen on CT scan | |
Aggressive fibromatosis or desmoid tumor is a rare condition. Desmoid tumors arise from cells called fibroblasts, which are found throughout the body and provide structural support, protection to the vital organs, and play a critical role in wound healing. These tumors tend to occur in women in their thirties, but can occur in anyone at any age. They can be either relatively slow-growing or malignant. However, aggressive fibromatosis is locally aggressive and can cause life-threatening problems or even death when they compress vital organs such as intestines, kidneys, lungs, blood vessels, or nerves. Most cases are sporadic, but some are associated with familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP). Approximately 10% of individuals with Gardner's syndrome, a type of FAP with extracolonic features, have desmoid tumors.[1]
The World Health Organization reclassified desmoid tumors (termed desmoid-type fibromatosis) as a specific type of tumor in the category of intermediate (locally aggressive) fibroblastic and myofibroblastic tumors.[2]
Histologically they resemble very low-grade fibrosarcomas,[3] but they are very locally aggressive and tend to recur even after complete resection. There is a tendency for recurrence in the setting of prior surgery; in one study, two-thirds of patients with desmoid tumors had a history of prior abdominal surgery.[4]
Signs and symptoms
The clinical presentation for Aggressive fibromatosis is the following:[5]
- Pain
- Constipation (if located Intra-abdominal desmoid tumors)
- Restrict movement ( if located Extra-abdominal desmoid tumors )
Risk factor
Risk factors for desmoid disease amongst FAP patients include female sex, a 3' APC mutation, a positive family history, and a history of previous abdominal surgery.[6]
Diagnosis
Classification
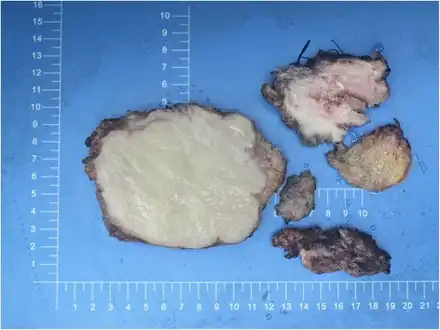 Macroscopically, desmoid tumors were yellowish white on the cut and often poorly circumscribed
Macroscopically, desmoid tumors were yellowish white on the cut and often poorly circumscribed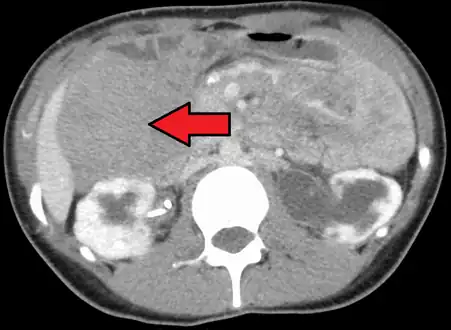 Desmoid tumor
Desmoid tumor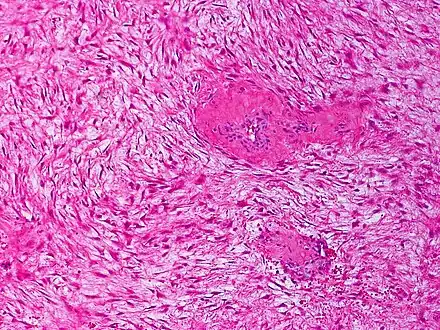 Desmoid fibromatosis, H&E stain. Banal fibroblasts infiltrate the adjacent tissue in fascicles. Mitoses may be infrequent.
Desmoid fibromatosis, H&E stain. Banal fibroblasts infiltrate the adjacent tissue in fascicles. Mitoses may be infrequent.
Desmoid tumors may be classified as extra-abdominal, abdominal wall, or intra-abdominal (the last is more common in patients with FAP). It is thought that the lesions may develop in relation to estrogen levels or trauma/operations.
A 3' APC mutation is the most significant risk factor for intra-abdominal desmoid development amongst FAP patients.[7] FAP patients presenting with an abdominal wall desmoid pre-operatively are at an increased risk of developing an intra-abdominal desmoid post-operatively.[8]
Desmoid tumours of the breast are rare. Although benign, they can mimic breast cancer on physical examination, mammography and breast ultrasound and can also be locally invasive. Even though they occur sporadically, they can also be seen as a part of Gardner's syndrome. A high index of suspicion and a thorough triple examination protocol is necessary to detect rare lesions like a desmoid tumour which can masquerade as breast carcinoma. Desmoid tumour of the breast may present a difficulty in the diagnosis especially where imaging studies are not conclusive and suggest a more ominous diagnosis.[9]
Treatment
Treatment may consist of watchful waiting, complete surgical removal, radiation therapy, antiestrogens (e.g. Tamoxifen), NSAIDs, chemotherapy, or ablation (cold, heat, ultrasound). Treatment with oral tyrosine kinase inhibitor drugs (e.g. imatinib, sorafenib, pazopanib) show promising success rates.[10][11][12]
Patients with desmoid tumors should be evaluated by a multi-disciplinary team of surgeons, medical oncologists, radiation oncologists, and geneticists. There is no cure for desmoid tumors; when possible, patients are encouraged to enlist in clinical trials.[13]
A biopsy is always indicated as the definitive method to determine nature of the tumour. Management of these lesions is complex, the main problem being the high rates of recurrence in FAP associated disease. Conversely, for intra-abdominal fibromatosis without evidence of FAP, although extensive surgery may still be required for local symptoms, the risk of recurrence appears to be lower.[14] Wide surgical resection with clear margins is the most widely practiced technique with radiation, chemotherapy, or hormonal therapy being used to reduce the risk of recurrence.[9]
Intestinal transplant is a treatment option for those patients with complicated desmoid tumor, such as those involving the mesenteric root, or those with intestinal failure resulting from the tumor or prior interventions.[15]
References
- ↑ Nieuwenhuis MH, De Vos Tot Nederveen Cappel W, Botma A, et al. (February 2008). "Desmoid tumors in a Dutch cohort of patients with familial adenomatous polyposis". Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology. 6 (2): 215–9. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2007.11.011. PMID 18237870.
- ↑ Sbaraglia M, Bellan E, Dei Tos AP (April 2021). "The 2020 WHO Classification of Soft Tissue Tumours: news and perspectives". Pathologica. 113 (2): 70–84. doi:10.32074/1591-951X-213. PMC 8167394. PMID 33179614.
- ↑ "desmoid" at Dorland's Medical Dictionary
- ↑ Lynch HT, Fitzgibbons R (December 1996). "Surgery, desmoid tumors, and familial adenomatous polyposis: case report and literature review". The American Journal of Gastroenterology. 91 (12): 2598–601. PMID 8946994.
- ↑ "Desmoid tumor: MedlinePlus Genetics". medlineplus.gov. Archived from the original on 26 October 2021. Retrieved 21 April 2022.
- ↑ Sinha A, Clark SK (2010). "Risk factors predicting desmoid occurrence in patients with familial adenomatous polyposis: a meta-analysis". Colorectal Disease. 13 (11): 1222–1229. doi:10.1111/j.1463-1318.2010.02345.x. PMID 20528895. S2CID 26117431.
- ↑ Sinha A, Clark SK (June 2010). "Risk factors predicting intra-abdominal desmoids in familial adenomatous polyposis: a single centre experience". Techniques in Coloproctology. 14 (2): 141–6. doi:10.1007/s10151-010-0573-4. PMID 20352275. S2CID 24922322.
- ↑ Sinha A, Clark SK (2010). "Surgical prophylaxis in familial adenomatous polyposis: do pre-existing desmoids outside the abdominal cavity matter?". Familial Cancer. 9 (3): 407–11. doi:10.1007/s10689-010-9342-9. PMID 20428953. S2CID 20685381.
- 1 2 Rammohan A, Wood JJ (2012). "Desmoid tumour of the breast as a manifestation of Gardner's syndrome". International Journal of Surgery Case Reports. 3 (5): 139–142. doi:10.1016/j.ijscr.2012.01.004. PMC 3312056. PMID 22370045.
- ↑ Ganeshan, Dhakshina moorthy; Amini, Behrang; Nikolaidis, Paul; Assing, Matthew; Vikram, Raghunandan (2019). "Current Update on Desmoid Fibromatosis". Journal of Computer Assisted Tomography. 43 (1): 29–38. doi:10.1097/RCT.0000000000000790. PMC 6331223. PMID 30211798.
- ↑ Alman, Ben; Attia, Steven; Baumgarten, Christina; Benson, Charlotte; Blay, Jean-Yves; Bonvalot, Sylvie; Breuing, Jessica; Cardona, Ken; Casali, Paolo G.; Coevorden, Frits van; Colombo, Chiara; Tos, Angelo P. Dei; Dileo, Palma; Ferrari, Andrea; Fiore, Marco; Frezza, Anna M.; Garcia, Jesica; Gladdy, Rebecca; Gounder, Mrinal; Gronchi, Alessandro; Haas, Rick; Hackett, Sam; Haller, Florian; Hohenberger, Peter; Husson, Olga; Jones, Robin L.; Judson, Ian; Kasper, Bernd; Kawai, Akira; Kogosov, Vlada; Lazar, Alex J.; Maki, Robert; Mathes, Tim; Messiou, Christina; Navid, Fariba; Nishida, Yoshihiro; Palassini, Elena; Penel, Nicolas; Pollock, Robert; Pieper, Dawid; Portnoy, Marlene; Raut, Chandrajit P.; Roets, Evelyne; Sandrucci, Sergio; Sbaraglia, Marta; Stacchiotti, Silvia; Thornton, Katherine A.; Graaf, Winette van der; Zande, Kim van der; Houdt, Winan J. van; Villalobos, Victor; Wagner, Andrew J.; Wardelmann, Eva; Wartenberg, Markus; Watson, Sarah; Weiss, Aaron; Zafiropoulos, Nikolaos (1 March 2020). "The management of desmoid tumours: A joint global consensus-based guideline approach for adult and paediatric patients". European Journal of Cancer. 127: 96–107. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2019.11.013. PMID 32004793. S2CID 210998595.
- ↑ https://www.dtrf.org/diagnosis-and-treatment/ Archived 2021-10-25 at the Wayback Machine. Retrieved 22 October 2021.
- ↑ "About Desmoid Tumors". Archived from the original on 2015-07-27. Retrieved 2015-08-04.
- ↑ Wilkinson MJ, Fitzgerald JE, Thomas JM, Hayes AJ, Strauss DC (2012). "Surgical resection for non-familial adenomatous polyposis-related intra-abdominal fibromatosis". British Journal of Surgery. 99 (5): 706–13. doi:10.1002/bjs.8703. PMID 22359346. S2CID 205512855.
- ↑ Chatzipetrou, Maria A.; Tzakis, Andreas G.; Pinna, Antonio D.; Kato, Tomoaki; Misiakos, Evangelos P.; Tsaroucha, Alexandra K.; Weppler, Deborah; Ruiz, Phillip; Berho, Mariana; Fishbein, Thomas; Conn, Harold O.; Ricordi, Camillo (March 2001). "Intestinal transplantation for the treatment of desmoid tumors associated with familial adenomatous polyposis". Surgery. 129 (3): 277–281. doi:10.1067/msy.2001.110770. PMID 11231455.
External links
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |