Erythema gyratum repens
| Erythema gyratum repens | |
|---|---|
.jpg.webp) | |
| Symptoms | Expanding swirly wavy red lines, scale, itch[1] |
| Usual onset | Older adults (60s)[1] |
| Causes | Cancer: lung cancer, oesophageal cancer, breast cancer[1] |
| Diagnostic method |
|
| Differential diagnosis | Necrolytic migratory erythema, erythema migrans, erythrokeratodermia variabilis, subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus, tinea corporis[1] |
| Treatment | Treat underlying cause[1] |
| Medication | Antihistamines[2] |
| Prognosis | Resolves with successful cancer treatment[1] |
| Frequency | Rare, male:females (2:1)[1] |
Erythema gyratum repens is a skin rash that has a strong association with internal cancers.[1] It characteristically presents with red wavy lines, generally in older adults.[1] These regular whirly rings rapidly and repetitively appear within existing ones, expanding outward at a rate of up to 1cm a day, giving the impression that the rash is moving.[3] The resulting pattern is similar to wood grain.[1] There is often an intense itch and scale over the leading edge, which may be slightly raised.[2] Around one in 10 affected individuals have thick skin of the palms of the hands.[1] In some, the skin may become extremely dry.[3]
The cause is believed to have an immunological base.[4] 80% of cases have an underlying cancer, of which almost half have lung cancer.[1] Other cancers reported to be associated include cancers of the oesophagus and breast, and less frequently gastric cancer, uterine cancer, throat cancer, pancreas cancer and lymphoma.[1] The rash generally precedes the cancer diagnosis by around 9-months.[2] Non-cancer associations include tuberculosis of the lung.[3] Sometimes no cause is found.[3]
Diagnosis is generally by its appearance, although tests may be required to exclude other conditions.[3] These tests may include blood tests such as a complete blood count, PSA, and antinuclear antibodies.[1] A cancer may be located using chest X-ray, mammogram, CT scan, and endoscopy.[1] Necrolytic migratory erythema, erythema migrans, tinea corporis, erythrokeratodermia variabilis, and subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus are some of many other skin conditions that may appear similar.[1]
Treatment and outlook depend on the underlying cause.[1] Antihistamines may help to reduce the itch, although the role of applying a steroid cream is unclear.[2][5] The rash typically resolves with successful cancer treatment.[3]
The condition is rare.[1] Males are affected twice as frequently as females.[1] J. A. Gammel first described the condition in 1952, in an individual who was later found to have breast cancer.[6][7]
Signs and symptoms
Erythema gyratum repens characteristically presents as wavy red lines on the skin.[1] These regular whirly rings rapidly and repetitively appear within existing ones, expanding outward at a rate of up to 1cm a day, giving the impression that the rash is moving.[3] The resulting pattern is similar to wood grain.[1] There is typically an intense itch and scale over the leading edge, which may be slightly raised.[2] The trunk and limbs are most frequently affected.[5] Thickening of the skin of the palms co-exists in around 10% of affected individuals, whatever the underlying cause.[1] The skin may become extremely dry.[3] Onset is generally in older adults; after the age of 60-years.[1]
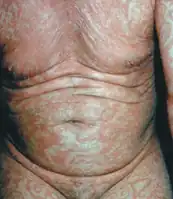 Erythema gyratum repens
Erythema gyratum repens.jpg.webp) Erythema gyratum repens
Erythema gyratum repens Erythema gyratum repens
Erythema gyratum repens
Cause
The cause is believed to have an immunological base.[4] 80% of cases have an underlying cancer, of which almost half have lung cancer.[1] Other cancers reported to be associated include cancers of the oesophagus, breast, stomach, uterus, throat, pancreas and blood.[1] The rash generally precedes the cancer diagnosis by around 9-months.[2] Less frequently, the cause may be tuberculosis of the lung, or no cause is found.[3] Other rare reported associations have included cryptogenic organizing pneumonia and rheumatoid arthritis.[2]
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is generally by its appearance.[3] Tests include blood tests such as a complete blood count which may reveal raised eosinophils.[2] Other blood tests include PSA, antinuclear antibodies and biochemistry.[1] Medical imaging may locate a cancer; chest X-ray, mammogram, CT scan of pelvis and abdomen.[1] If indicated then an endoscopy may be required; colonoscopy, gastroscopy.[1]
Differential diagnosis
Necrolytic migratory erythema, erythema migrans, tinea corporis, erythrokeratodermia variabilis, and subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus are some of many other skin conditions that may appear similar.[1]
Treatment
Treatment and outlook depend on the underlying cause.[1] Antihistamines may help to reduce the itch, although the role of applying a steroid cream is unclear.[2][5] The rash typically resolves with successful cancer treatment.[3]
Epidemiology
The condition is rare.[1] Males are affected twice as frequently as females.[1]
History
J. A. Gammel first described the condition in 1952, in an individual who was later found to have breast cancer.[6][7]
See also
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 Griffiths, Christopher E. M.; Bleiker, Tanya O.; Creamer, Daniel; Ingram, John R.; Simpson, Rosalind C. (2022). "19. Reactive inflammatory erythemas". Rook's Dermatology Handbook. Hoboken: Wiley-Blackwell. p. 259. ISBN 978-1-119-42819-0. Archived from the original on 2023-08-11. Retrieved 2023-08-05.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 James, William D.; Elston, Dirk; Treat, James R.; Rosenbach, Misha A.; Neuhaus, Isaac (2020). "7. Erythema and urticaria". Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology (13th ed.). Edinburgh: Elsevier. p. 144. ISBN 978-0-323-54753-6. Archived from the original on 2023-08-11. Retrieved 2023-08-07.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Bolognia, Jean L.; Schaffer, Julie V.; Duncan, Karynne O.; Ko, Christine (2021). "15. Figurate erythemas". Dermatology Essentials (2nd ed.). Elsevier. pp. 142–148. ISBN 978-0-323-70971-2. Archived from the original on 2023-08-08. Retrieved 2023-08-05.
- 1 2 Motta, Adriana; González, Luis Fernando; García, Gonzalo; Guzmán, Jennifer; Prada, Lorena; Herrera, Hugo; Rolon, Mariam (2022). "11. Inflammatory skin diseases presenting with erythema, urticaria and purpura". Atlas of Dermatology: Inflammatory, Infectious and Tumoral Skin Diseases. Springer. pp. 310–311. ISBN 978-3-030-84106-5. Archived from the original on 2023-08-08. Retrieved 2023-08-06.
- 1 2 3 "Erythema gyratum repens | DermNet". dermnetnz.org. Archived from the original on 8 August 2023. Retrieved 6 August 2023.
- 1 2 Boehner, Alexander; Neuhauser, Ruth; Zink, Alexander; Ring, Johannes (July 2021). "Figurate erythemas - update and diagnostic approach". Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft = Journal of the German Society of Dermatology: JDDG. 19 (7): 963–972. doi:10.1111/ddg.14450. ISSN 1610-0387. PMID 34046996. Archived from the original on 2023-08-08. Retrieved 2023-08-05.
- 1 2 Gammel, J. A. (October 1952). "Erythema gyratum repens; skin manifestations in patient with carcinoma of breast". A.M.A. Archives of Dermatology and Syphilology. 66 (4): 494–505. doi:10.1001/archderm.1952.01530290070010. ISSN 0096-5979. PMID 12975861. Archived from the original on 2023-08-08. Retrieved 2023-08-05.
External links
| Classification |
|---|